Los LOS Neisseria divertículos son protuberancias de la pared intestinal que se producen con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy. La afección de tener divertículos (llamada diverticulosis Diverticulosis A pathological condition characterized by the presence of a number of colonic diverticula in the colon. Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, including colon aging, motor dysfunction, increases in intraluminal pressure, and lack of dietary fibers. Diverticular Disease) es mayormente asintomática. Sin embargo, estos divertículos pueden volverse sintomáticos cuando se asocian a enfermedades. La diverticulitis Diverticulitis Inflammation of a diverticulum or diverticula. Diverticular Disease es la inflamación de los LOS Neisseria divertículos, que suele presentarse con dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal bajo y cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hábitos intestinales. La afección puede complicarse aún más con un absceso, una perforación, una fístula y una obstrucción intestinal. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum antibióticos, reanimación con líquidos y reposo intestinal. La cirugía es necesaria para las complicaciones, el fracaso del tratamiento médico y la enfermedad recurrente. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de hemorragia diverticular, se produce un cese espontáneo. La intervención invasiva será necesaria para las hemorragias persistentes o recurrentes.
Last updated: Jan 18, 2026
La
diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
A pathological condition characterized by the presence of a number of colonic diverticula in the colon. Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, including colon aging, motor dysfunction, increases in intraluminal pressure, and lack of dietary fibers.
Diverticular Disease es la presencia de múltiples divertículos, que son protuberancias
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum forma de saco de la pared intestinal.
La enfermedad diverticular es
diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
A pathological condition characterized by the presence of a number of colonic diverticula in the colon. Its pathogenesis is multifactorial, including colon aging, motor dysfunction, increases in intraluminal pressure, and lack of dietary fibers.
Diverticular Disease con síntomas asociados.
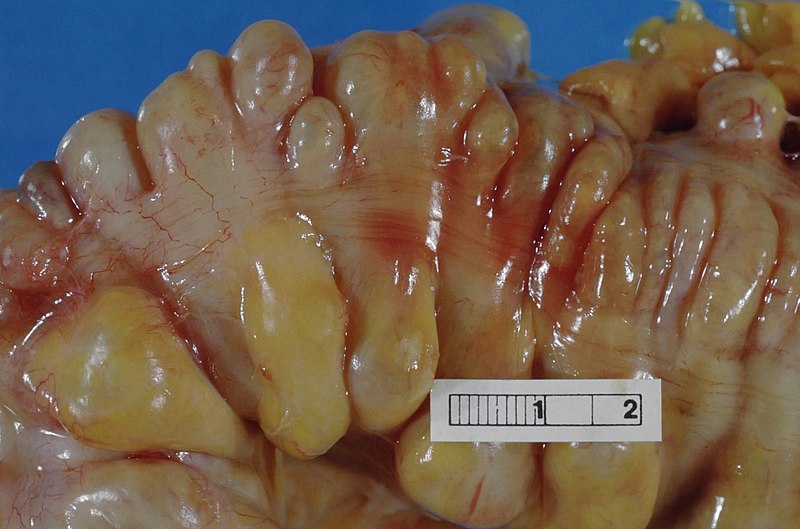
Diverticulosis: imagen que muestra el intestino grueso (colon sigmoide) con múltiples divertículos
Imagen: “Large bowel (sigmoid colon)” por Haymanj. Licencia: Dominio Público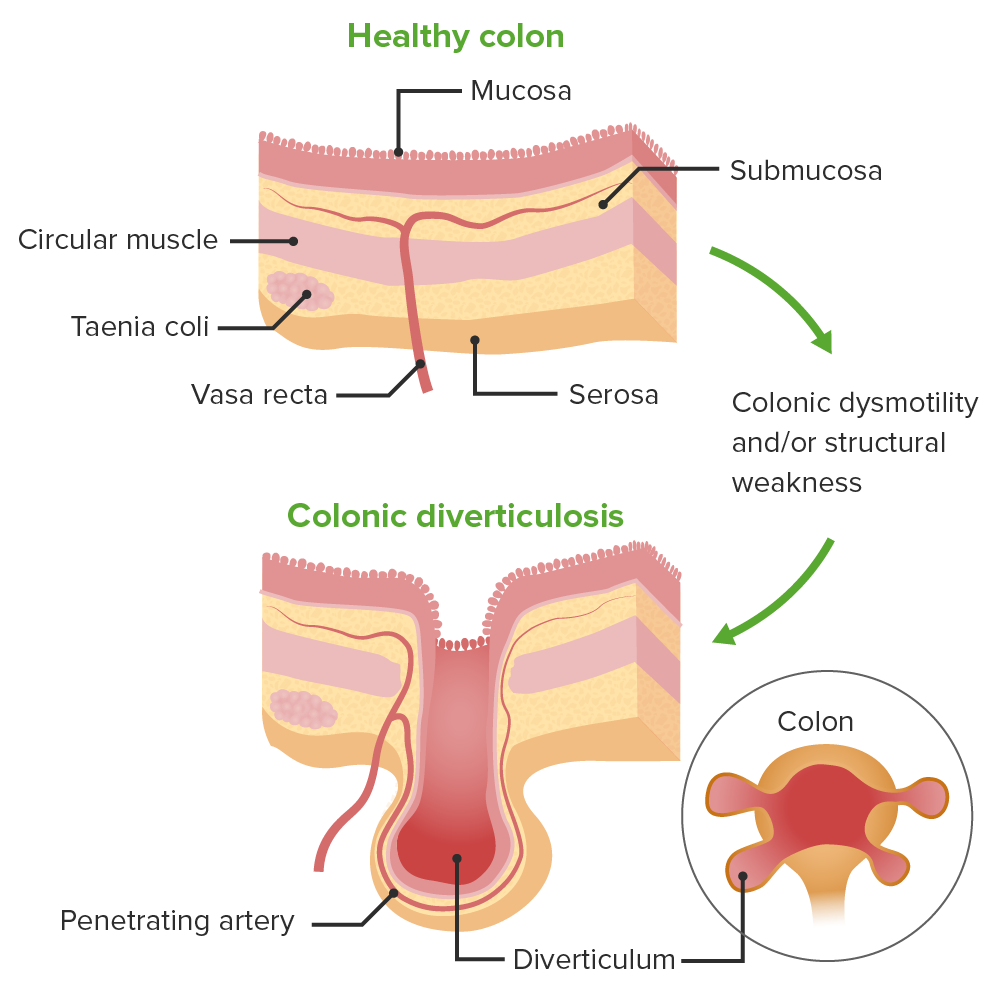
Fisiopatología del desarrollo de la diverticulosis a partir de un colon sano.
Los divertículos colónicos se forman cuando la mucosa y la submucosa se hernian a través de la envoltura que rodea los vasos rectos intramurales (vasos nutritivos).
La diverticulitis Diverticulitis Inflammation of a diverticulum or diverticula. Diverticular Disease suele ser leve, con el mesenterio y la grasa pericólica taponando una pequeña perforación. Una enfermedad más extensa puede provocar complicaciones.
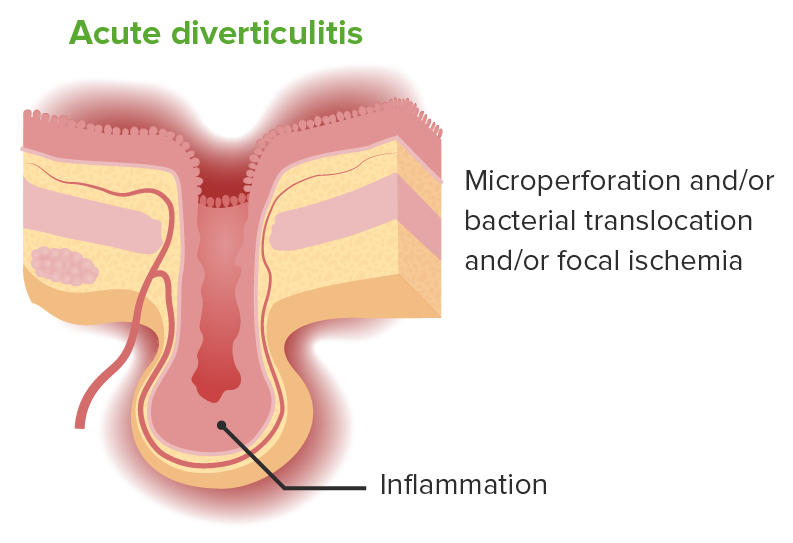
Fisiopatología de la diverticulitis.
La diverticulitis aguda es una inflamación localizada en un divertículo y en la mucosa circundante. El proceso puede incluir la microperforación o la translocación bacteriana, o la isquemia focal.
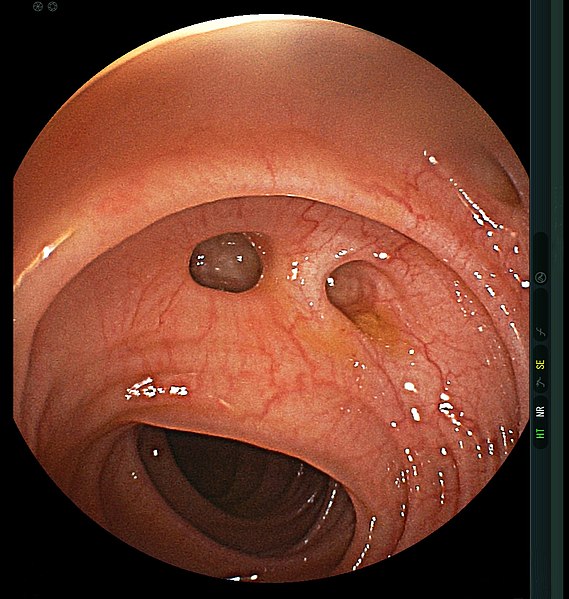
Diverticulosis: colonoscopia que muestra divertículos en el colon
Imagen: “Diverticulum” por MAC 06. Licencia: CC BY 4.0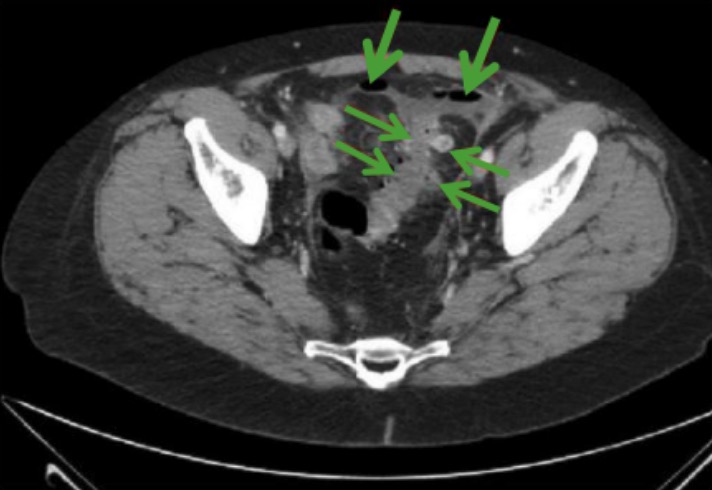
Imagen que ilustra la diverticulitis:
Tomografía computarizada que muestra diverticulitis perforada (flechas horizontales) y aire abdominal libre (flechas verticales)
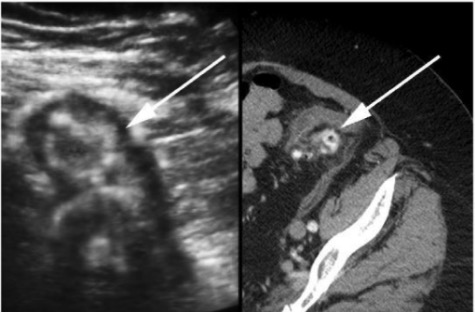
Imágenes de ultrasonido y tomografía computarizada de la diverticulitis:
Imagen por ultrasonido transabdominal de la paciente (izquierda) y tomografía computarizada corte axial (derecha) que revela divertículos inflamados (flecha).
Hallazgos de imagenología relacionados con la diverticulitis, como divertículos edematosos con paredes hipoecoicas engrosadas y centros hiperecoicos, y zonas hiperecoicas circundantes que representan grasa inflamada.
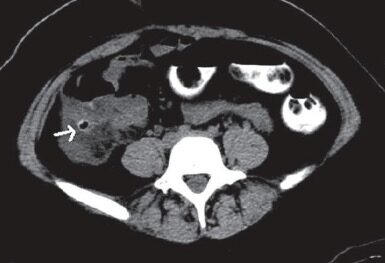
Imagenología que ilustra la diverticulitis: la TC con contraste oral muestra un divertículo cecal derecho inflamado (flecha).
Imagen: “Cecal diverticulitis” por Monika Sharma and Anjali Agrawal. Licencia: CC BY 2.0| Hinchey 1a | Flemón (localizado) |
|---|---|
| Hinchey 1b | Absceso pericolónico/mesentérico |
| Hinchey 2 | Absceso pélvico |
| Hinchey 3 | Peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury purulenta generalizada |
| Hinchey 4 | Peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury feculenta generalizada |
Justificación:
Procedimientos:
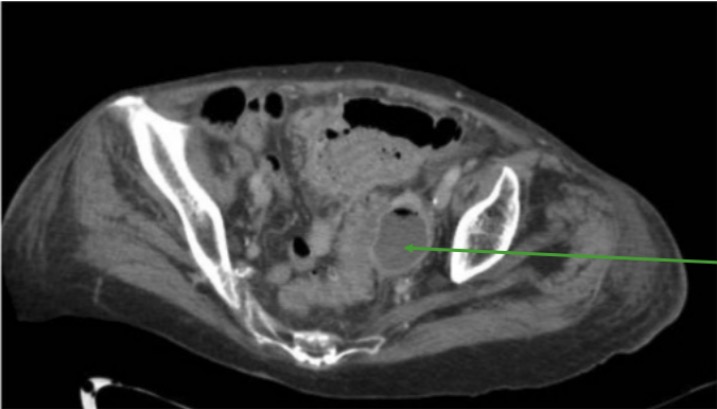
Imagen que ilustra un absceso relacionado con diverticulitis sigmoidea: TC que muestra una colección de líquido pericolónico con un nivel de aire-líquido (flecha verde) consistente con un absceso
