El dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello es uno de los LOS Neisseria motivos de consulta más comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la población general. Según la duración de los LOS Neisseria síntomas, puede ser aguda, subaguda o crónica. Hay muchas causas de dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello, como las enfermedades degenerativas, los LOS Neisseria traumatismos, las enfermedades reumatológicas y las infecciones. Los LOS Neisseria trastornos musculoesqueléticos pueden variar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gravedad desde una simple distensión hasta una radiculopatía y una mielopatía. Una historia clínica y examen físico cuidadosos son esenciales para descubrir la etiología y orientar el tratamiento. El tratamiento de la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello es conservador y basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la actividad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello es un síntoma de consulta frecuente.
Trastornos músculo-esqueléticos:
Enfermedades no músculo-esqueléticas:
El dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello puede clasificarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la duración de los LOS Neisseria síntomas:
Se pueden recordar las preguntas abiertas importantes que hay que hacer cuando se evalúa a un paciente con dolor Dolor Inflammation:
Examen básico:
Pruebas y signos especiales:
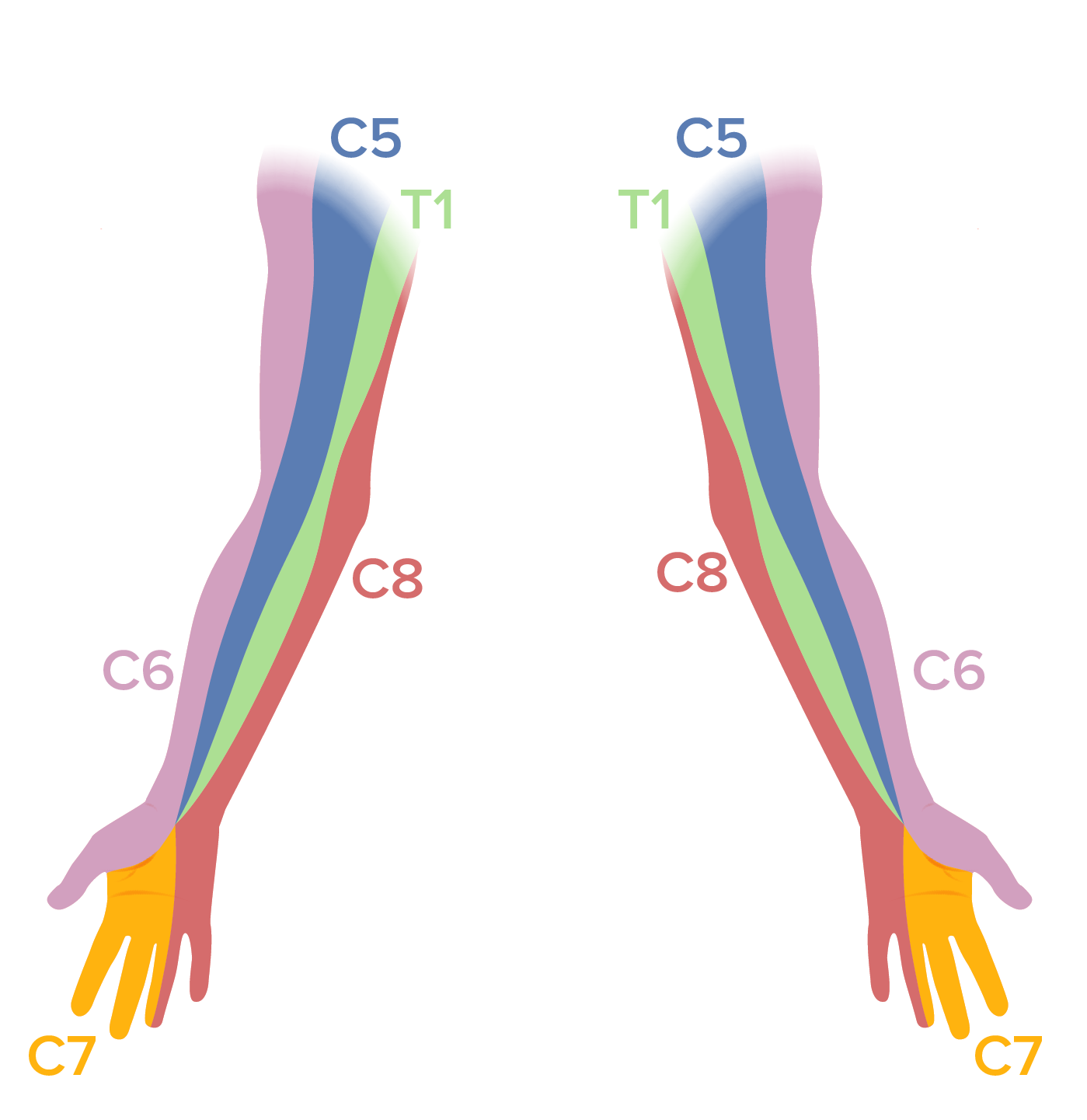
Dermatomas de las extremidades superiores:
Se debe realizar un examen sensorial en los pacientes con dolor de cuello. En los pacientes con radiculopatía cervical pueden observarse déficits sensoriales en el dermatoma afectado.
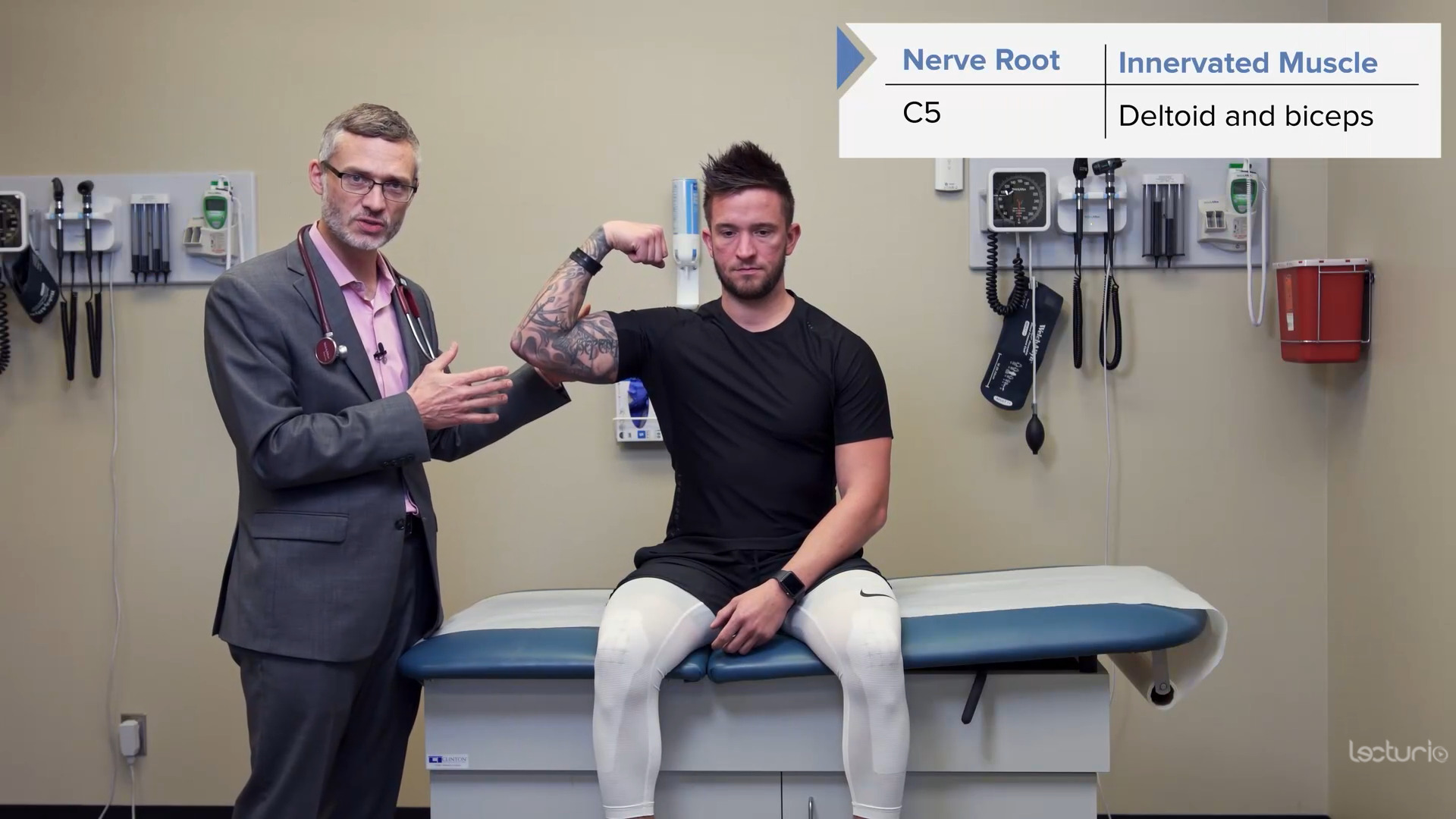
Pruebas de fuerza del miotoma C5, los deltoides y los bíceps
Imagen por Lecturio.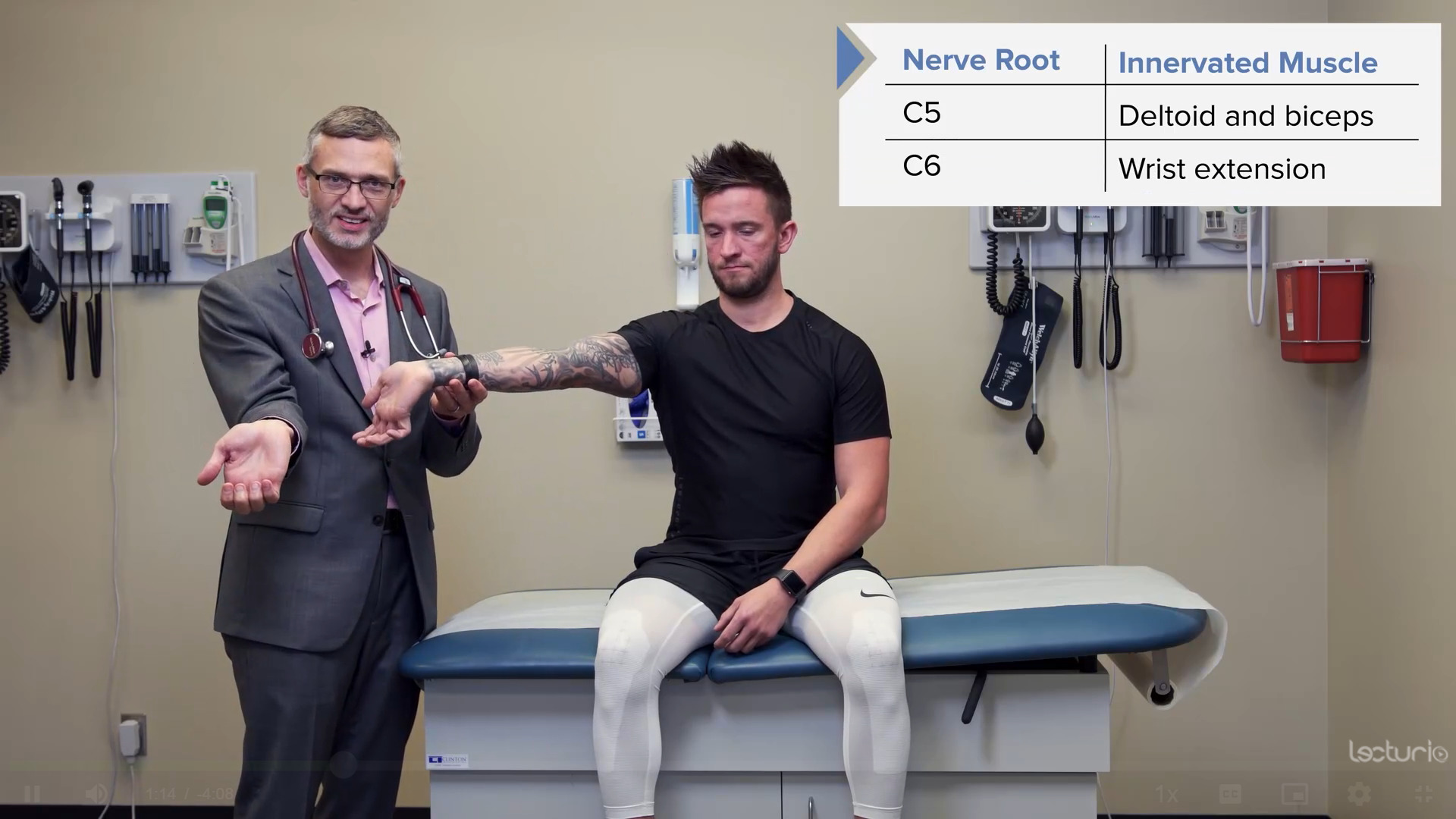
Pruebas de fuerza del miotoma C6, el tríceps y los extensores de la muñeca
Imagen por Lecturio.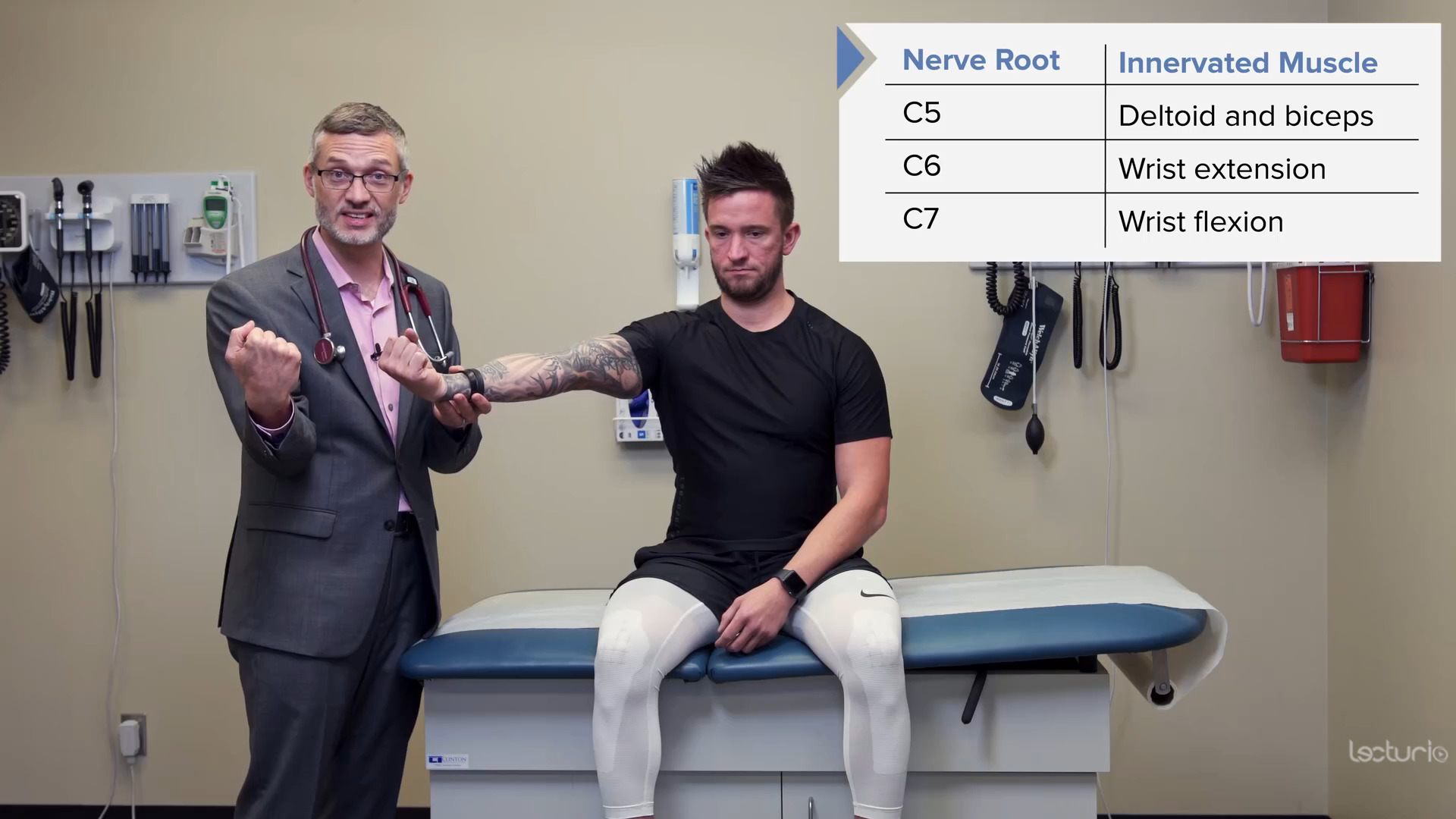
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma C7 y de los flexores de la muñeca
Imagen por Lecturio.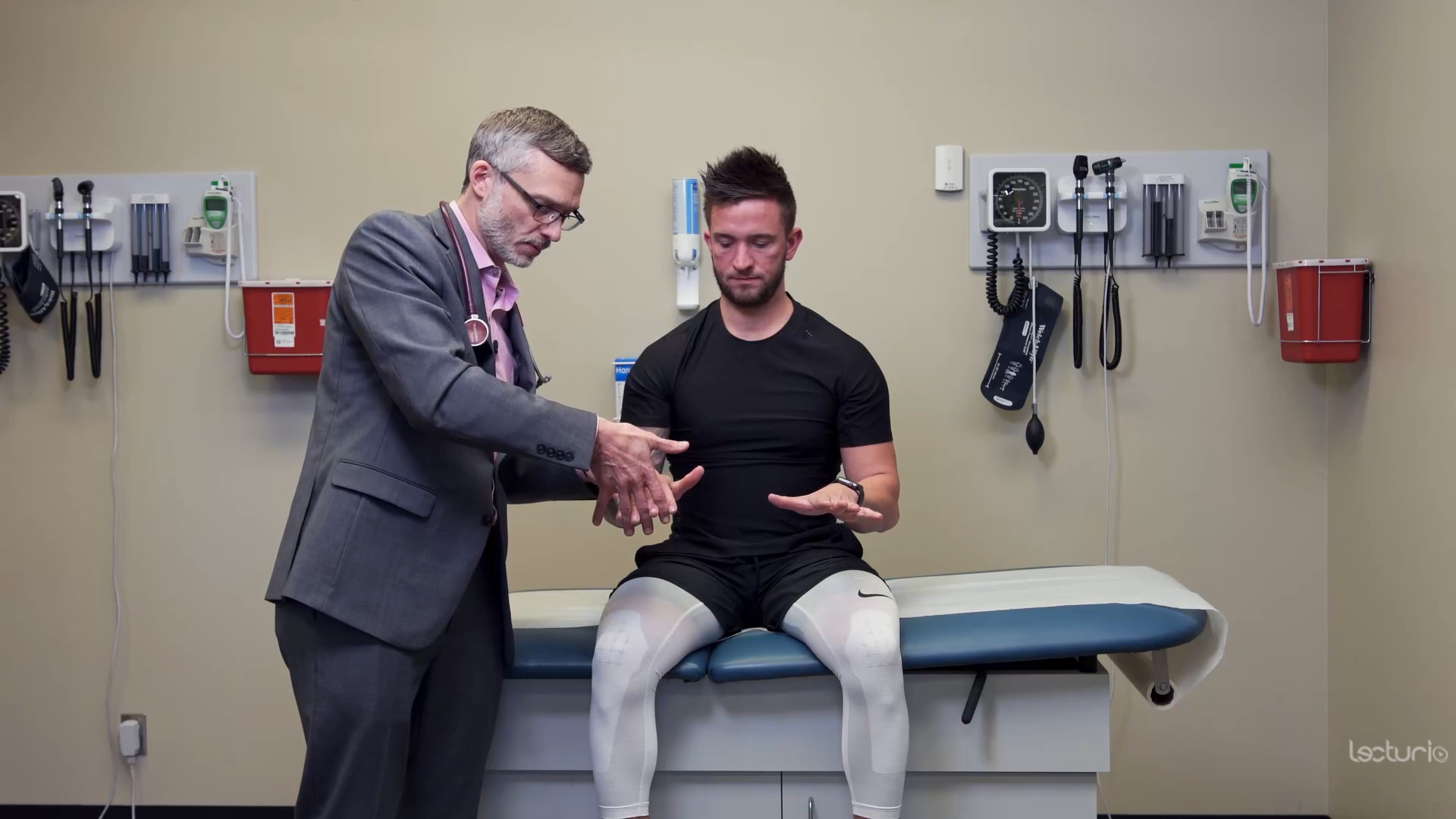
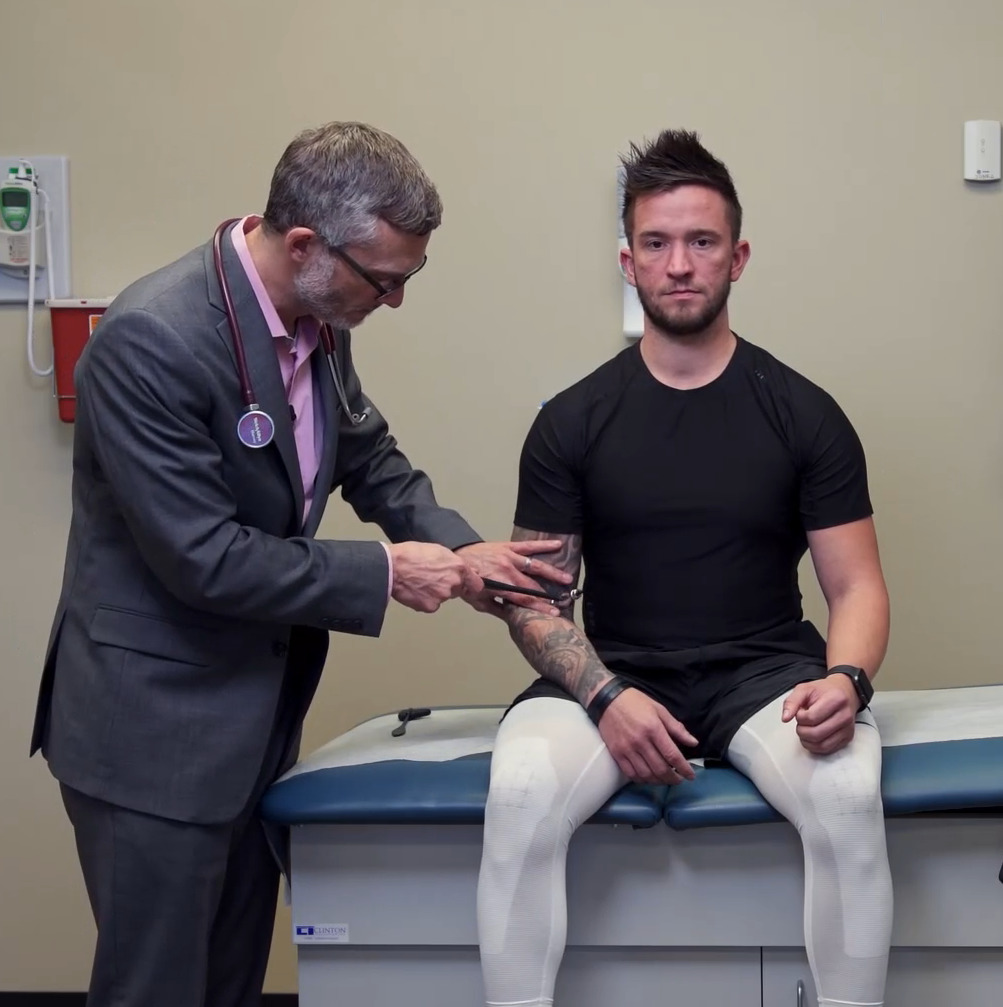
Prueba de fuerza de los miotomos C8 y T1 y de los músculos interóseos:
Obsérvese que el individuo aprieta los dedos del examinador.
Prueba de reflejo de la raíz nerviosa C5 y del reflejo del tendón del bíceps
Imagen por Lecturio.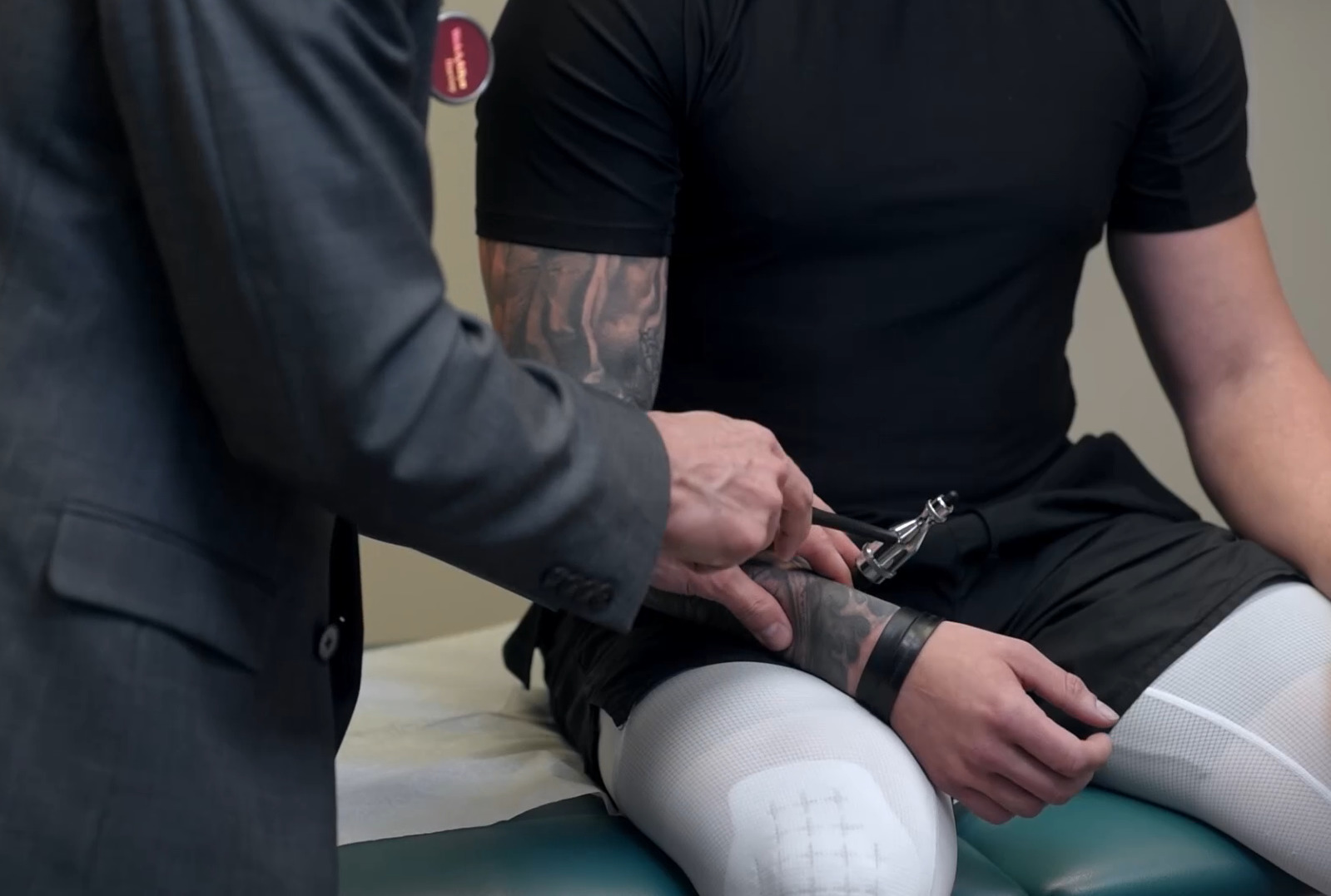
Prueba de reflejo de la raíz nerviosa C6 y del reflejo del tendón braquioradialx
Imagen por Lecturio.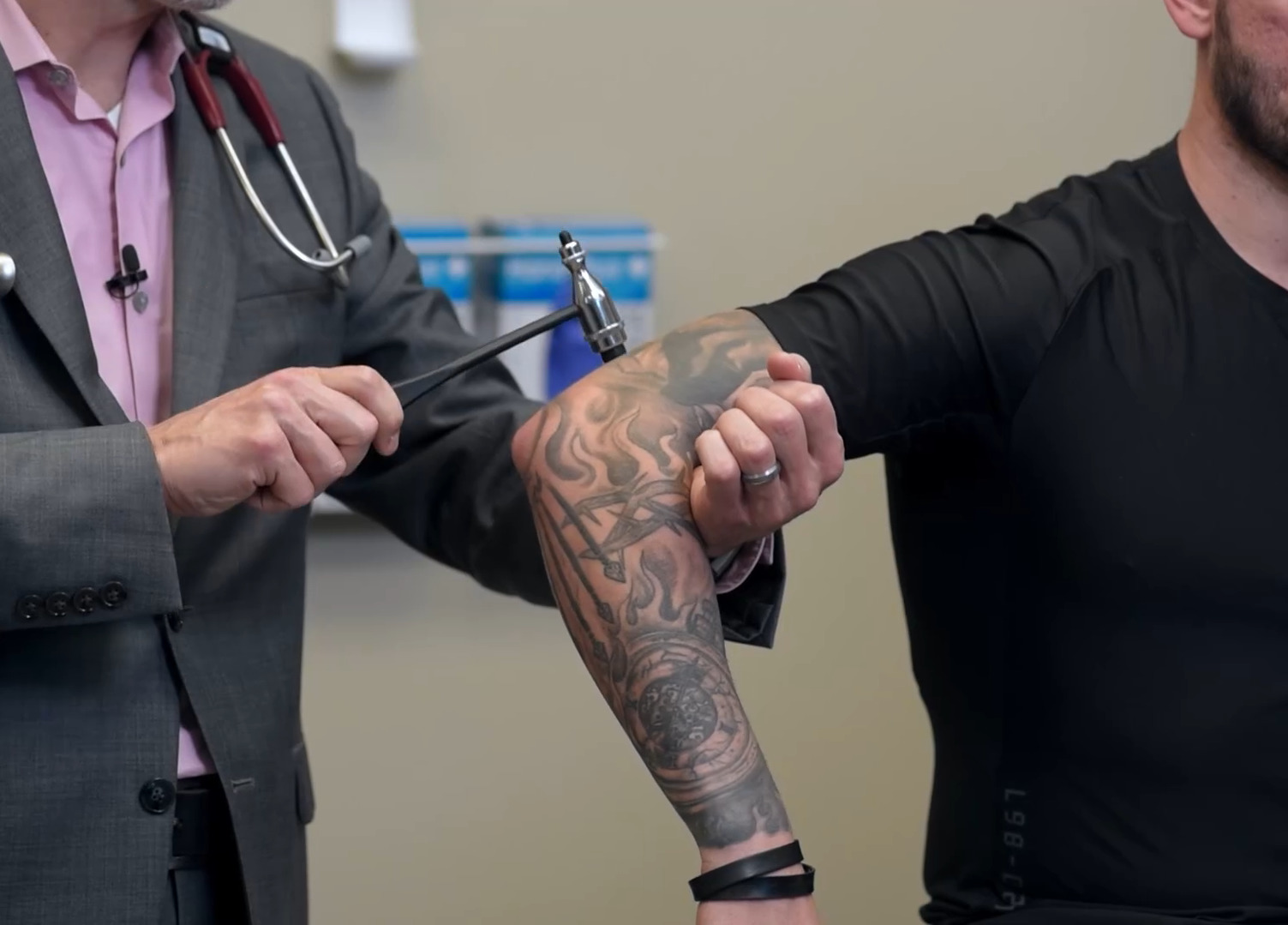
Prueba de reflejo de la raíz nerviosa C7 y del reflejo del tendón del tríceps
Imagen por Lecturio.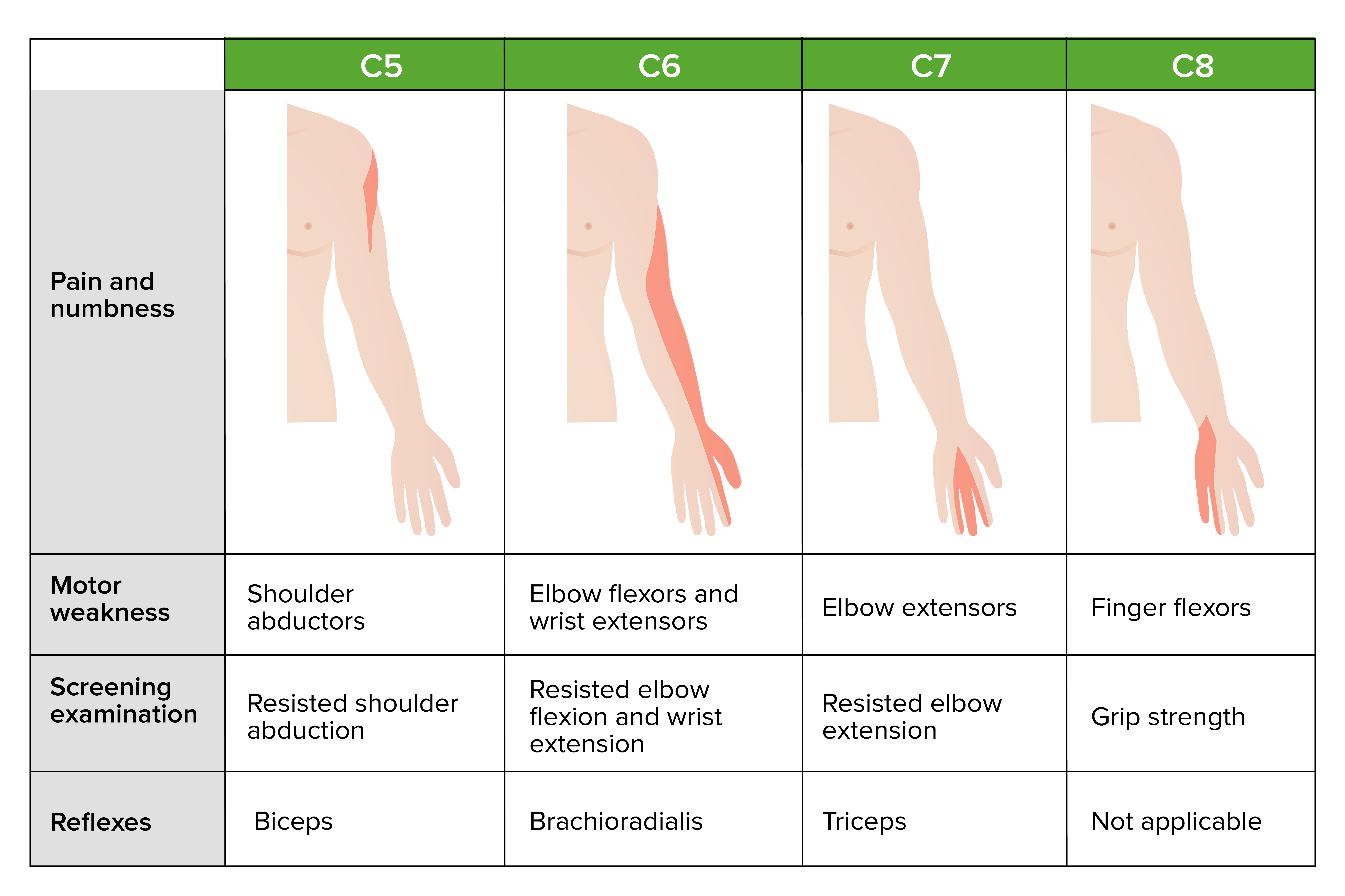
Síntomas y hallazgos debidos a síndromes radiculares cervicales comunes
Imagen por Lecturio.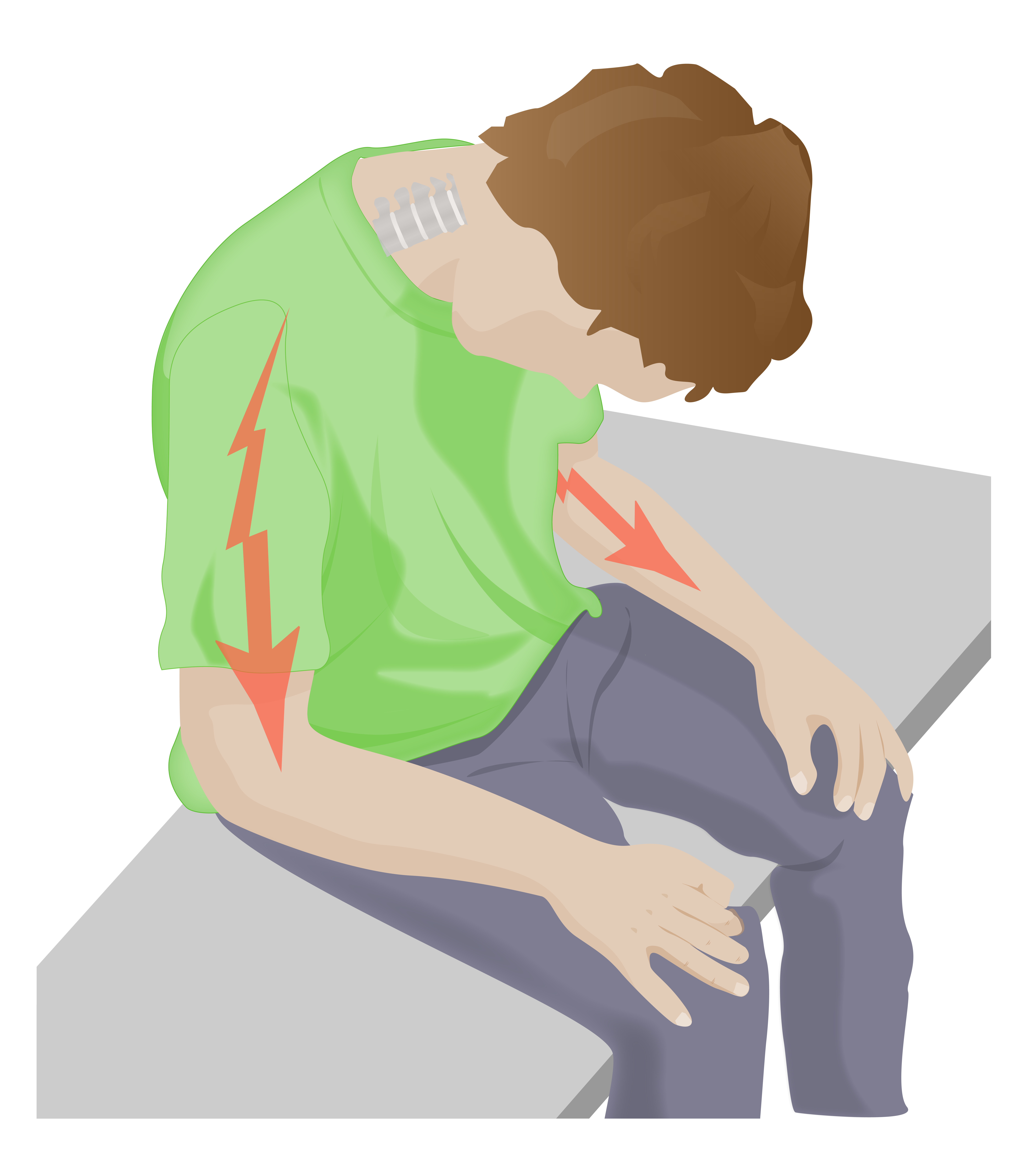
El signo de Lhermitte:
La flexión hacia delante del cuello provoca la irradiación del dolor hacia la columna vertebral o los brazos.
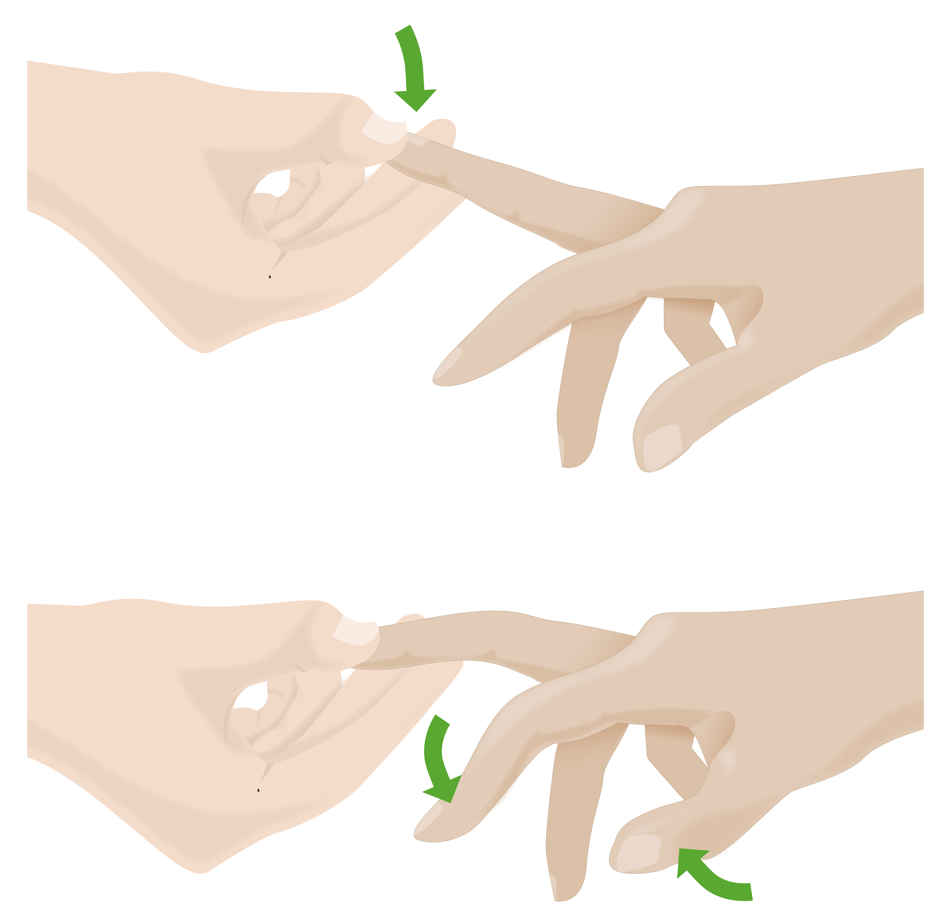
Signo de Hoffmann:
Si se desliza hacia abajo la uña del dedo medio, se produce una flexión del pulgar y del dedo índice, lo que puede indicar una mielopatía cervical.
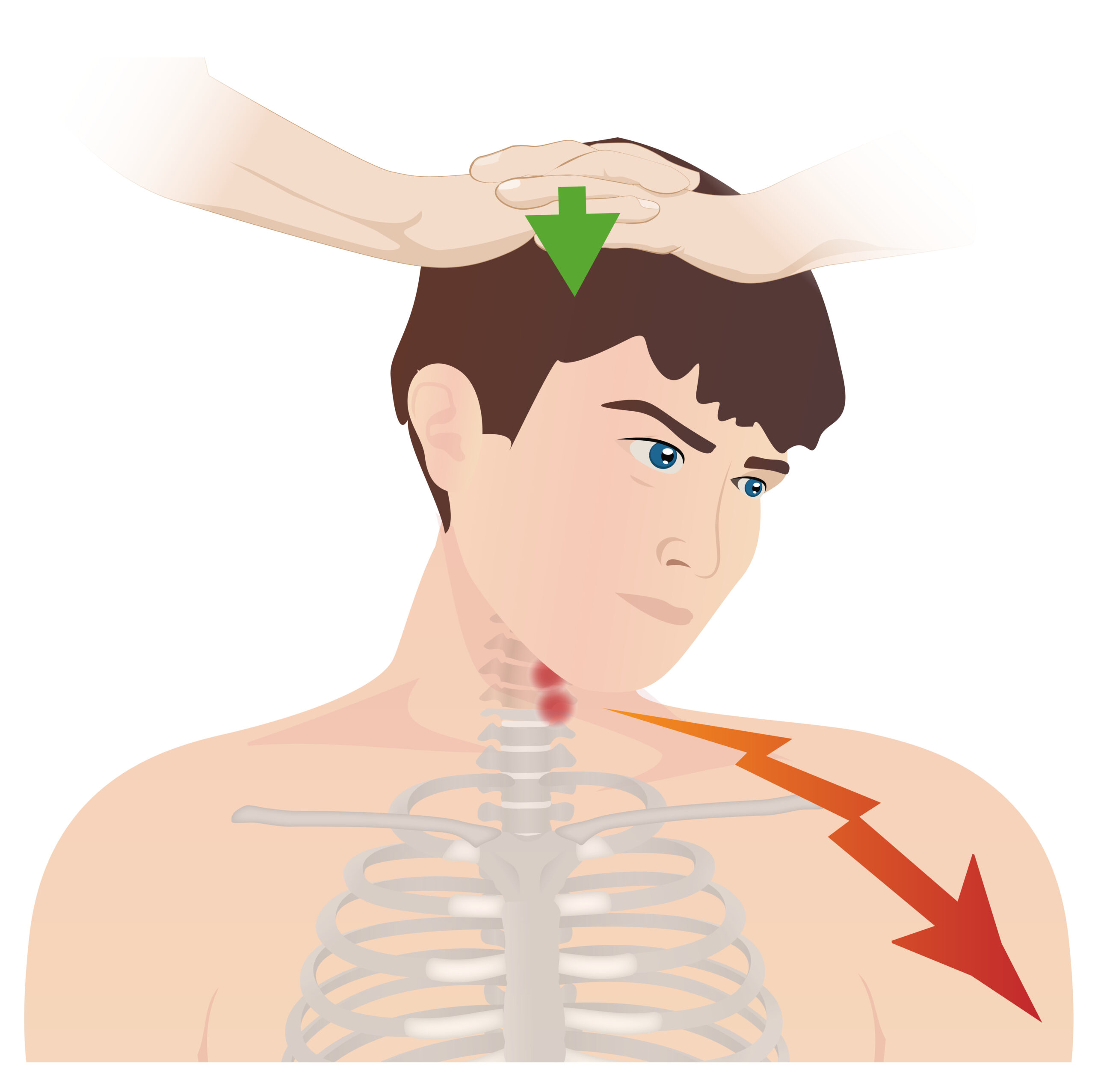
Prueba de Spurling:
Esta prueba se utiliza para la evaluación de radiculopatía cervical en pacientes que presentan dolor de cuello. La cabeza del paciente se gira hacia el lado afectado mientras se extiende. Se aplica una fuerza hacia abajo en la parte superior de la cabeza. La prueba es positiva si hay irradiación del dolor hacia el dermatoma correspondiente.
Los LOS Neisseria siguientes síntomas sugieren una patología grave e indican una evaluación urgente:
Los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos diferenciales relacionados con el dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello son amplios y pueden reducirse con los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos y la exploración física.
La siguiente tabla compara las pistas clínicas y de diagnóstico de algunos trastornos músculo-esqueléticos comunes que se manifiestan con dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello.
| Entidad | Características clínicas | Diagnóstico |
|---|---|---|
| Tensión cervical |
|
Clínico |
| Espondilosis cervical |
|
|
| Síndrome del latigazo cervical (whiplash injury, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) |
|
|
| Radiculopatía cervical |
|
|
| Mielopatía cervical |
|
RM muestra:
|
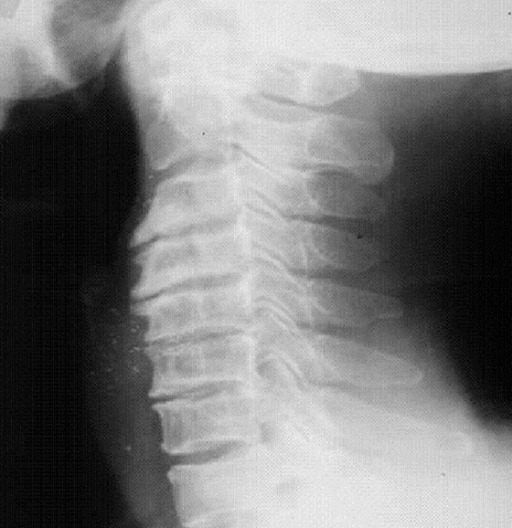
Representación radiográfica de la espondilosis cervical
Imagen: “fig1: Radiographic representation of cervical spondylosis.” por Lisa A Ferrara. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
a: RMN parasagital derecha ponderada en T2 de la columna cervical
b: Resonancia magnética axial ponderada en T1 a nivel C4-C5 que muestra una hernia de disco intervertebral en el agujero intervertebral C4-C5 derecho (flechas)
c: Disco herniado parcialmente realzado (flecha) después del medio de contraste
El tratamiento precoz del dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una evaluación inicial adecuada, la recuperación temprana del movimiento, el control del dolor Dolor Inflammation y una fisioterapia acertada.
Las medidas conservadoras suelen utilizarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes sin traumatismos importantes o signos de alarma.
Tratamiento general:
Terapia física y de movimiento:
Se pueden considerar las siguientes opciones, junto con el manejo del dolor Dolor Inflammation y/o la terapia física y rehabilitación: