La enfermedad de Graves es un trastorno autoinmune caracterizado por la presencia de anticuerpos circulantes del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de la hormona estimulante del tiroides (TSH), que provocan la hiperfunción de la glándula tiroides. Las características clínicas incluyen las del hipertiroidismo, así como orbitopatía, bocio y dermopatía/mixedema pretibial. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante pruebas de laboratorio tiroideas que muestran una TSH baja, hormonas tiroideas elevadas (tiroxina [ T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones] y triyodotironina [ T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5' position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones]) y anticuerpos receptores de tirotropina ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum particular el subtipo de inmunoglobulinas estimulantes de la tiroides). Si las pruebas iniciales no son diagnósticas, la captación de yodo radiactivo (aumento de la captación) y el ultrasonido tiroideo (agrandamiento difuso de la tiroides) proporcionan información diagnóstica. Las opciones de tratamiento incluyen fármacos antitiroideos, ablación con yodo radiactivo y cirugía.
Last updated: Jan 24, 2026
La enfermedad de Graves es un trastorno autoinmune en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos contra los LOS Neisseria receptores de la hormona estimulante de la tiroides (TSH) hacen que la glándula tiroides se encuentre hiperfuncionante. El síndrome puede tener las siguientes características:
Se considera que la susceptibilidad a la enfermedad de Graves es una combinación de múltiples factores.
Factores de riesgo:
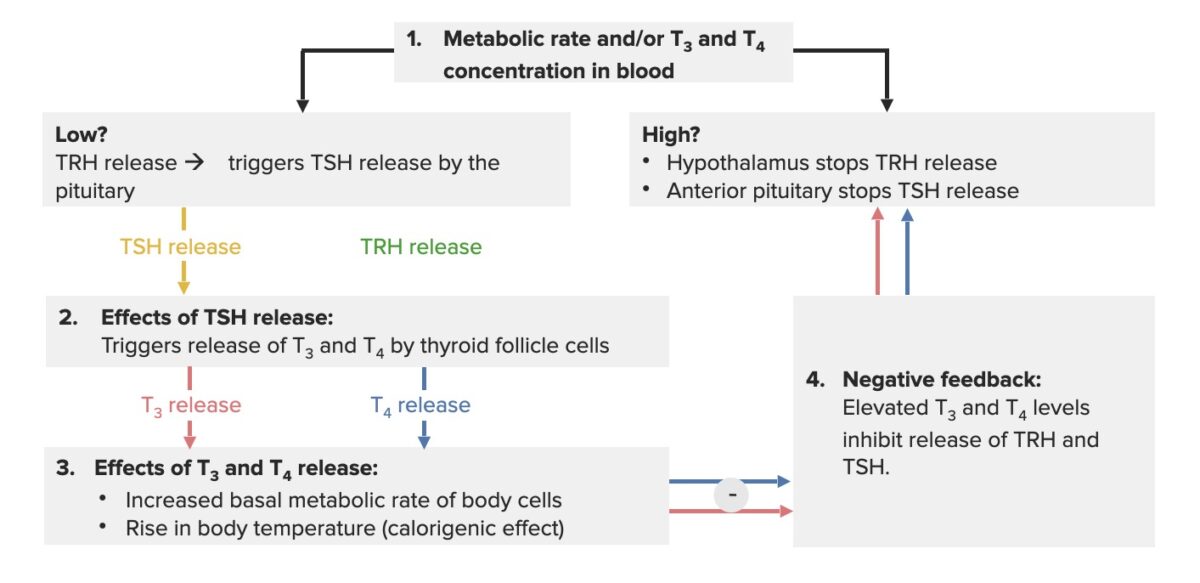
Bucle de retroalimentación del eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-tiroides:
Cuando las hormonas tiroideas son bajas, el hipotálamo libera la hormona liberadora de tirotropina (TRH), que hace que la glándula pituitaria secrete TSH. El efecto de este proceso es que la glándula tiroides produce tiroxina (T4) y triyodotironina (T3) (se produce más T4, ya que se convierte en T3). El aumento de las hormonas tiroideas (T3/T4 libre o no unida) crea una retroalimentación negativa, inhibiendo la liberación de TRH y TSH.
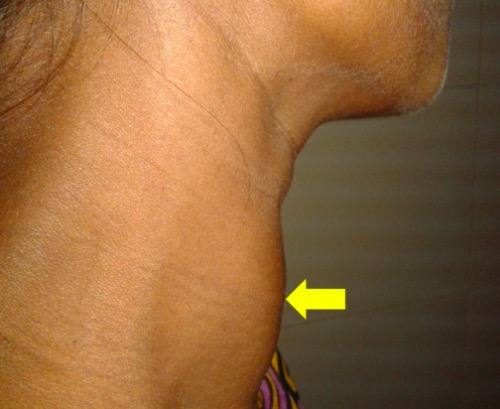
Bocio: glándula tiroides difusamente agrandada (flecha) en una mujer embarazada de 30 años
Imagen: “Diffusely enlarged thyroid gland” por Department of Cardiology, Dhaka Medical College Hospital, Dhaka, Bangladesh. Licencia: CC BY 4.0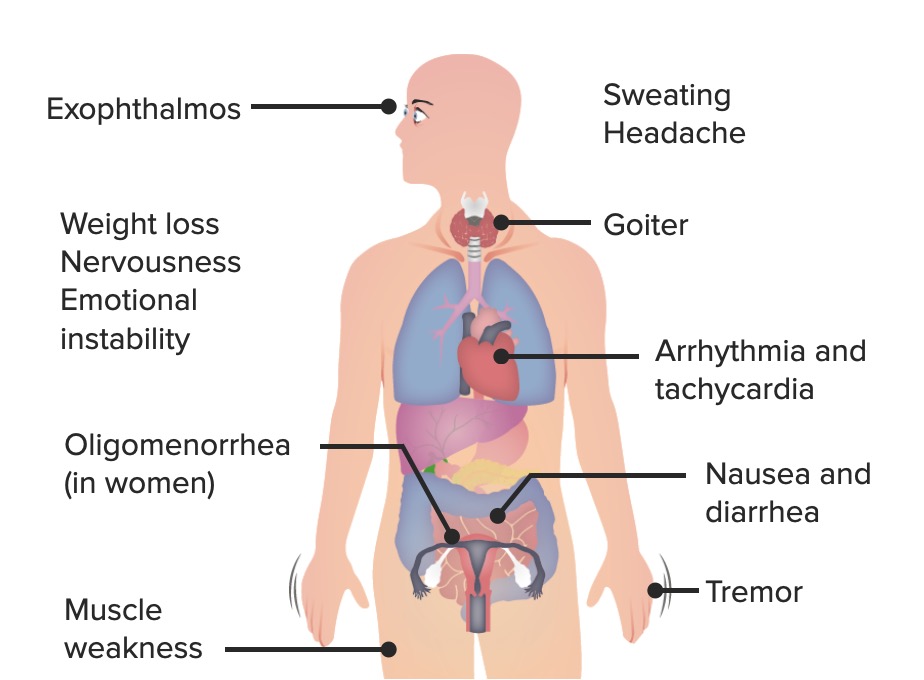
Los signos y síntomas más comunes de la enfermedad de Graves
Imagen por Lecturio.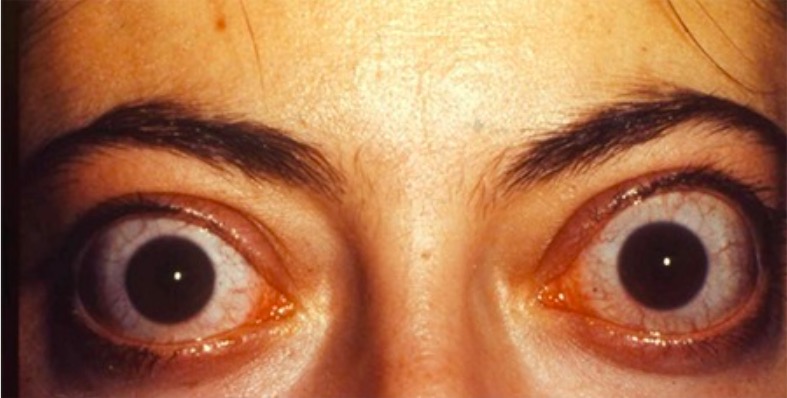
Efecto oftalmológico de la enfermedad de Graves: oftalmopatía asociada a tiroides infiltrativa bilateral en una mujer de 33 años
Imagen: “Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy” por Esra Şahlı and Kaan Gündüz. Licencia: CC BY 2.5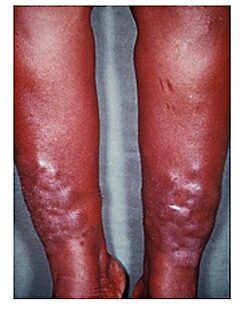
Mixedema
Imagen: “Myxedema” por Herbert L. Fred, MD and Hendrik A. van Dijk.Licencia: CCC POR 2.0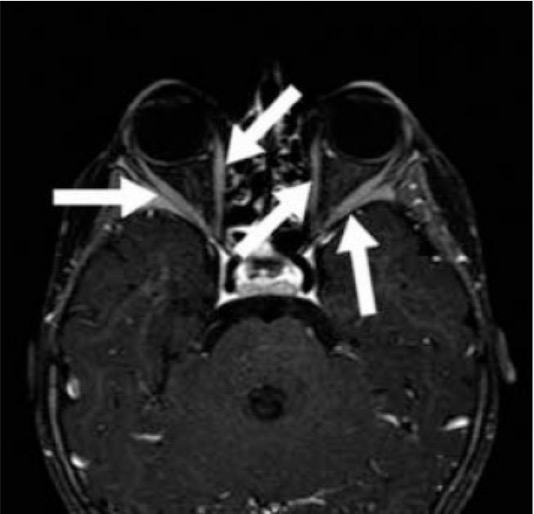
Oftalmopatía de Graves: la RM axial con contraste de un paciente de 2 años con enfermedad de Graves muestra un marcado realce de los músculos extraoculares (flechas) de las órbitas bilaterales.
Imagen: “T1 weighted fat saturated contrast enhanced axial MR” por Mustafa Kemal University School of Medicine, Department of Nuclear Medicine, Hatay, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.5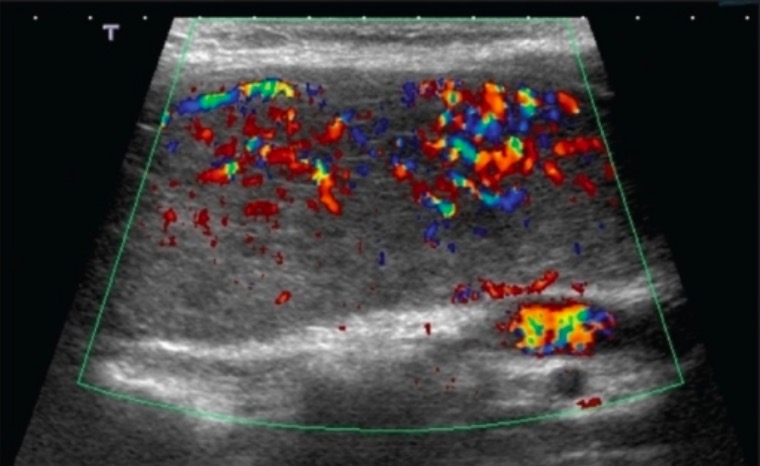
Ultrasonido tiroideo con Doppler en la enfermedad de Graves: una mujer de 28 años con enfermedad de Graves cuya ecografía con hallazgo Doppler muestra un flujo de color difuso que representa una vascularización intensa (“infierno tiroideo”)
Imagen: “Ultrasound of the thyroid” por Saleh Aldasouqi et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0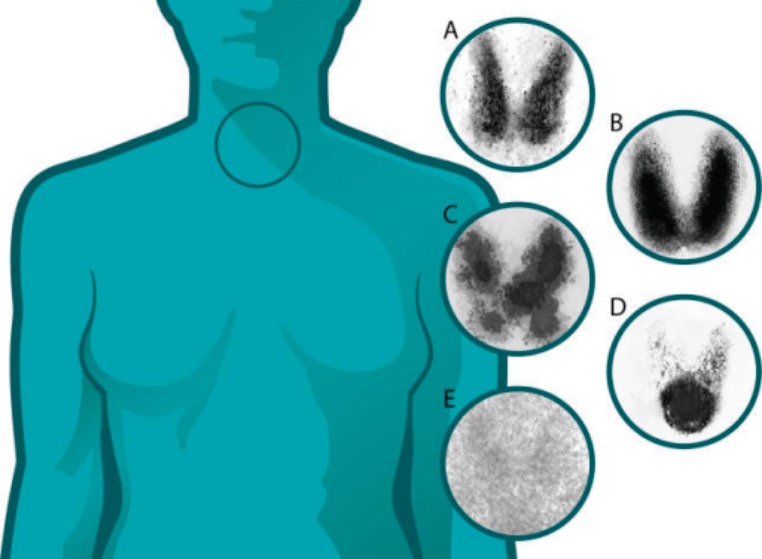
Escáneres de captación de tiroides (tiroiditis versus otras enfermedades de la tiroides):
A: normal
B: enfermedad de Graves: aumento difuso de la captación en ambos lóbulos tiroideos
C: bocio multinodular tóxico: áreas “calientes” y “frías” de captación desigual
D: adenoma tóxico: captación aumentada en un solo nódulo con supresión de la tiroides circundante
E: tiroiditis: captación disminuida o ausente