La fiebre maculosa de las Montañas Rocosas es una infección bacteriana causada por el parásito intracelular Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia rickettsii A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the etiologic agent of rocky mountain spotted fever. Its cells are slightly smaller and more uniform in size than those of rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia. La transmisión se produce a través de un vector artrópodo, más comúnmente la garrapata del perro americano ( Dermacentor variabilis Dermacentor Variabilis Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever). La fiebre maculosa de las Montañas Rocosas es frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sureste de Estados Unidos. Los LOS Neisseria primeros signos y síntomas de la fiebre maculosa de las Montañas Rocosas son inespecíficos e incluyen fiebre alta, cefaléa intensa y erupción cutánea. El sarpullido es característico, ya que comienza de forma periférica y se desplaza hacia el centro, y también aparece en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las manos y las plantas. Se requiere una alta sospecha clínica para el diagnóstico, y se recomienda el tratamiento empírico con doxiciclina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria 5 días siguientes al AL Amyloidosis inicio de los LOS Neisseria síntomas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La fiebre maculosa de las montañas rocosas es una enfermedad infecciosa causada por la bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia rickettsii A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the etiologic agent of rocky mountain spotted fever. Its cells are slightly smaller and more uniform in size than those of rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia, que suele ser transmitida por garrapatas.
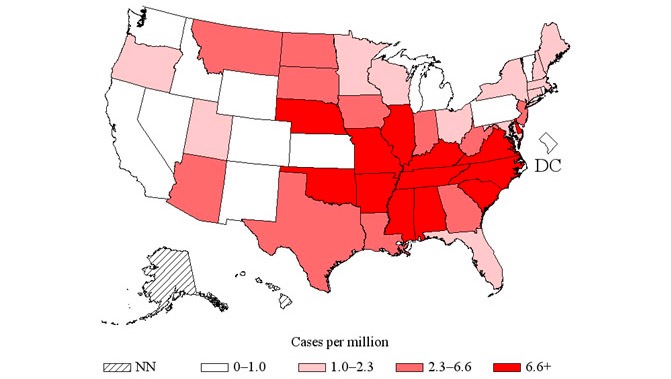
Distribución de la rickettsiosis de fiebre maculosa en Estados Unidos, de la que la fiebre maculosa de las montañas rocosas es un tipo, 2014
Imagen: “US distribution of spotted fever rickettsiosis” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público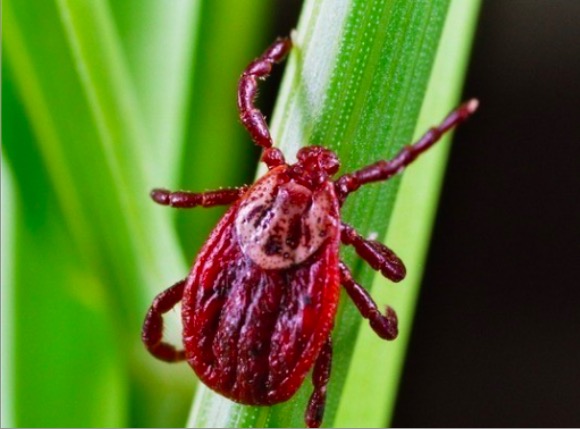
Garrapata Dermacentor adulta
Imagen: “Adult Dermacentor spp. tick” por Center for Infectious Diseases and Travel Medicine, University Hospital Freiburg, Hugstetter Strasse, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Los LOS Neisseria síntomas suelen aparecer entre 2–14 días después de la exposición a la picadura de una garrapata infectada. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas iniciales pueden ser imprecisos e inespecíficos (fiebre, malestar general). Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden no ser conscientes de la exposición a las garrapatas.
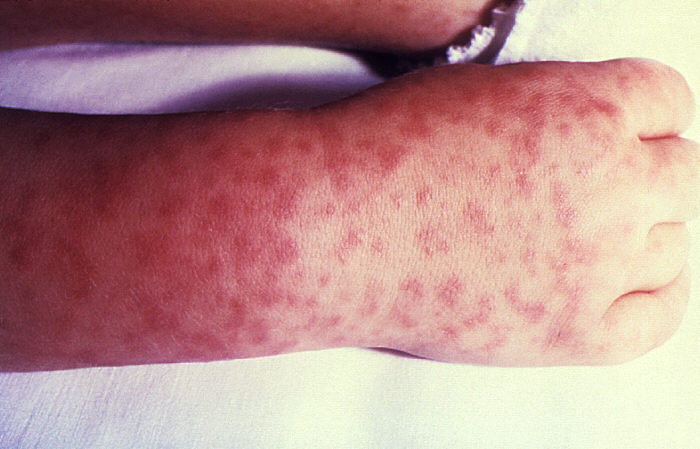
Erupción clásica de la FMMR, maculopapular y que no perdona las plantas de los pies y las palmas de las manos
Imagen: “Child’s right hand and wrist” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público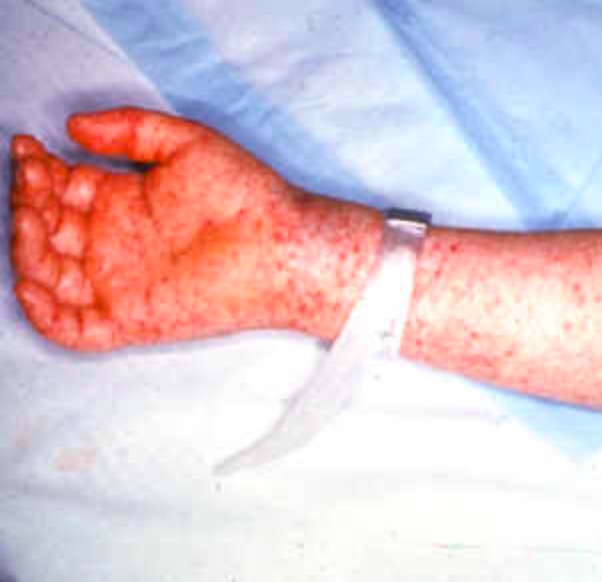
Erupción clásica de la fiebre maculosa de las montañas rocosas, maculopapular y que no perdona las plantas de los pies y las palmas de las manos
Imagen: “Rocky mountain spotted fever” por el CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLas complicaciones de una infección no tratada pueden incluir:
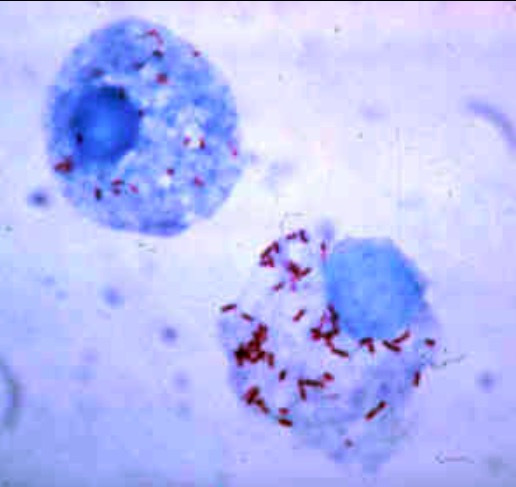
R. rickettsii teñido con Giemsa en las células de una garrapata
Imagen: “Gimenez stain” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público