La enfermedad celíaca (también conocida como esprúe celíaco o enteropatía por gluten Gluten Prolamins in the endosperm of seeds from the triticeae tribe which includes species of wheat; barley; and rye. Celiac Disease) es una reacción autoinmune a la gliadina, que es un componente del gluten Gluten Prolamins in the endosperm of seeds from the triticeae tribe which includes species of wheat; barley; and rye. Celiac Disease. La enfermedad celíaca está estrechamente relacionada con el HLA-DQ2 y el HLA-DQ8. La respuesta inmunitaria se localiza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el intestino delgado proximal y provoca los LOS Neisseria hallazgos histológicos característicos de atrofia de las vellosidades, hiperplasia de las criptas y linfocitosis intraepitelial. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar diarrea y síntomas relacionados con la malabsorción (esteatorrea, pérdida de peso y deficiencias nutricionales). Los LOS Neisseria pacientes se someten a pruebas serológicas de anticuerpos y el diagnóstico se confirma mediante una biopsia del intestino delgado. El tratamiento requiere una dieta sin gluten Gluten Prolamins in the endosperm of seeds from the triticeae tribe which includes species of wheat; barley; and rye. Celiac Disease de por vida.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria factores ambientales, inmunológicos y genéticos contribuyen al AL Amyloidosis proceso de la enfermedad:
Los LOS Neisseria péptidos del gluten Gluten Prolamins in the endosperm of seeds from the triticeae tribe which includes species of wheat; barley; and rye. Celiac Disease desencadenan la respuesta inmunitaria innata en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células epiteliales intestinales, lo que provoca daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mucosa del intestino delgado proximal (duodeno distal y yeyuno proximal) mediados por células T.
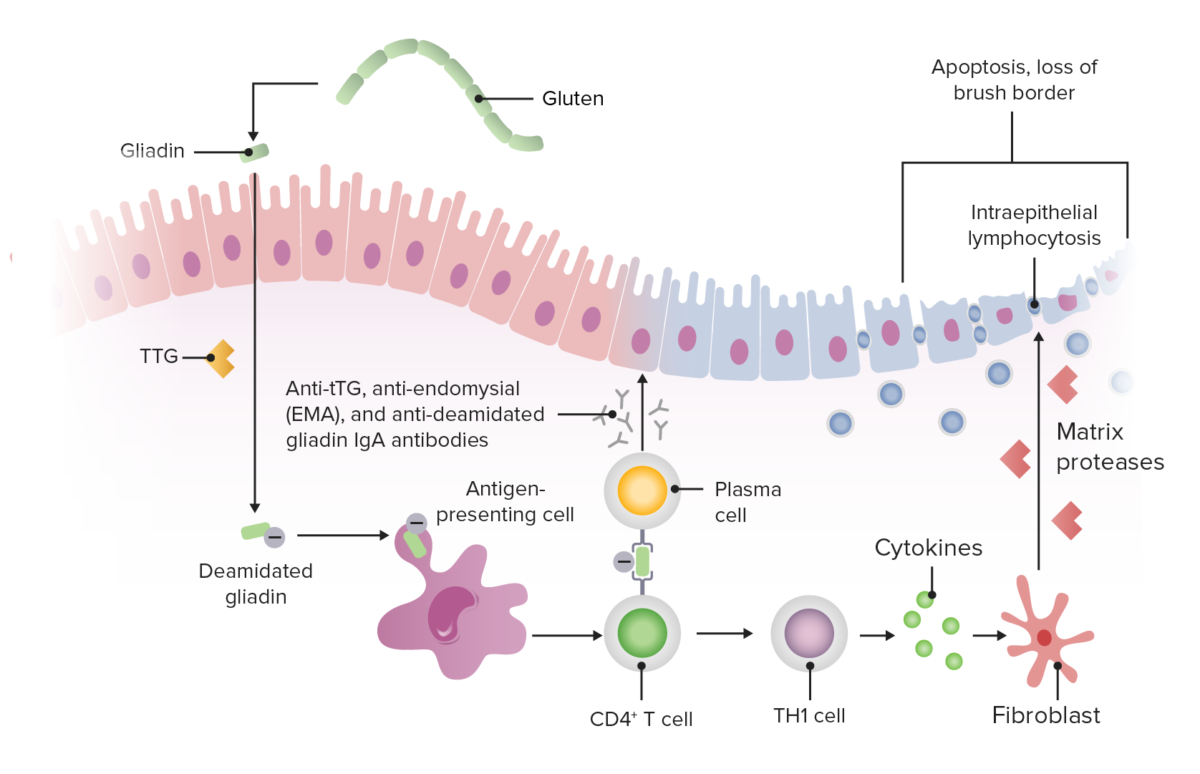
Fisiopatología de la enfermedad celíaca
Imagen por Lecturio.La enfermedad celíaca puede presentarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la infancia o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la 3ra o 4ta década de la vida.
