La escoliosis es una alteración estructural de la columna vertebral caracterizada por una curvatura lateral de la columna superior a 10 grados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el plano coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT). La escoliosis se puede clasificar como idiopática ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos) o secundaria a condiciones subyacentes. Otras clasificaciones se basan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la etiología, la ubicación y la gravedad. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan asimetría espinal y, a menudo, tienen dolor Dolor Inflammation asociado. El diagnóstico es inicialmente clínico y luego se confirma con una radiografía. El tratamiento puede ser conservador o quirúrgico, dependiendo de la gravedad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La escoliosis es una curvatura espinal lateral de la columna de más de 10 grados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el plano coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT), generalmente acompañada de grados variables de rotación.
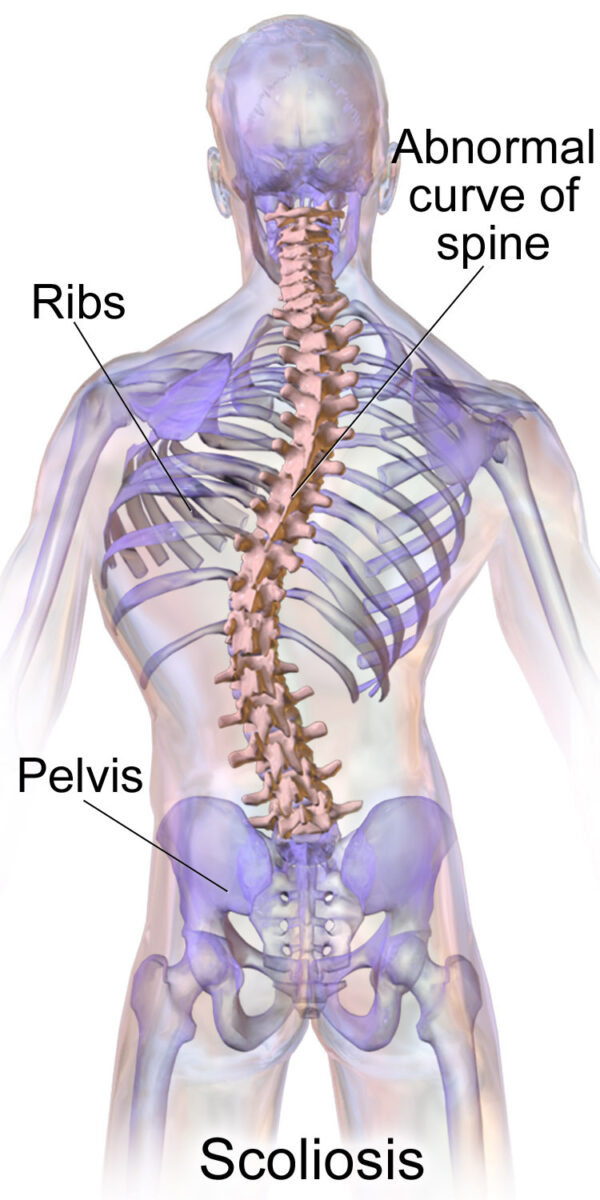
Escoliosis
Imagen: “Blausen 0785 Escoliosis 01” por Blausen. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La escoliosis puede desarrollarse de novo o como una continuación de la escoliosis congénita, idiopática o de desarrollo temprano. La carga desigual en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la columna vertebral produce y exacerba la curvatura patológica que se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la escoliosis.
