El flutter auricular es una taquicardia supraventricular regular que se caracteriza por una frecuencia cardíaca auricular de entre 240/min y 340/min (normalmente 300/min), un bloqueo de la conducción del nódulo auriculoventricular (AV) y un patrón de “dientes de sierra” en el electrocardiograma (ECG). Hay muchas causas cardíacas y no cardíacas, pero los pacientes suelen tener una enfermedad cardíaca estructural subyacente. Los síntomas incluyen palpitaciones, falta de aire, dolor torácico, mareo y náuseas. El tratamiento es similar al de la fibrilación auricular, centrándose en el control del ritmo y la prevención de la embolización sistémica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El flutter auricular está causado por un circuito eléctrico macro reentrante (el circuito reentrante abarca una gran zona de la aurícula):
Flutter auricular típico:
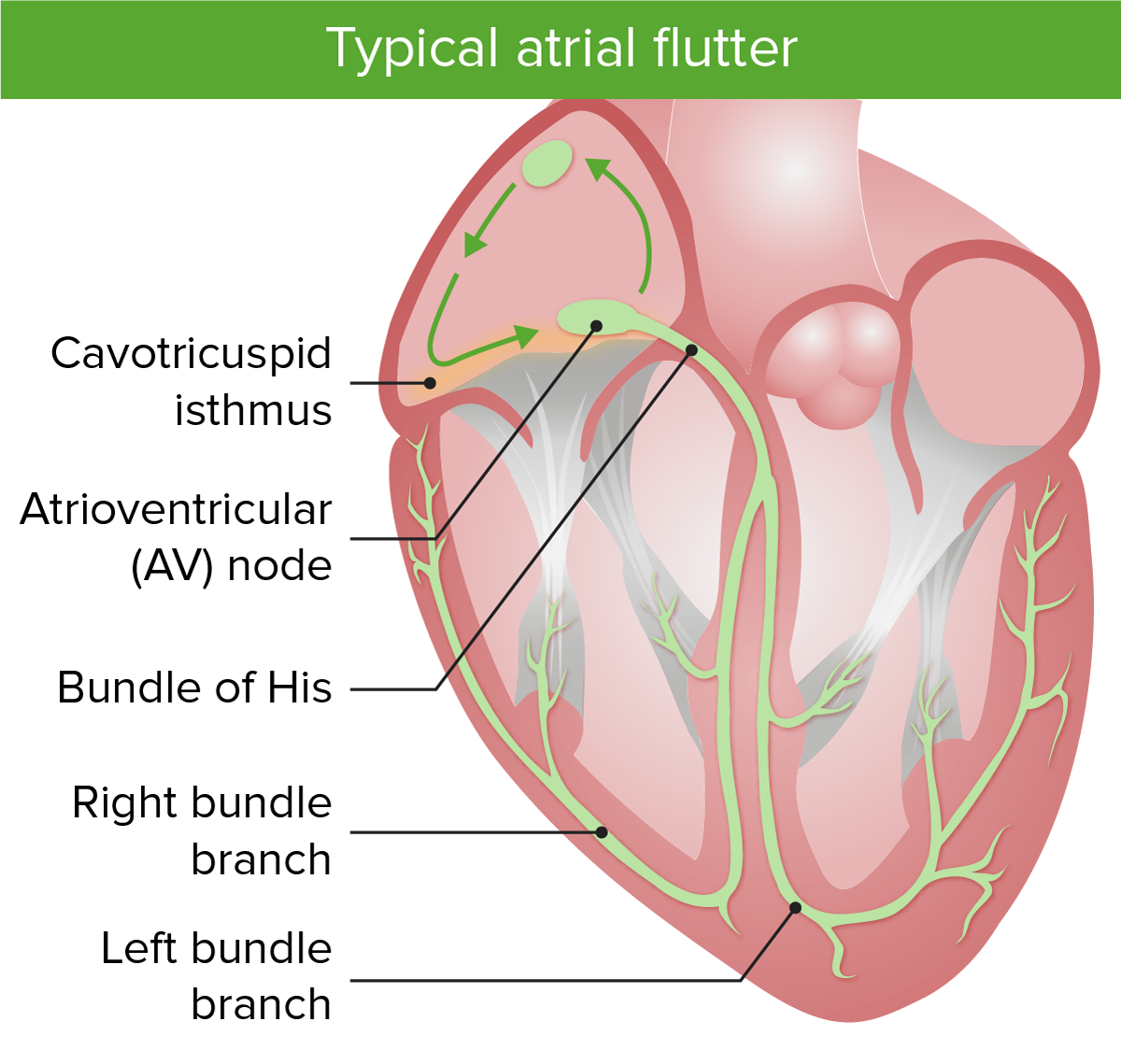
La imagen muestra los circuitos macro reentrantes en el flutter auricular típico. Obsérvese que el istmo cavotricuspídeo está implicado en el flutter auricular típico.
