El asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis es una enfermedad respiratoria inflamatoria crónica caracterizada por la hiperreactividad bronquial y la obstrucción del flujo de aire. Se cree que es el resultado de la compleja interacción de factores del huésped y del medioambiente que aumentan la predisposición a la enfermedad, asociada a inflamación que provoca síntomas y cambios estructurales. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar sibilancias, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome y disnea. El diagnóstico se confirma con una prueba de función pulmonar que muestra un patrón obstructivo reversible. El tratamiento, basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la gravedad de los LOS Neisseria síntomas, incluye broncodilatadores y corticosteroides inhalados para controlar la inflamación. Se han desarrollado agentes biológicos dirigidos a los LOS Neisseria mediadores inflamatorios para el asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis persistente grave.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis es un trastorno inflamatorio crónico de las vías respiratorias:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis establecida, existen diferentes desencadenantes que pueden exacerbar los LOS Neisseria síntomas. Estos incluyen los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
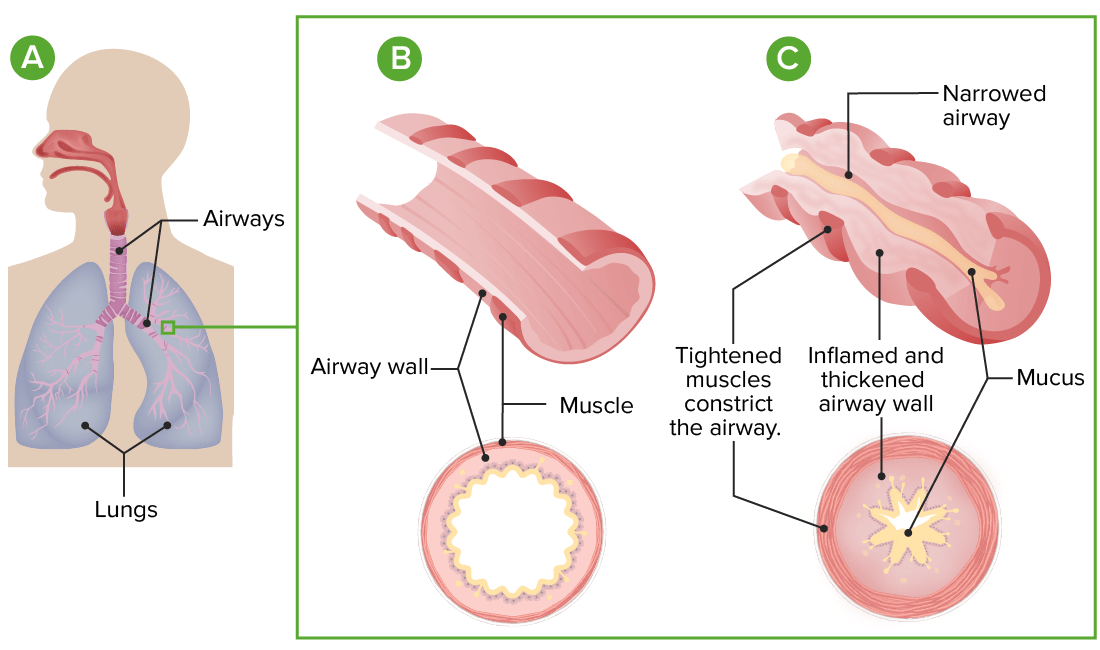
Fisiopatología del asma:
A: Anatomía del pulmón y de las vías respiratorias
B: Sección transversal de una vía aérea normal
C: En el asma, la constricción exagerada de las vías respiratorias, la inflamación y el aumento de la producción de moco conducen a la restricción del flujo de aire.
