El eritema nodoso es una paniculitis (inflamación de la grasa subcutánea) inmunomediada causada por una reacción de hipersensibilidad de tipo IV (de tipo retardado). Suele manifestarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres jóvenes como nódulos eritematosos y sensibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara anterior de las piernas. La etiología subyacente varía y puede estar asociada a una infección, a la exposición a medicamentos, a la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal, al AL Amyloidosis embarazo o a una neoplasia. Las lesiones suelen autorresolverse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 8 semanas sin dejar cicatrices. El tratamiento se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum identificar y tratar la causa subyacente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Epidemiología:
Etiología:
| Clasificación | Etiologías | Ejemplos |
|---|---|---|
| Causas infecciosas | Bacteriana |
|
| Viral |
|
|
| Fúngica |
|
|
| Causas no infecciosas | Drogas |
|
| Malignidad |
|
|
| Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal |
|
|
| Varios |
|
Una reacción inmune mediada por varios antígenos da lugar a la inflamación de la grasa subcutánea.
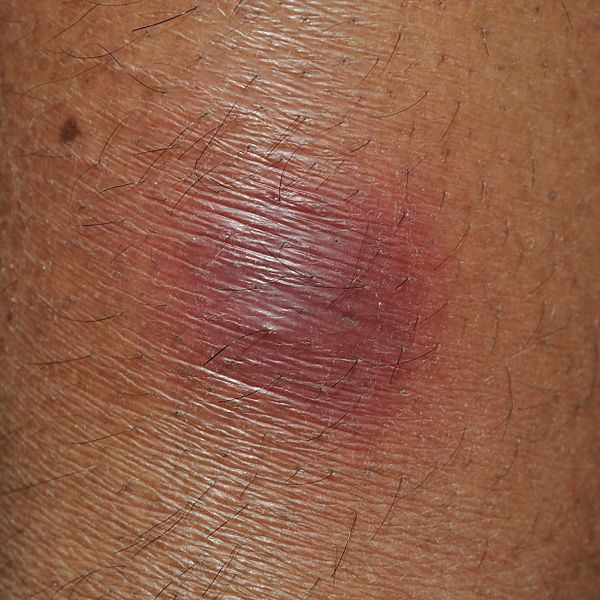
El eritema nodoso es una inflamación de las células grasas bajo la piel (paniculitis) que se caracteriza por nódulos o bultos rojos y sensibles que suelen aparecer en la cara anterior de ambas piernas.
Imagen: “Erythema nodosum” por Biswarup Ganguly. Licencia: CC BY 3.0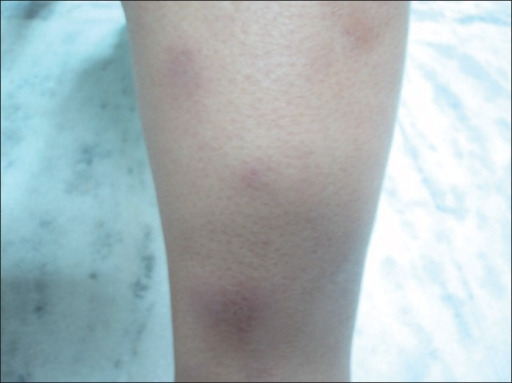
Eritema nodoso: presentación atípica de una enfermedad común
Imagen: “Erythematous, papulo-nodular skin lesions over the shin” por Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0