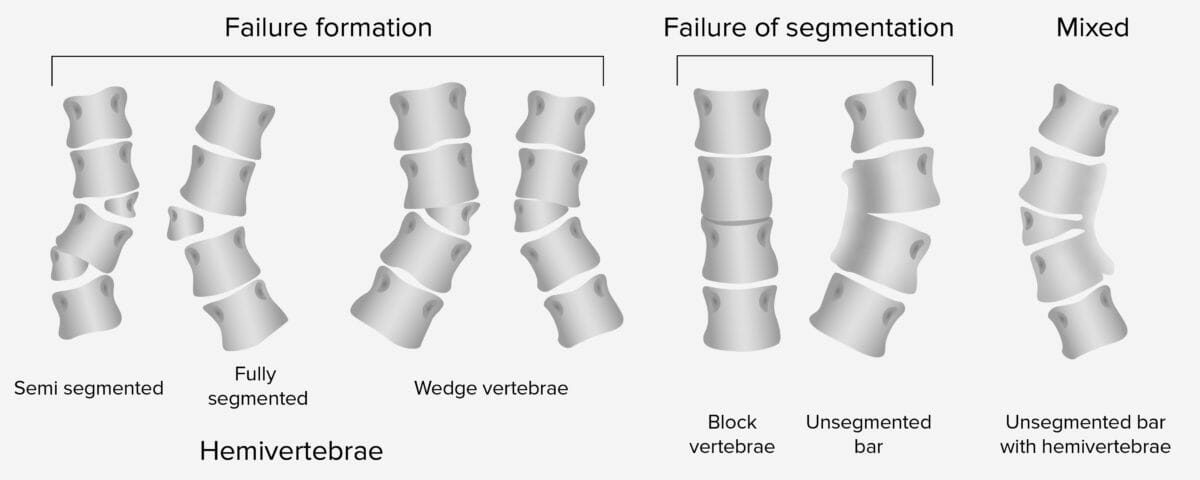
Clasificación de la escoliosis congénita
Imagen por Lecturio.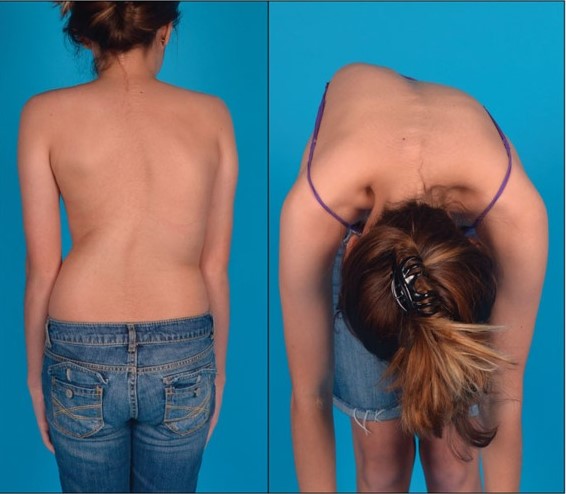
Ejemplo de un paciente con escoliosis realizando la flexión hacia delante, o prueba de Adam, mostrando la “joroba” que se desarrolla cuando el paciente se inclina, demostrando una prueba positiva de escoliosis.
Imagen: “Idiopathic scoliosis in an adolescent female” por Swarkar Sharma et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Medición de la joroba costal de un paciente con escoliosis en la posición de flexión hacia adelante usando un escoliómetro:
El examinador está buscando la lectura más alta detectada en la columna torácica.
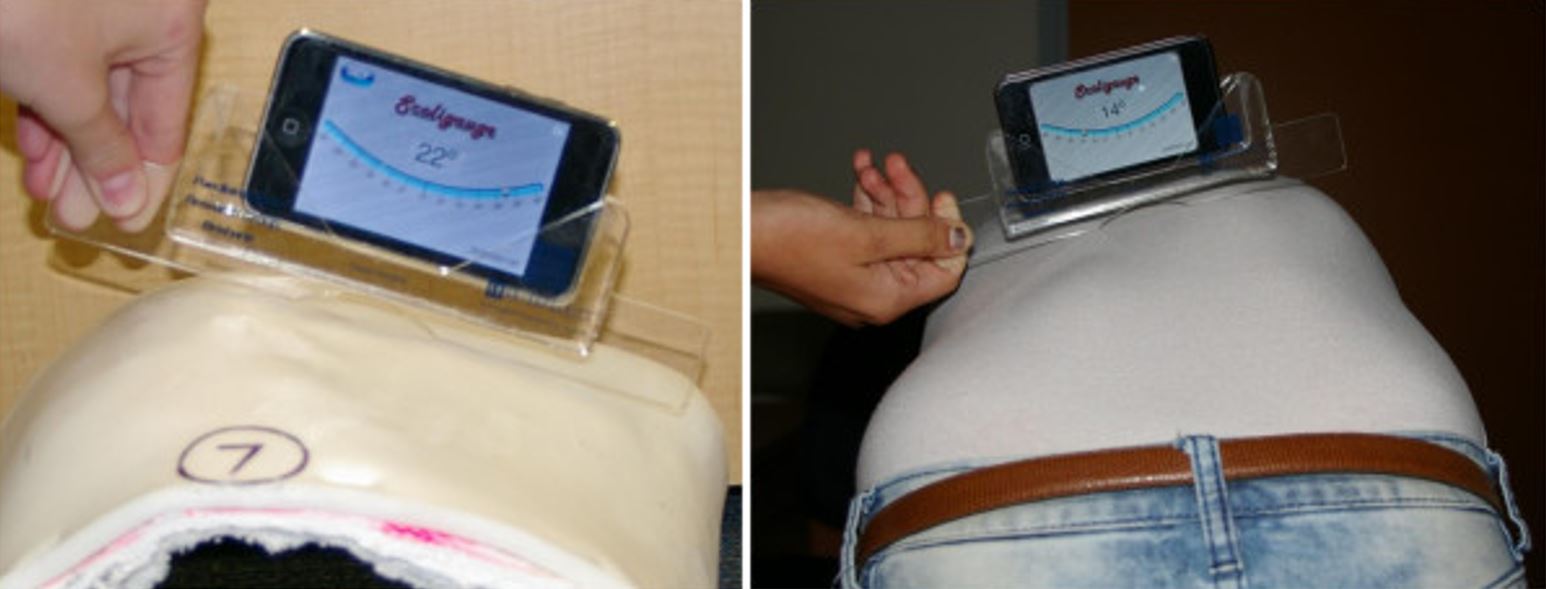
Medición de la joroba costal en un modelo de yeso (izquierda) y un paciente con escoliosis (derecha), usando un teléfono inteligente y la aplicación Scoliogauge en combinación con una funda acrílica para reflejar las dimensiones del escoliómetro tradicional.
