Los LOS Neisseria factores de crecimiento hematopoyéticos son una familia de glucoproteínas responsables de la proliferación y diferenciación de las células progenitoras hematopoyéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea. La eritropoyetina, la trombopoyetina, el factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos (G-CSF) y el factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos ( GM-CSF GM-CSF An acidic glycoprotein of mw 23 kda with internal disulfide bonds. The protein is produced in response to a number of inflammatory mediators by mesenchymal cells present in the hemopoietic environment and at peripheral sites of inflammation. GM-CSF is able to stimulate the production of neutrophilic granulocytes, macrophages, and mixed granulocyte-macrophage colonies from bone marrow cells and can stimulate the formation of eosinophil colonies from fetal liver progenitor cells. GM-CSF can also stimulate some functional activities in mature granulocytes and macrophages. White Myeloid Cells: Histology) se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ciertos casos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria que la hematopoyesis normal está alterada debido a un tratamiento (e.g., quimioterapia) o una enfermedad subyacente (e.g., anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types aplásica). Comúnmente, los LOS Neisseria agentes estimulantes de la eritropoyesis se administran como parte del tratamiento de la anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types inducida por quimioterapia y la anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types secundaria a la ERC. G-CSF y GM-CSF GM-CSF An acidic glycoprotein of mw 23 kda with internal disulfide bonds. The protein is produced in response to a number of inflammatory mediators by mesenchymal cells present in the hemopoietic environment and at peripheral sites of inflammation. GM-CSF is able to stimulate the production of neutrophilic granulocytes, macrophages, and mixed granulocyte-macrophage colonies from bone marrow cells and can stimulate the formation of eosinophil colonies from fetal liver progenitor cells. GM-CSF can also stimulate some functional activities in mature granulocytes and macrophages. White Myeloid Cells: Histology se administran para tratar la neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia inducida por quimioterapia. Los LOS Neisseria agentes estimulantes de la trombopoyesis se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la prevención o el tratamiento de la trombocitopenia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria factores de crecimiento hematopoyéticos son glucoproteínas que regulan la proliferación, diferenciación y maduración de las células progenitoras, así como la función de las células maduras.
| Citocinas/factores de crecimiento | Función | Agente(s) farmacológico(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Eritropoyetina | Estimula la eritropoyesis, incluida la diferenciación |
|
| Factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos ( GM-CSF GM-CSF An acidic glycoprotein of mw 23 kda with internal disulfide bonds. The protein is produced in response to a number of inflammatory mediators by mesenchymal cells present in the hemopoietic environment and at peripheral sites of inflammation. GM-CSF is able to stimulate the production of neutrophilic granulocytes, macrophages, and mixed granulocyte-macrophage colonies from bone marrow cells and can stimulate the formation of eosinophil colonies from fetal liver progenitor cells. GM-CSF can also stimulate some functional activities in mature granulocytes and macrophages. White Myeloid Cells: Histology) | Estimula las células progenitoras mieloides | Sargramostim Sargramostim Hematopoietic Growth Factors |
| Factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos (G-CSF) | Estimula las células precursoras de neutrófilos |
|
| Trombopoyetina (TPO) | Estimula la trombopoyesis |
|
| IL-11 | Estimula la trombopoyesis | Oprelvekin Oprelvekin Hematopoietic Growth Factors |
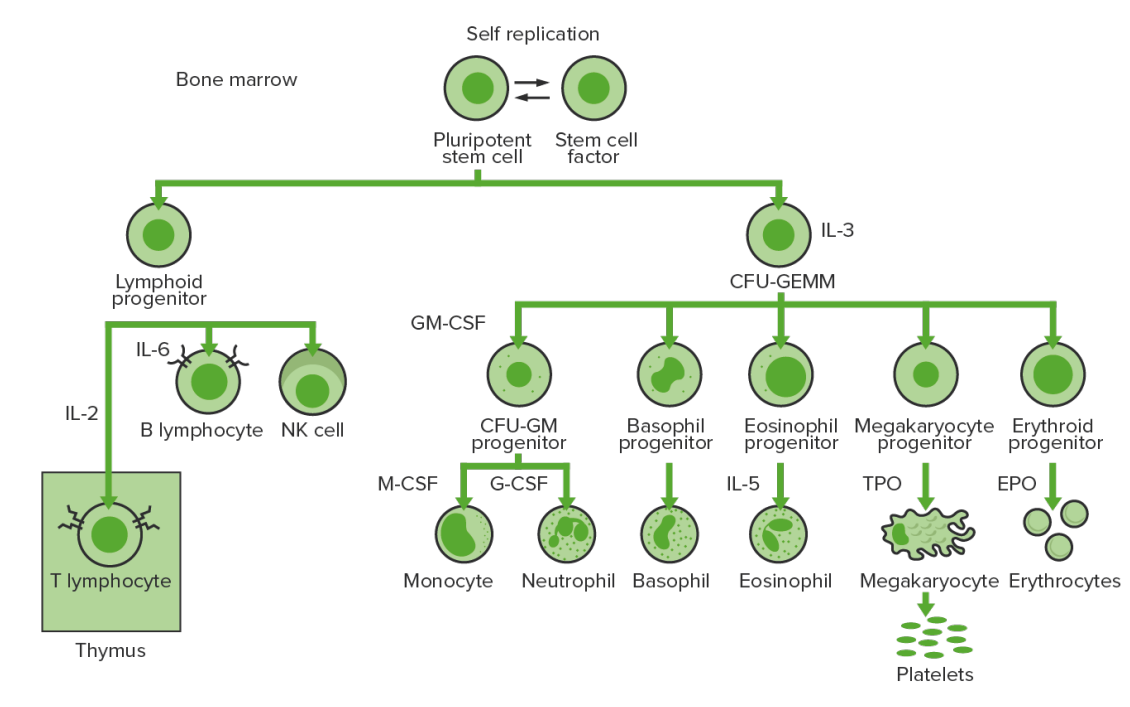
Hematopoyesis de la médula ósea: proliferación y diferenciación de los elementos formes de la sangre.
IL-3: interleucina-3
CFU-GEMM: unidad formadora de colonias: granulocitos, eritrocitos, monocitos, megacariocitos
IL-2: interleucina-2
IL-6: interleucina-6
CFU-GM: unidad formadora de colonias-granulocitos-macrófagos
GM-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
M-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de macrófagos
G-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos
IL-5: interleucina-5
NK: célula asesina natural
TPO: trombopoyetina
EPO: eritropoyetina
Los LOS Neisseria agentes estimulantes de la eritropoyesis son sustancias farmacológicas que estimulan la producción de eritrocitos y se utilizan para tratar la anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types debida a una variedad de afecciones.
| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Farmacocinética | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoetina alfa |
|
|
|
| Darbepoetina alfa |
|
Anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology.
Anemia: Overview and Types de 2do grado por:
|
|
| Metoxipolietilenglicol-epoetina beta |
|
Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types de 2do grado por ERC |
Los LOS Neisseria factores de crecimiento mieloides son agentes que estimulan la proliferación y diferenciación de ≥ 1 tipo de células mieloides y se utilizan para tratar los LOS Neisseria recuentos bajos de neutrófilos.
| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Farmacocinética | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filgrastim Filgrastim A recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) that is used in the treatment and prevention of neutropenia, preparation and collection of blood progenitor cells, and for use in peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Hematopoietic Growth Factors |
|
|
|
| Pegfilgrastim Pegfilgrastim Hematopoietic Growth Factors |
|
|
|
| Sargramostim Sargramostim Hematopoietic Growth Factors |
|
|
|
Los LOS Neisseria factores de crecimiento trombopoyéticos estimulan la trombopoyesis mediante la acción de la IL-11 o mediante la activación del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de TPO.
| Medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Farmacocinética | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oprelvekin Oprelvekin Hematopoietic Growth Factors | Estimula la megacariocitopoyesis y la trombopoyesis |
|
Previene la trombocitopenia grave en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes que reciben quimioterapia para el cáncer no mieloide |
| Romiplostim Romiplostim Hematopoietic Growth Factors | ↑ Plaquetas al AL Amyloidosis unirse al AL Amyloidosis receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de TPO |
|
|
| Eltrombopag Eltrombopag Hematopoietic Growth Factors |
|
|
Para todos los LOS Neisseria agentes, la hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento o a los LOS Neisseria componentes es una contraindicación.