El factor de necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage tumoral ( TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es una citoquina importante, liberada principalmente por macrófagos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta a estímulos. Entre los LOS Neisseria factores estimulantes se incluye; la presencia de productos microbianos, células muertas y lesiones. Esta proteína pertenece a la superfamilia TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF), un grupo de ligandos y receptores que realizan funciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la respuesta inflamatoria, la morfogénesis y la proliferación celular. El factor de necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage tumoral interactúa con 2 receptores, que inician vías de transducción de señales que conducen a diferentes respuestas celulares (inflamación, supervivencia celular o apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage). La activación inapropiada o desenfrenada de la señalización de TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) produce inflamación crónica, como se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum enfermedades autoinmunes (e.g., artritis reumatoide, psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is a common T-cell-mediated inflammatory skin condition. The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be due to genetic inheritance and environmental triggers. There are 4 major subtypes, with the most common form being chronic plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis). El mecanismo de inhibición del TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia utilizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de estas enfermedades inflamatorias.
Last updated: May 18, 2023
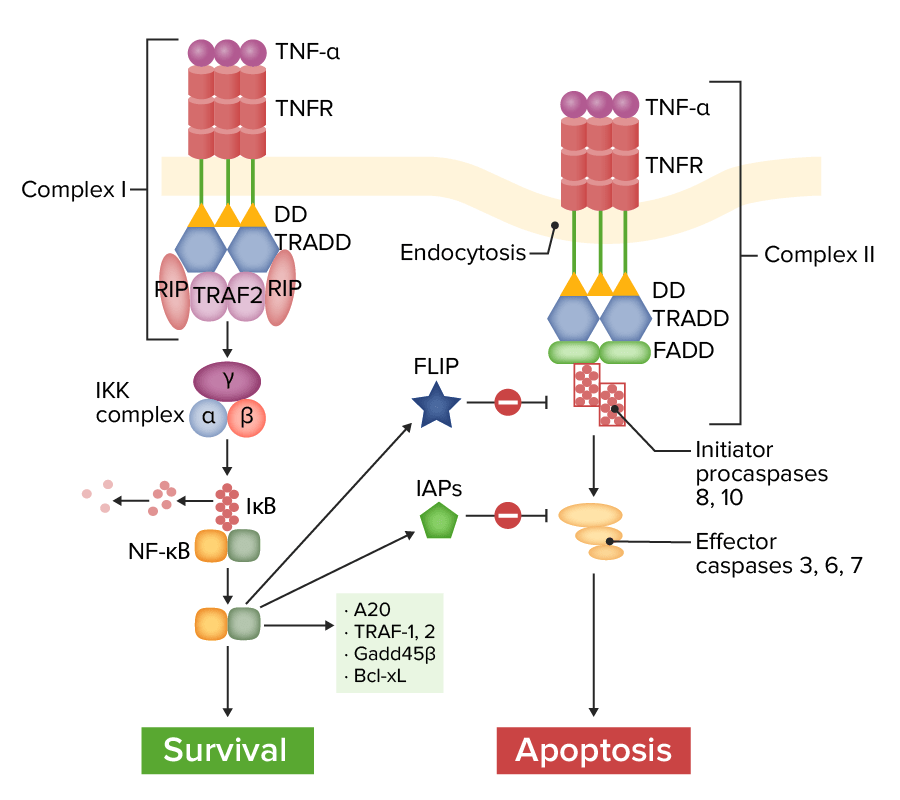
Vía de señalización del receptor 1 del factor de necrosis tumoral (TNFR1, por sus siglas en inglés):
Complejo I (a la izquierda): Con la ligadura del TNF-α, el receptor del factor de necrosis tumoral recluta varias moléculas adaptadoras, lo que da lugar a la activación del factor nuclear kappa-B (NF-κB), que induce varios genes antiapoptóticos y señales de supervivencia. La proteína inhibidora FLICE (FLIP) y las proteínas inhibidoras de la apoptosis (IAP) modulan e inhiben la vía de la apoptosis. Complejo II (a la derecha): Sin ciertas proteínas adaptadoras (TRAF-2, RIP), el TNFR conduce al reclutamiento de la proteína asociada a Fas con dominio de muerte (FADD, por sus siglas en inglés). La caspasa-8 se activa y se libera en el citoplasma, activando las caspasas efectoras para inducir la apoptosis.
IκB: inhibidor de NF-κTRAF-2: factor asociado al receptor del TNF.
Imagen por Lecturio.