| Componente | Clasificación | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermitente | Persistente: leve | Persistente: moderada | Persistente: grave | |
| Síntomas | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2 pero < 7 días/semana | Diario | Varias veces al AL Amyloidosis día |
| Uso de broncodilatadores de acción corta | ≤ 2 días/semana | > 2/semana | Diario | Varias veces/día |
| Despertares nocturnos | ≤ 2 / mes | 3-4 / mes | ≥ 1 / semana | Nocturno |
| Limitación de actividad | Ninguno | Menor | Algunos | Extremo |
| Función pulmonar | FEV1 > 80% | FEV1 > 80% | FEV1 60 %–80% | FEV1 <60% |
| Exacerbaciones que requieren corticoesteroides sistémicos | 0–1/año | ≥ 2/año | ||
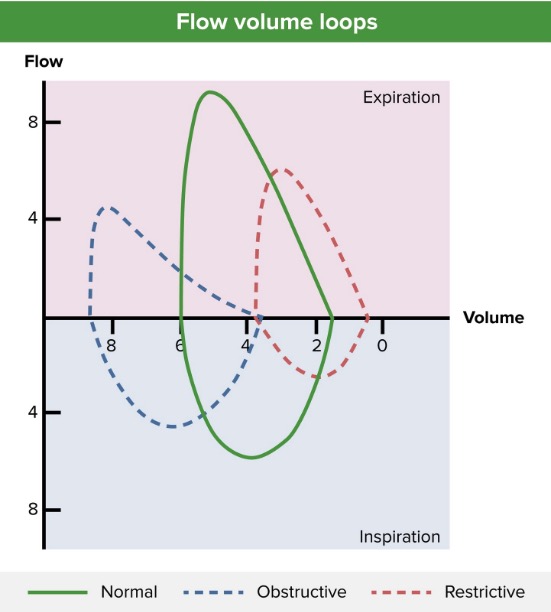
La curva de flujo-volumen (línea azul) que muestra un patrón obstructivo de espiración, un flujo espiratorio máximo reducido (aproximadamente 4 L/seg) y una hiperinflación pulmonar (aproximadamente 4 L en el volumen residual y > 8 L tras la inspiración completa). Se muestra un patrón normal (línea verde) y un patrón restrictivo (línea roja) para comparar.
Imagen por Lecturio.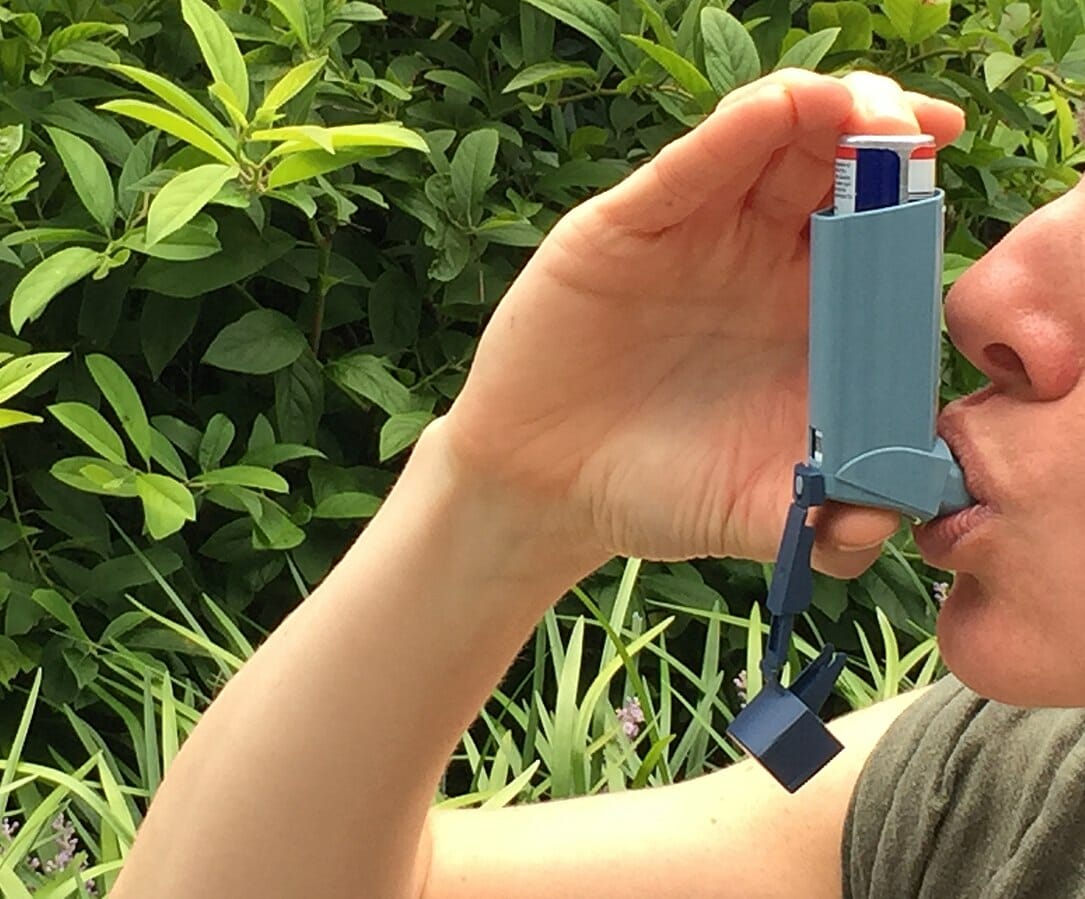
Una individuo que utiliza un inhalador para el asma (un método de administración de medicamentos inhalados).
