El cáncer es la segunda causa principal de muerte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria EE. UU. después de las enfermedades cardiovasculares. Muchos tumores malignos son tratables o curables, pero algunos pueden reaparecer. Por lo tanto, a todos los LOS Neisseria tumores malignos se les debe asignar un grado y una etapa para guiar el tratamiento y determinar el pronóstico. El grado tumoral clasifica un tumor Tumor Inflammation por su histología y forma parte del sistema de estadificación TNM ( tumor Tumor Inflammation, ganglios, metástasis) aceptado internacionalmente, que se utiliza para caracterizar la extensión de la enfermedad. La enfermedad metastásica se refiere al AL Amyloidosis cáncer que se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia diseminado más allá del sitio del tumor Tumor Inflammation primario.
Last updated: Jan 21, 2026
La clasificación es la evaluación histológica de las células tumorales según su estado de diferenciación.
La clasificación se realiza para la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria tipos de tumores, pero hay excepciones específicas.
Clasificación del tumor Tumor Inflammation:
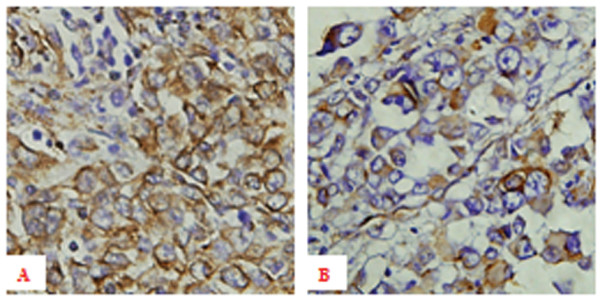
Expresión inmunohistoquímica de vimentina en individuos con melanoma:
A: Alta expresión de vimentina en tejido de melanoma primario con metástasis hematógena ×400
B: Expresión baja de vimentina en tejido de melanoma primario sin metástasis hematógena ×400
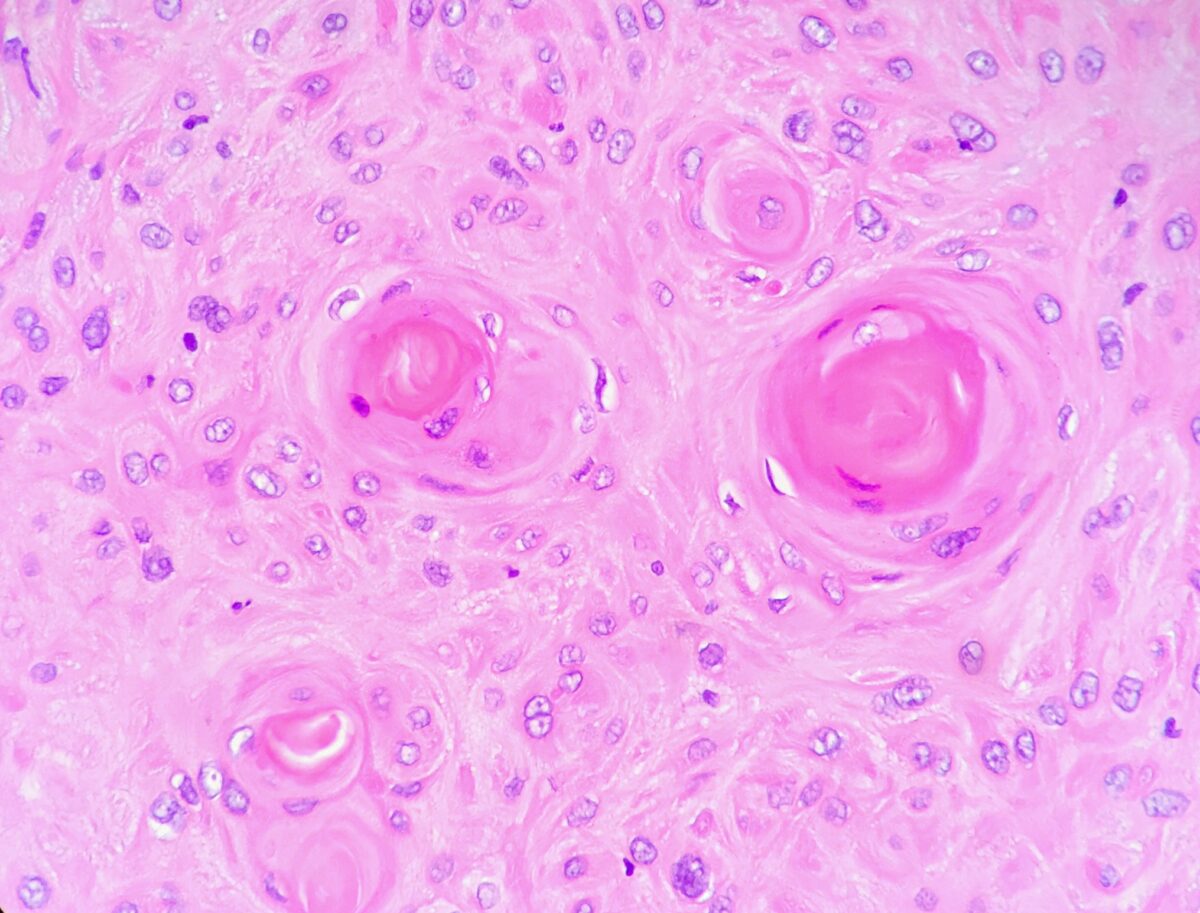
Perlas de queratina visualizadas en un carcinoma de células escamosas bien diferenciado (de bajo grado) de laringe
Imagen: “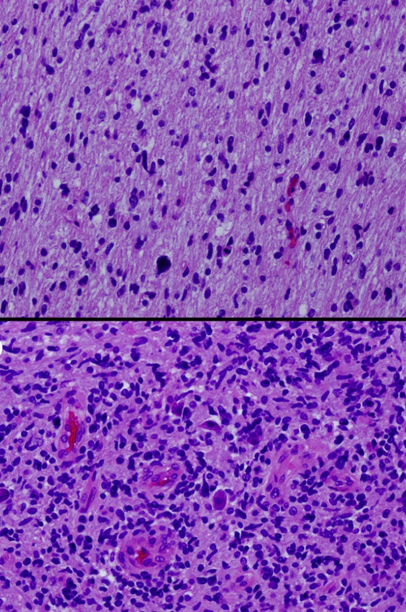
Histología de glioma que muestra tinciones de hematoxilina y eosina de diferentes secciones de un solo tumor que muestra áreas de bajo grado (superior) y alto grado (inferior)
Imagen: “Histologic geographic variability of DIPG” por Katherine E. Warren. Licencia: CC BY 3.0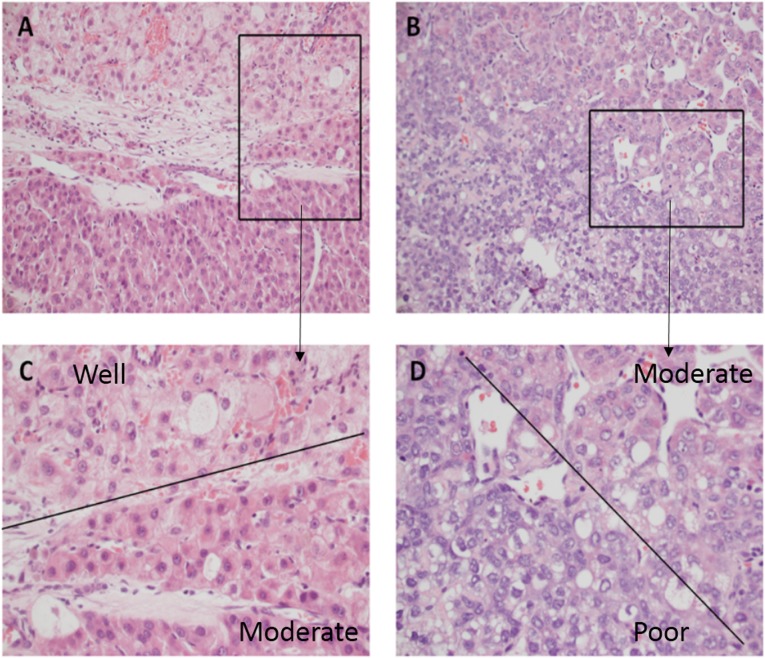
Graduación del tumor del carcinoma hepatocelular: estos tumores suelen ser muy heterogéneos.
C: Una parte del tumor es de grado 1 (la morfología de las células tumorales era similar a la de las células hepáticas normales, con aumento del núcleo/citoplasma), mientras que un área adyacente es de grado 2 (que contiene hepatocitos oncocíticos marcadamente agrandados con algo de núcleo). pleomorfismo y angulación).
D: Un área de grado 2 es adyacente a un área de grado 3 (las formas de las células son bastante irregulares, las células tumorales muestran un marcado pleomorfismo).
La estadificación del cáncer describe la extensión de la enfermedad y se usa para ayudar a comunicarse con otros miembros del equipo médico y quirúrgico para tomar decisiones sobre el tratamiento y el pronóstico. Por ejemplo, con el cáncer de colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy, después de la cirugía y la estadificación patológica, la quimioterapia administrada a personas con enfermedad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estadio III erradica las micrometástasis, reduce la probabilidad de recurrencia de la enfermedad y aumenta las tasas de curación.
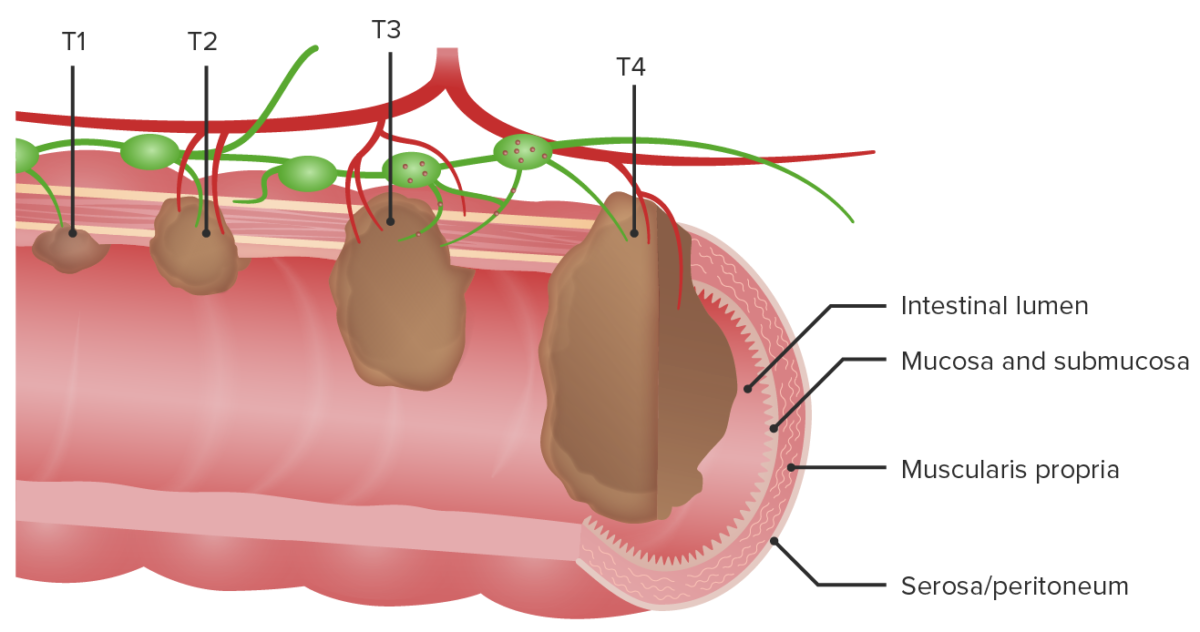
Ejemplo de estadificación T1-T4 para un tumor en el colon
T1: El tumor invade la submucosa (a través de la muscularis mucosa pero no hacia la muscularis propria).
T2: El tumor invade la muscularis propria.
T3: El tumor invade a través de la muscularis propria hacia los tejidos circundantes.
T4: Extensión directa a través de la serosa, invadiendo el peritoneo visceral o adhiriéndose a órganos adyacentes
La metástasis es la diseminación de un tumor Tumor Inflammation desde su sitio primario a lugares cercanos o distantes.
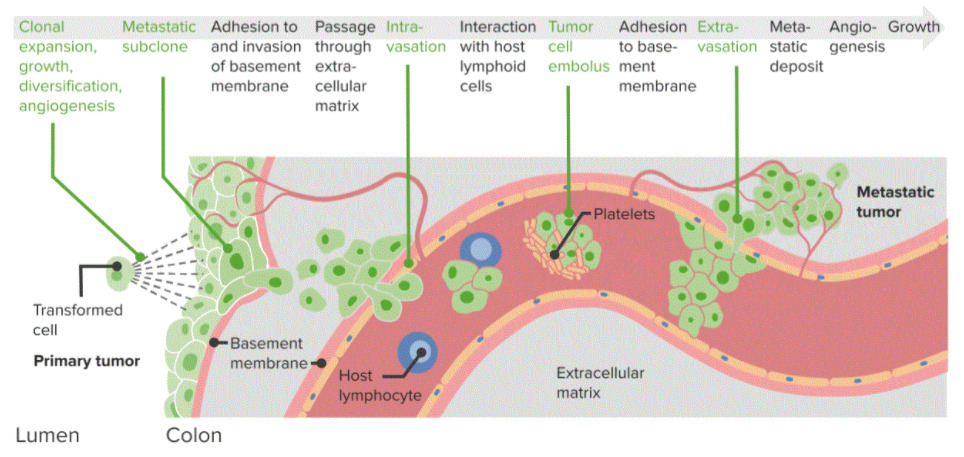
Diagrama de la metástasis del cáncer:
Proceso paso a paso que conduce a la diseminación tumoral de un tumor primario a un tumor metastásico. Estos pasos se basan en la adhesión y la diseminación a través de la membrana basal, la interacción con las células linfoides y la extravasación y el depósito metastásico.
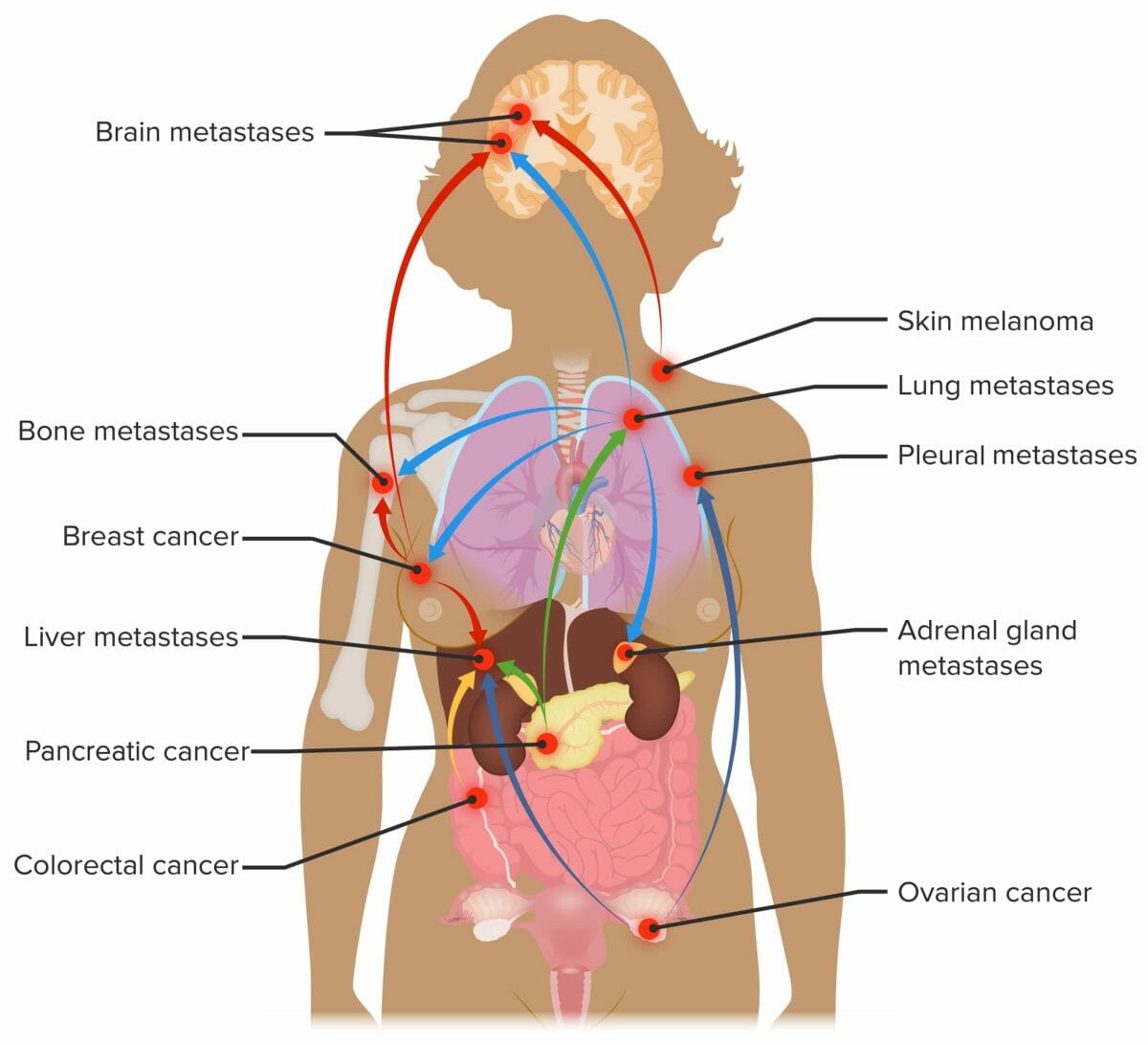
Sitios de metástasis:
Sitios comunes de metástasis para cánceres con alta incidencia, como cáncer de mama, pulmón y colorrectal.