Imagen: “Sigmoid diverticulitis” por Department of Surgery, Macerata Hospital, Macerata, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 4.0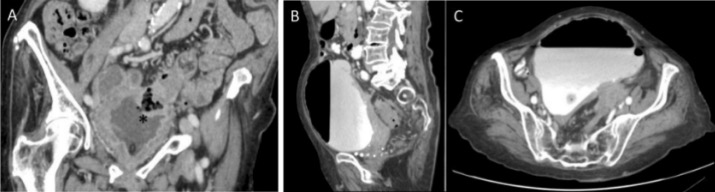
Fístula colovesical:
A: engrosamiento de la pared del intestino y la vejiga (asterisco negro)
B y C: recogida de contraste y aire en la vejiga
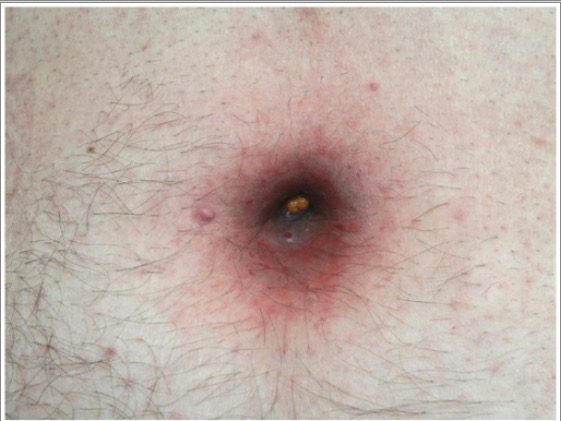
Diverticulitis fistulizante al ombligo: el ombligo y la piel periumbilical inflamados y macerados con material fecal en la fosa umbilical
Imagen: “Diverticulitis fistulizing to the umbilicus” por Second Department of Surgery, Democritus University of Thrace, Medical School, 68 100 Alexandroupolis, Greece. Licencia: CC BY 3.0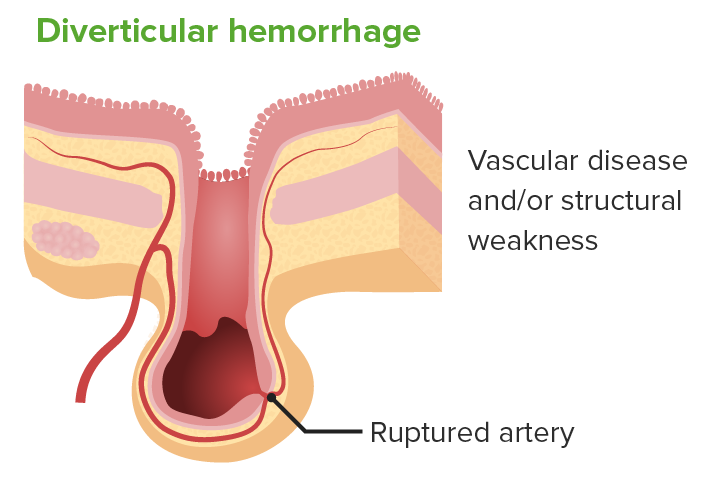
Ilustración de una hemorragia diverticular:
La hemorragia arterial puede complicar la diverticulosis, siendo la enfermedad vascular o la debilidad estructural los factores que probablemente contribuyan a ella. Es la fuente más común de sangrado digestivo inferior.
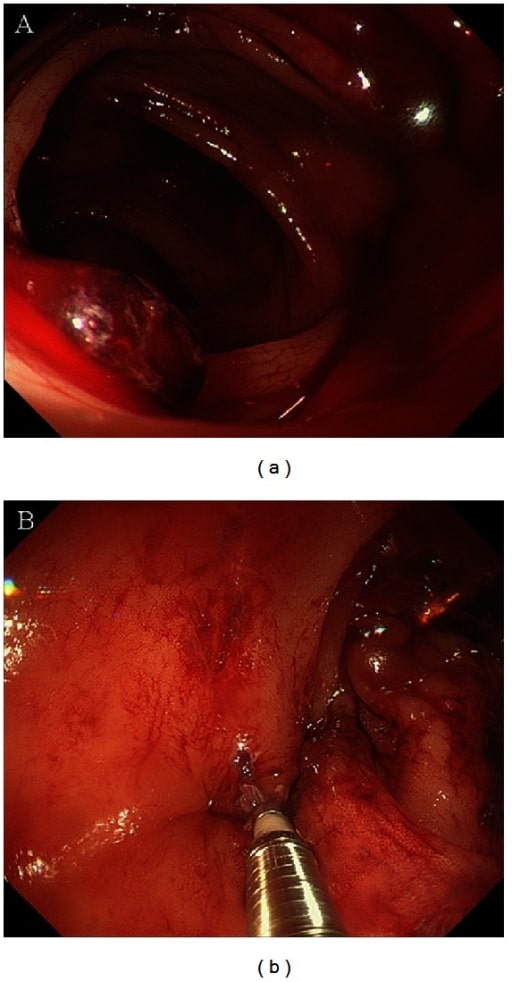
Hemorragia diverticular:
(a) vista de colonoscopia de una hemorragia diverticular en la flexión hepática
(b) tratamiento endoscópico mediante hemoclips