Imagen: “Adult Using an Asthma Inhaler (29251369035)” por National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). Licencia: CC BY 2.0El tratamiento de emergencia es para la exacerbación severa del asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis, no para el tratamiento inicial del paciente ambulatorio.
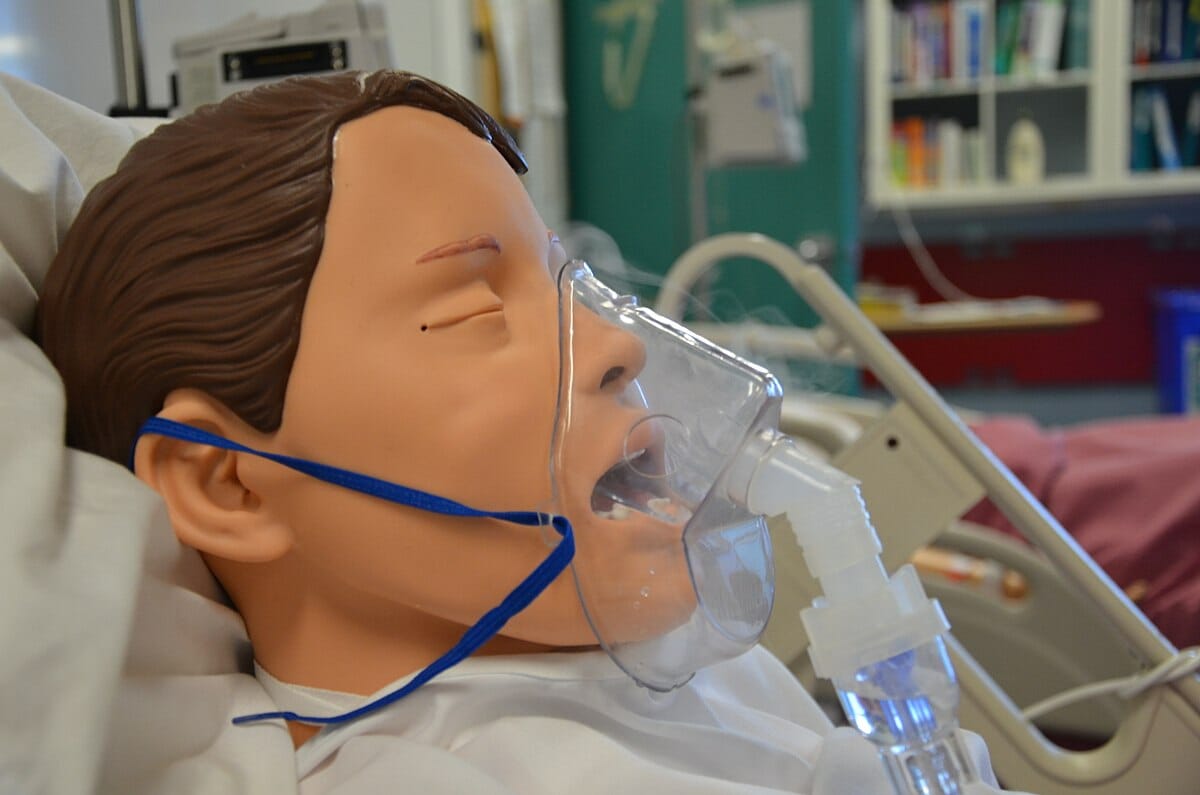

La administración de medicamentos inhalados a través de un nebulizador puede ser necesaria para el alivio emergente de los síntomas.
Imagen: “Administering inhaled medication” por British Columbia Institute of Technology (BCIT). Licencia: CC BY 4.0