A continuación se resumen las manifestaciones y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos de laboratorio del síndrome de malabsorción:
| Manifestaciones | Hallazgos de laboratorios |
|---|---|
| Esteatorrea (heces voluminosas, malolientes y de color claro) | Aumento de la grasa fecal debido a la malabsorción de grasas |
| Diarrea (aumento del contenido fecal) | Aumento de la brecha de osmolalidad de las heces debido a las grasas e hidratos de carbono no absorbidos |
| Pérdida de peso/falta de crecimiento/desgaste muscular | Disminución de la absorción de D-xilosa debido a la incapacidad de absorber cualquier contenido alimenticio |
| Hemorragia/equimosis a repetición | Prolongación del TP/INR (tiempo de protrombina/relación internacional normalizada) debido a la incapacidad de absorber la vitamina K |
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types microcítica | Ferritina baja debido a la incapacidad de absorber el hierro |
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types macrocítica | Bajo nivel de B12 o ácido fólico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum suero debido a la incapacidad de absorber la vitamina B12 y B9 |
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation óseo/fracturas por traumatismos mínimos | Osteopenia Osteopenia Osteoporosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la radiografía simple y osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la absorciometría de rayos X de doble energía debido a la incapacidad de absorber el calcio y la vitamina D |
| Intolerancia a la leche | Prueba de tolerancia a la lactosa anormal debido a la incapacidad de absorber la lactosa |
| Edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema | Disminución de las proteínas séricas y de la albúmina debido a la incapacidad de absorber los LOS Neisseria aminoácidos de la dieta |
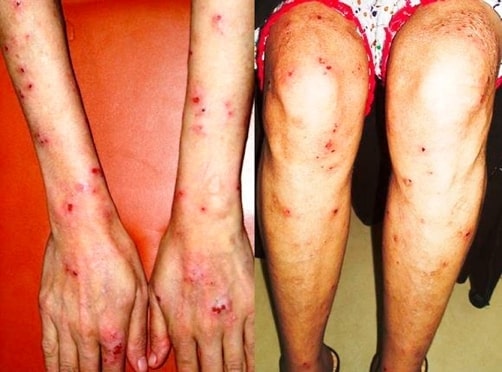
Erupción de dermatitis herpetiforme que afecta a la superficie extensora de los antebrazos, las manos y las extremidades inferiores en un paciente con enfermedad celíaca
Imagen: “Skin lesions on dorsum of hand and legs” por Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital (Stadium Road), Karachi (74800), Pakistan. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La enfermedad celíaca también se asocia con:
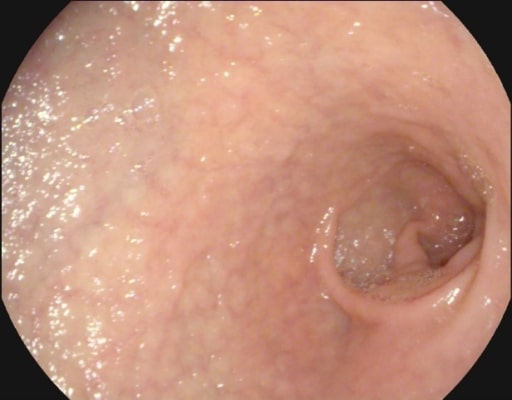
Atrofia de la mucosa y vascularidad submucosa observadas en la endoscopia de un paciente con enfermedad celíaca
Imagen: “Atrophy with visible vessel pattern in the duodenal bulb” por “Dr. Carol Davila” Central Military University Emergency Hospital, Bucharest, Romania ; “Carol Davila” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0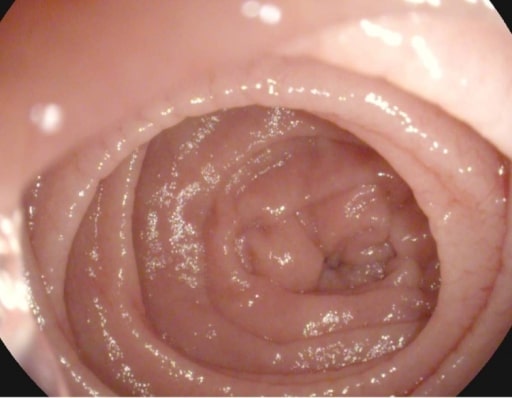
Festoneado de los pliegues de Kerckring en un paciente con enfermedad celíaca
Imagen: “Atrophy with visible vessel pattern in the duodenal bulb” por “Dr. Carol Davila” Central Military University Emergency Hospital, Bucharest, Romania; “Carol Davila” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0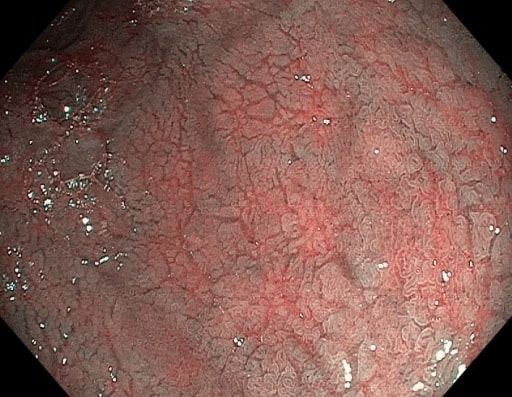
Fisuras de la mucosa y vasos submucosos prominentes vistos en la endoscopia en un paciente con enfermedad celíaca
Imagen: “NBI” por “Dr. Carol Davila” Central Military University Emergency Hospital, Bucharest, Romania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0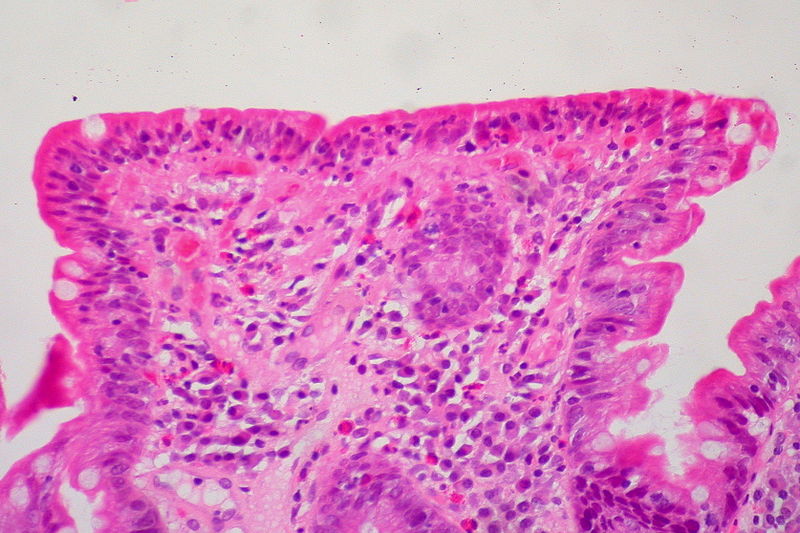
Biopsia del intestino delgado que muestra el amontonamiento de linfocitos (células azules), la pérdida de vellosidades y la profundización (hiperplasia) de las criptas
Imagen: “Celiac Sprue, Small Bowel Biopsy” por Ed Uthman from Houston, TX, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0