Imagen por Lecturio.Flutter auricular atípico:
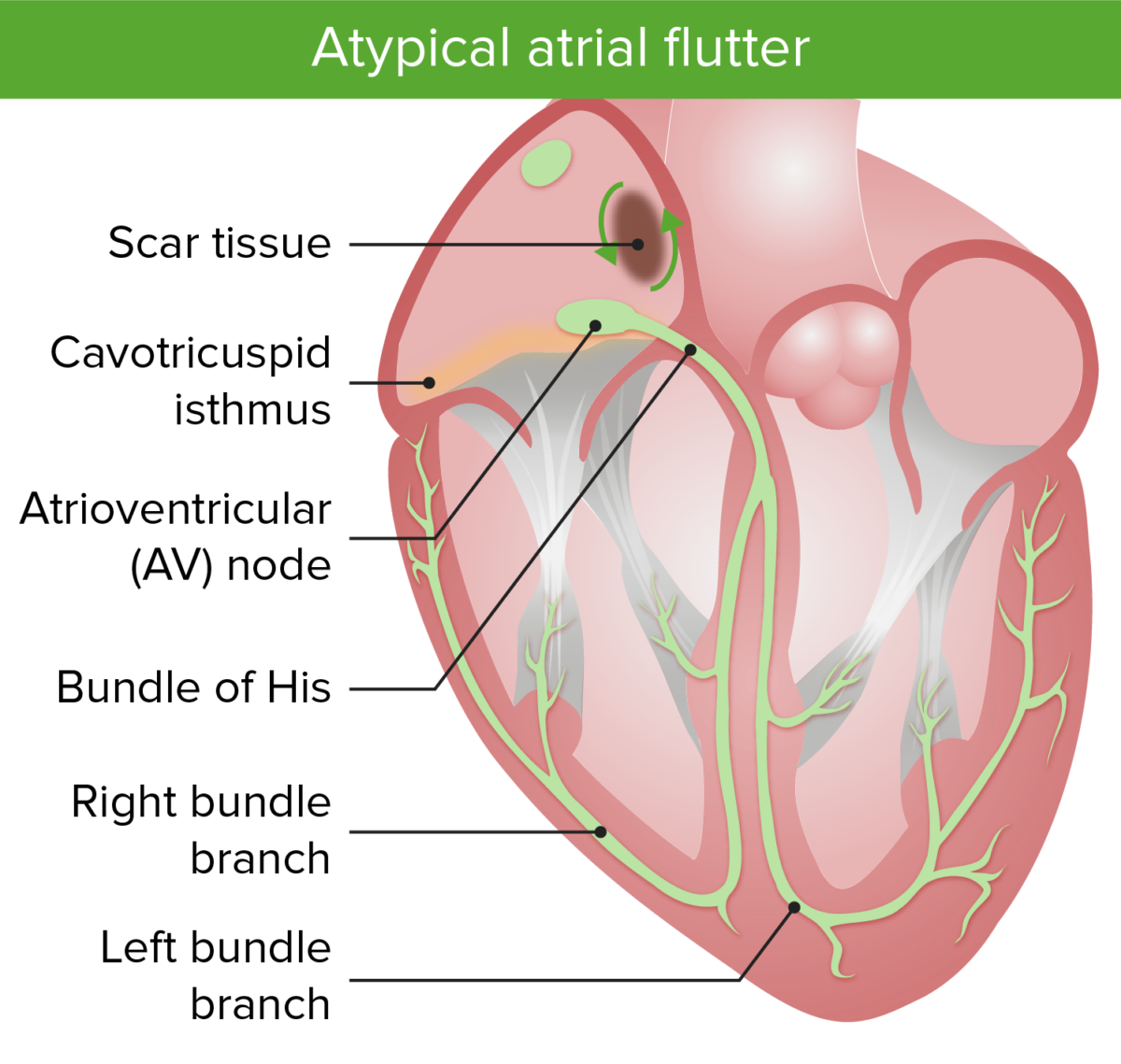
La imagen muestra los circuitos macro reentrantes en el flutter auricular atípico. Obsérvese que el flutter auricular atípico se concentra alrededor de una zona de tejido cicatricial.