Imagen: “Measurement of the rib hump” por Izatt MT, Bateman GR, Adam CJ. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El diagnóstico se realiza inicialmente clínicamente y luego se confirma mediante radiografías, que mostrarán la presencia de una curvatura espinal. La escoliosis idiopática es un diagnóstico de exclusión.
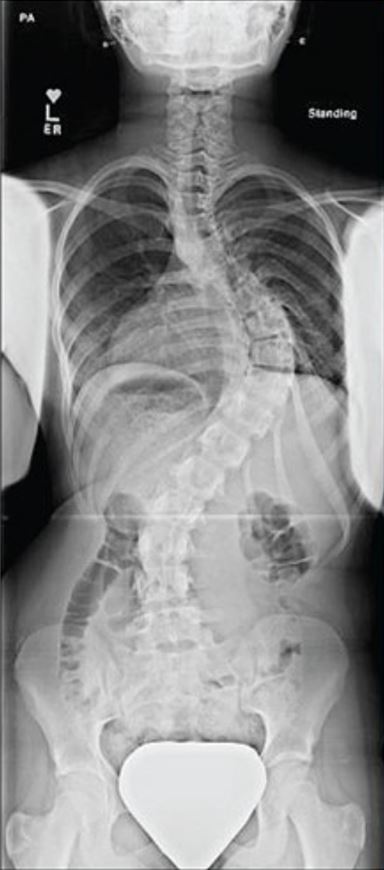
Radiografía de un paciente con levoscoliosis torácica
Imagen: “Idiopathic scoliosis in an adolescent female” por Sharma, S., et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, cortada por Lecturio.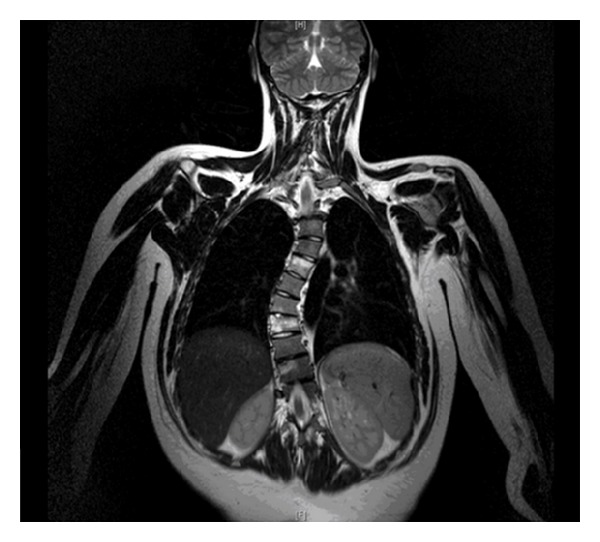
RM de un paciente con osteomielitis recurrente que causa dextroscoliosis torácica
Imagen: “Coronal Thoracic Spine MRI image” por Alexander Armstrong et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0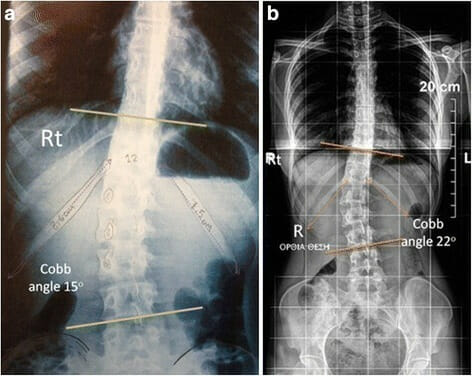
Curva idiopática lumbar derecha con ángulo de Cobb de 15° b: Curva idiopática lumbar derecha con ángulo de Cobb de 22°.
Imagen: “Right lumbar idiopathic curve 15° of Cobb angle, the right 12th rib is longer, similarly in figure b, in a right lumbar idiopathic curve 22° of Cobb angle, the right 12th rib is longer” por Theodoros B Grivas. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El tratamiento varía de conservador a quirúrgico según el grado de escoliosis.
El pronóstico de la escoliosis depende de la causa subyacente, las comorbilidades y la deformidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el momento de la presentación.
Las siguientes condiciones están asociadas con la escoliosis: