La difteria es una enfermedad infecciosa causada por Corynebacterium diphtheriae que suele provocar una enfermedad respiratoria con inflamación membranosa de la faringe, dolor de garganta, fiebre, inflamación de los ganglios y debilidad. El signo distintivo es una lámina de material grueso y gris que cubre la parte posterior de la garganta. La difteria también puede manifestarse como una enfermedad cutánea que da lugar a lesiones cutáneas inespecíficas. En fases avanzadas, la difteria puede dañar el corazón, los riñones y el sistema nervioso. Se diagnostica mediante un cultivo de hisopado faríngeo y se trata con terapia antibiótica y la antitoxina diftérica.
Last updated: Jan 21, 2023
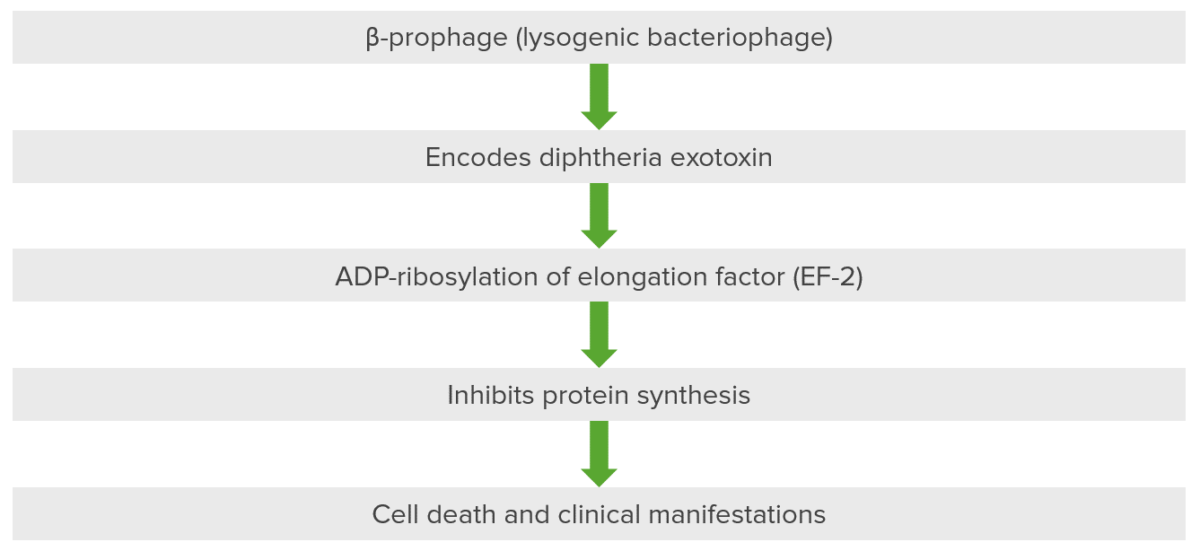
Patogénesis de las enfermedades asociadas a Corynebacterium: la exotoxina de la difteria inactiva el factor de elongación (EF-2) a través de la ribosilación ADP
Este bacteriófago, un profago beta, se introduce en la célula y en el ADN del organismo anfitrión, dando lugar a la codificación de la exotoxina diftérica. La exotoxina tiene 3 dominios: 1 está presente en el fragmento A y es catalítico, mientras que 2 están presentes en el fragmento B para la unión al receptor y la inserción y translocación en la membrana. La exotoxina es la principal causa de la enfermedad en la difteria porque ribosila el ADP presente en el factor de elongación. El factor de elongación, concretamente el factor de elongación 2 (EF-2), es fundamental para la elongación de las cadenas de proteínas. La exotoxina de la difteria inhibe el EF-2 de manera que no se sintetiza la proteína, lo que provoca la muerte celular y las manifestaciones clínicas secundarias.
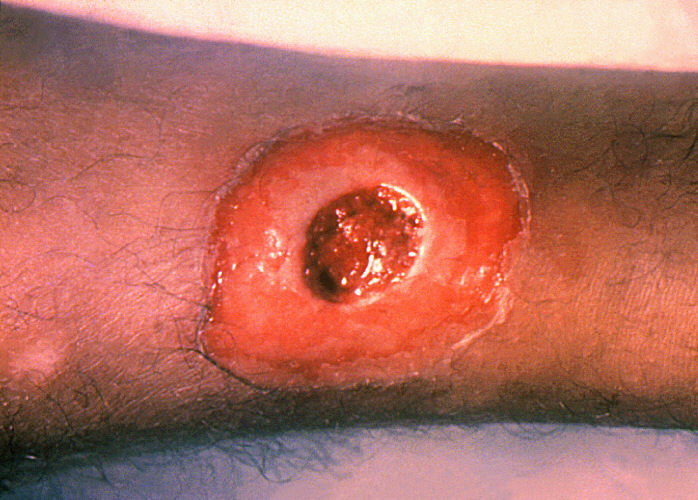
Signo clínico de un paciente con difteria cutánea (herida): úlcera crónica que no cicatriza
Image: “A diphtheria skin lesion on the leg” por CDC/Public Health Image Library (PHIL). Licencia: Dominio público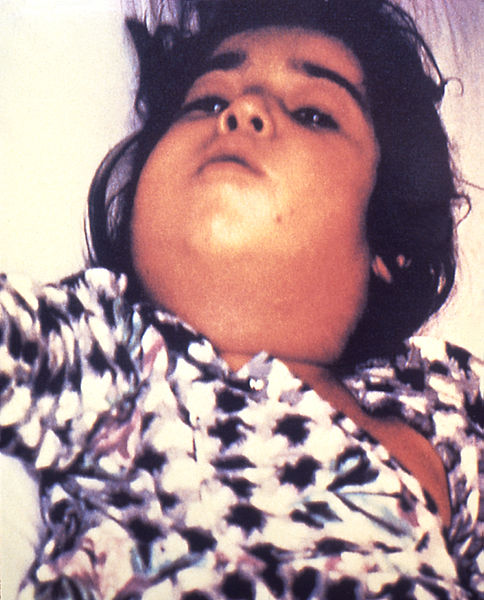
Signo clínico de un paciente con difteria respiratoria: linfadenopatía grave con aspecto de “cuello de toro”
Image: “Diphtheria bull neck” por CDC/Public Health Image Library (PHIL). Licencia: Dominio público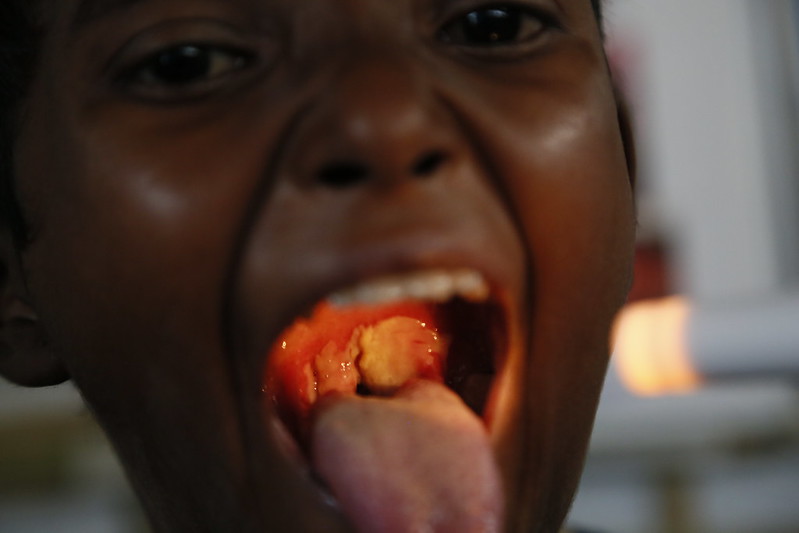
Paciente pediátrico con difteria que presenta una membrana blanca-grisácea característica que cubre la pared faríngea posterior
Image: “A doctor with the UK’s Emergency Medical Team checks a child for symptoms of Diphtheria in a makeshift clinic in the Kutupalong camp for Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh” por Russell Watkins/Department for International Development. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Puntos clave a recordar sobre la difteria:
ABCDEFG: ADP-ribosylation (ADP-ribosilación), Beta-prophage (Beta-profago), Corynebacterium Corynebacterium Corynebacteria are gram-positive, club-shaped bacilli. Corynebacteria are commonly isolated on tellurite or Loeffler’s media and have characteristic metachromatic granules. The major pathogenic species is Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which causes a severe respiratory infection called diphtheria. Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Elongation factor 2 (Factor de Elongación 2), Granules (Gránulos)
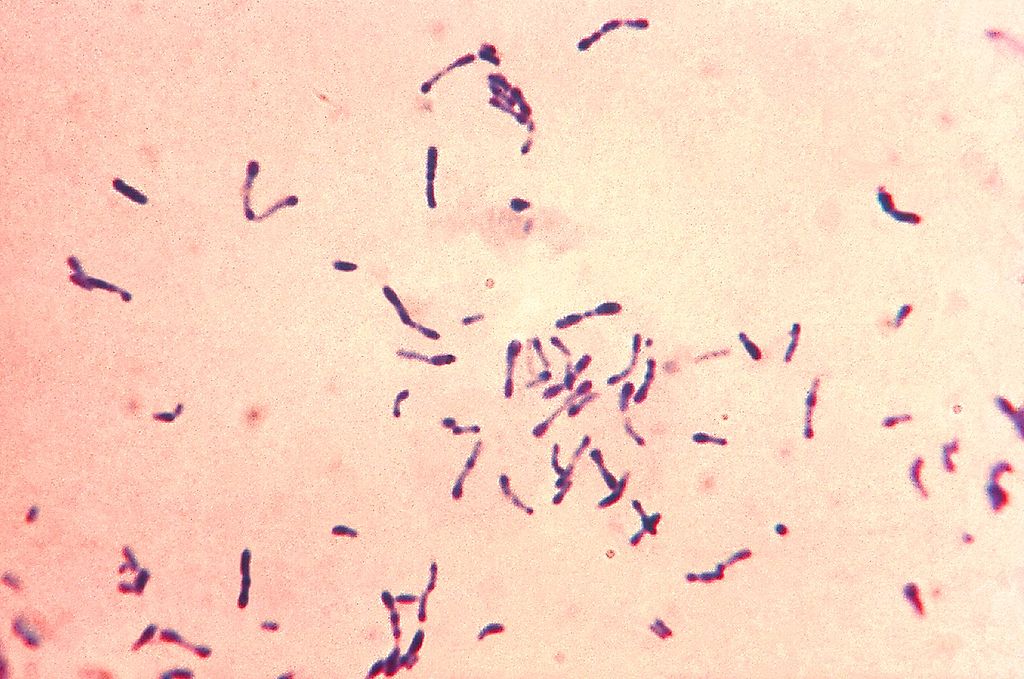
Bacterias Gram-positivas C. diphtheriae con gránulos azules metacromáticos. Las bacterias se cultivaron en el medio de Loeffler para realzar los característicos gránulos metacromáticos. Obsérvese la forma de bastón y la formación en Y y V.
Image: “Gram-positive Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Public Health Image Library (PHIL). Licencia: Dominio Público
Un hisopado de garganta inoculado con C. diphtheriae se cultiva en un plato Petri que contiene medio Tinsdale complementado con el componente de agar telurito. Las colonias de color gris-negro, cada una rodeada de un halo marrón oscuro, son características de C. diphtheriae en agar telurito. Imagen: “Corynebacterium diphtheriae” de la Biblioteca de Imágenes de Salud Pública (PHIL). Licencia: Dominio Público
Las posibles complicaciones asociadas a la difteria son:
El diagnóstico diferencial de la difteria respiratoria incluye:
Referencias