La encefalomielitis diseminada aguda es una afección desmielinizante, monofásica, inflamatoria, mediada por el sistema inmunitario que afecta a la sustancia blanca del cerebro y a la médula espinal. Como la encefalomielitis postinfecciosa rápidamente progresiva, la encefalomielitis diseminada aguda se caracteriza por la desmielinización en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cerebro y la médula espinal como resultado de la inflamación que sigue a una infección o inmunización.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La encefalomielitis diseminada aguda es un déficit neurológico agudo causado por un ataque autoinmune al AL Amyloidosis cerebro y a la médula espinal que conduce a la desmielinización multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma.
Se deben cumplir todos los LOS Neisseria siguientes criterios para un diagnóstico de encefalomielitis diseminada aguda pediátrica:
Aunque no existen criterios diagnósticos formales para la encefalomielitis diseminada aguda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos, el diagnóstico se basa típicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum encefalopatía, déficits neurológicos polifocales y hallazgos característicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la resonancia magnética.
La etiología de la encefalomielitis diseminada aguda no se comprende completamente, pero la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos se presentan tras infecciones y una minoría tras la vacunación. La enfermedad asociada a anticuerpos MOG (MOGAD) se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia convertido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un diagnóstico solapante frecuente, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños.
La fisiopatología de la encefalomielitis diseminada aguda no está clara; sin embargo, se proponen 2 teorías principales:
Antecedentes:
Signos y síntomas:
Hallazgos del examen físico:
Leucoencefalitis hemorrágica aguda:
Meningismo
Los signos de Brudzinski y Kernig son positivos en el contexto de cualquier afección que cause inflamación de las meninges (también conocida como meningismo). Estas afecciones incluyen meningitis y leucoencefalitis hemorrágica aguda.
Encefalomielitis diseminada aguda con afectación del sistema nervioso periférico:
El diagnóstico clínico se puede confirmar mediante imagenología del SNC y pruebas de laboratorio.
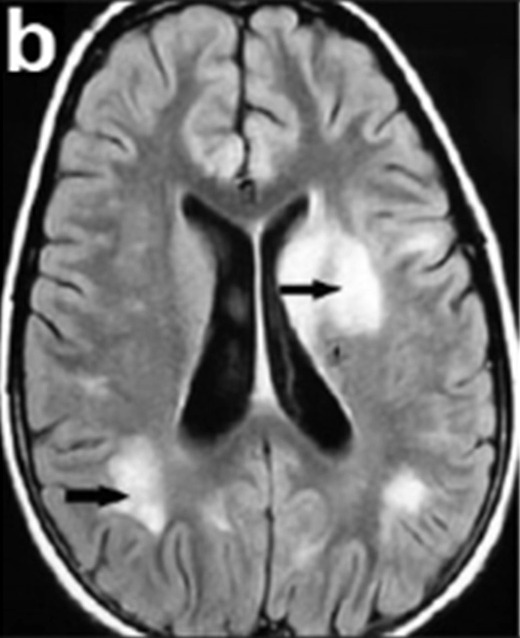
Una RM típica de un individuo con encefalomielitis diseminada aguda: observe el patrón irregular de la inflamación del parénquima cerebral (flechas negras).
Imagen: “MRI scan of a patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)” por Kamate M, Chetal V, Tonape V, Mahantshetti N, Hattiholi V. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editada por Lecturio.