Imagen por Lecturio.| Complicación | Posibles síntomas | Hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la exploración física | |
|---|---|---|---|
Cardíacas:
|
Insuficiencia cardíaca |
|
|
| Isquemia miocárdica |
|
|
|
Tromboembólicas:
|
Accidente cerebrovascular/accidente cerebrovascular isquémico transitorio |
|
Déficits focales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el examen neurológico |
| Infarto esplénico |
|
|
|
| Infarto intestinal |
|
|
|
| Infarto renal |
|
|
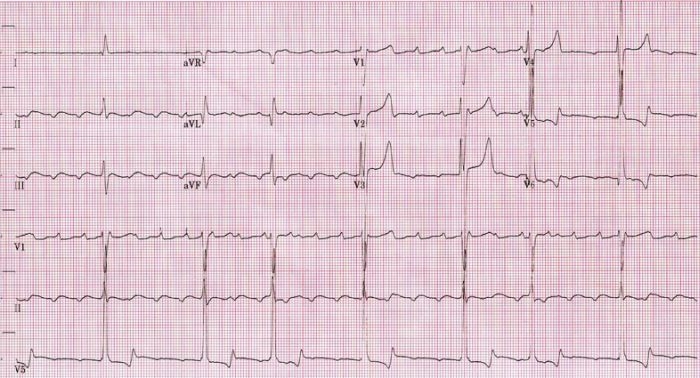
Un ECG que muestra un flutter auricular lento con una longitud de ciclo auricular de 400 ms (frecuencia auricular de 150/min).
Imagen: “Atrial rate of 150/min” por Dept. of Cardiology, Beth Israel Medical Center. 16th Street and 1st Avenue. New York, New York 10003, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.5.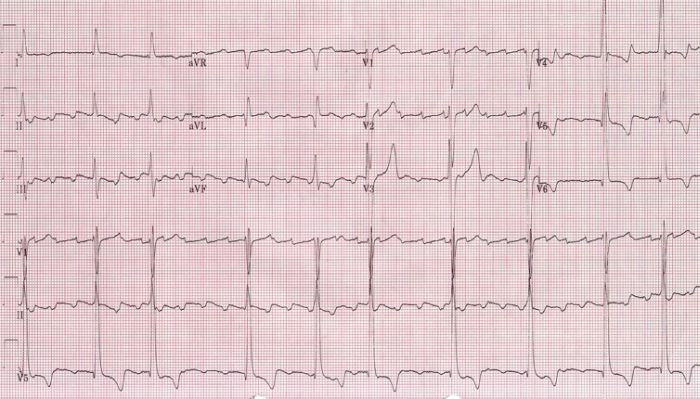
Un ECG que muestra un flutter auricular más rápido con una longitud de ciclo auricular de 280 ms (frecuencia auricular de 214/min).
Imagen: “Atrial rate of 214/min” por Dept. of Cardiology, Beth Israel Medical Center. 16th Street and 1st Avenue. New York, New York 10003, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.5.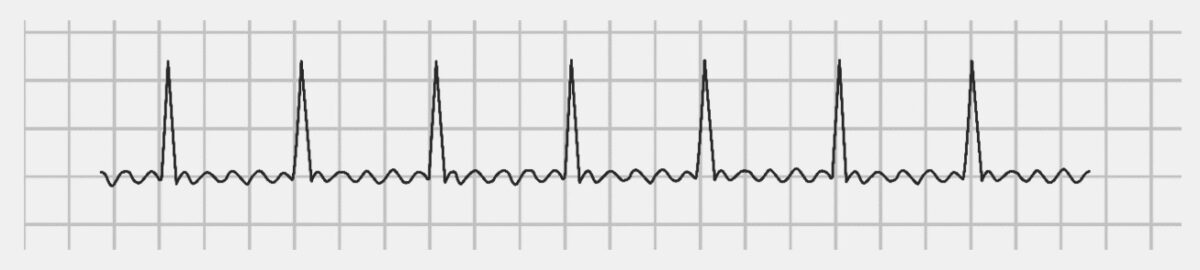
Un ECG que muestra la clásica apariencia de “diente de sierra” en el flutter auricular.
Imagen por Lecturio.| C | Congestive heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) (insuficiencia cardíaca) | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension (hipertensión) | 1 |
| A | Age (≥ 75 years) (edad ≥ 75 años) | 2 |
| D | Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus) | 1 |
| S | Stroke, TIA TIA Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or thromboembolism Thromboembolism Obstruction of a blood vessel (embolism) by a blood clot (thrombus) in the blood stream. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (accidente cerebrovascular, accidente cerebrovascular isquémico transitorio o tromboembolismo) | 2 |
| V | Vascular disease (enfermedad vascular) | 1 |
| A | Age 65–74 years (edad 65–74 años) | 1 |
| Sc | Sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria category (female) (sexo femenino) | 1 |