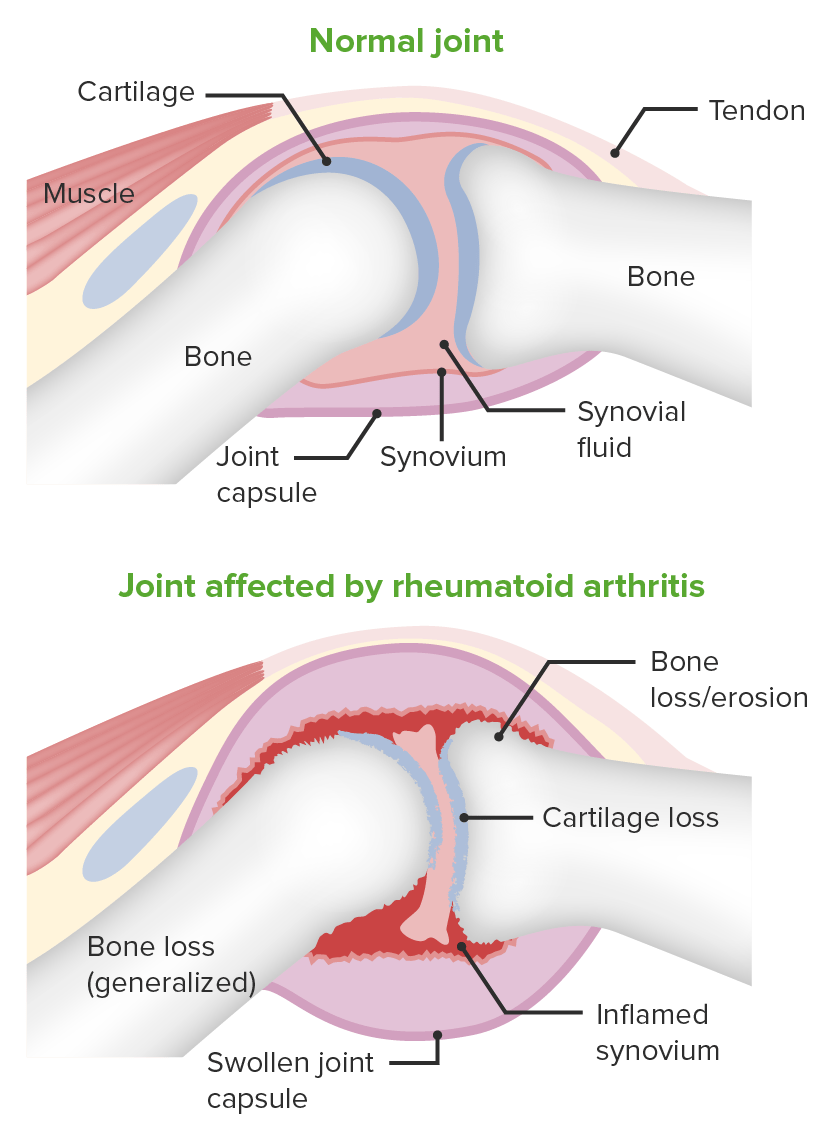
Imagen que demuestra la patología de la artritis reumatoide:
Se muestran los cambios en el espacio articular.
El factor de necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage tumoral tiene múltiples efectos biológicos y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ciertas afecciones (e.g., artritis reumatoide), se han observado niveles elevados de TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF). El mecanismo de inhibición de TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia utilizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de enfermedades inflamatorias.
| Terapia anti-TNF | Mecanismo de acción | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|
| Infliximab Infliximab A chimeric monoclonal antibody to tnf-alpha that is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticuerpo quimérico recombinante (que tiene una región variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables murina y una región constante de IgG1 humana) que se une al AL Amyloidosis TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) y evita la interacción con el receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors |
|
| Etanercept Etanercept A recombinant version of soluble human tnf receptor fused to an IgG Fc fragment that binds specifically to tumor necrosis factor and inhibits its binding with endogenous tnf receptors. It prevents the inflammatory effect of tnf and is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis; psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Immunosuppressants | Proteína de fusión que se une y neutraliza el TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) y la linfotoxina |
|
| Adalimumab Adalimumab A humanized monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to tnf-alpha and blocks its interaction with endogenous tnf receptors to modulate inflammation. It is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; psoriatic arthritis; Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticuerpo monoclonal IgG1 totalmente humanizado que bloquea la unión del TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) a los LOS Neisseria receptores |
|
| Golimumab Golimumab Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticuerpo monoclonal IgG1 completamente humanizado con alta afinidad y especificidad por TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) |
|
| Certolizumab Certolizumab Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) | Anticuerpo monoclonal humanizado pegilado específico de TNF TNF Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a major cytokine, released primarily by macrophages in response to stimuli. The presence of microbial products and dead cells and injury are among the stimulating factors. This protein belongs to the TNF superfamily, a group of ligands and receptors performing functions in inflammatory response, morphogenesis, and cell proliferation. Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) |
|