La artritis idiopática juvenil, antes conocida como artritis reumatoide juvenil, es un grupo heterogéneo de enfermedades inflamatorias caracterizadas por la inflamación de 1 o más articulaciones y es la enfermedad reumática pediátrica más común. La artritis idiopática juvenil se clasifica de acuerdo con su presentación clínica y el diagnóstico se realiza con los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del examen físico, así como con pruebas de laboratorio de confirmación que muestran evidencia de inflamación y hallazgos característicos de las radiografías. El tratamiento está dirigido a prevenir la pérdida de la función y controlar o limitar el daño articular, con un pronóstico variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables según el tipo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La artritis idiopática juvenil, antes conocida como artritis reumatoide juvenil, es la enfermedad reumatológica crónica más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la población pediátrica. Si bien existen múltiples subgrupos con distintas patogénesis, la característica clave es la artritis.
La artritis idiopática juvenil es un término que se usa para describir un grupo de afecciones inflamatorias de las articulaciones que afectan a niños menores de 16 años y que duran 6 semanas o más.
La clasificación se realiza según la sintomatología (según la International League of Associations for Rheumatology):
Si bien la susceptibilidad genética tiene un rol en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la artritis idiopática juvenil, la etiología y patogénesis exactas de la enfermedad no se comprenden completamente. Se cree que la artritis idiopática juvenil es causada por una interacción entre las exposiciones ambientales y la predisposición genética.
Componente ambiental:
Componente genético :
La presentación de artritis idiopática juvenil es variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables secundaria a la naturaleza heterogénea de los LOS Neisseria diversos subgrupos, pero hay algunas características comunes.
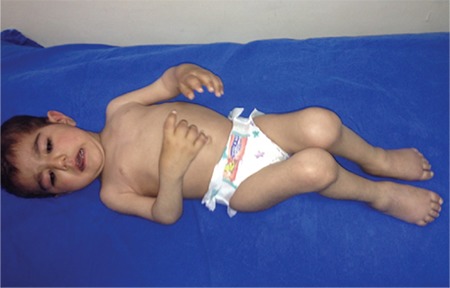
Afectación articular generalizada en la artritis idiopática juvenil poliarticular
Imagen: “Widespread joint involvement in polyarticular juvenile idopathic arthritis” por Kenan Barut et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.5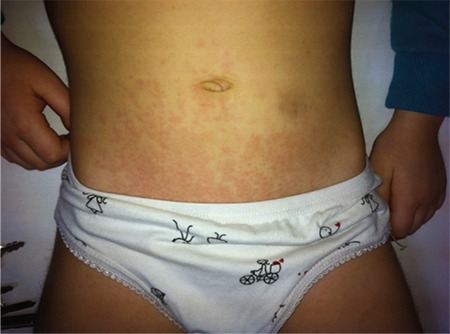
Erupción típica en la artritis idiopática juvenil sistémica
Imagen: “Typical rash in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis” por Kenan Barut et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.5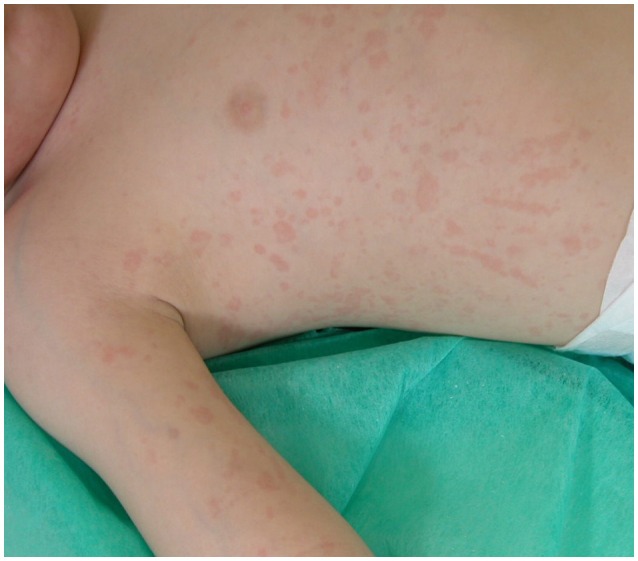
Erupción macular salmón en la artritis idiopática juvenil sistémica
Imagen: “Salmon-macular rash in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis” por Gabriella Giancane et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0| Oligoarticular | Poliarticular | Sistémica | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Número de articulaciones afectadas | Menos de 5 | > 5 | Ninguna |
| Tipos de articulaciones afectadas |
|
|
|
| Características sistémicas |
|
La uveítis es menos frecuente |
|
El diagnóstico de la artritis idiopática juvenil se basa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del examen físico. Los LOS Neisseria datos de laboratorio y la imagenología contribuyen a la confirmación del diagnóstico y la exclusión de otras enfermedades.
Hallazgos variables relacionados con la gravedad y el tipo de enfermedad; se utiliza a menudo para evaluar otros diagnósticos:
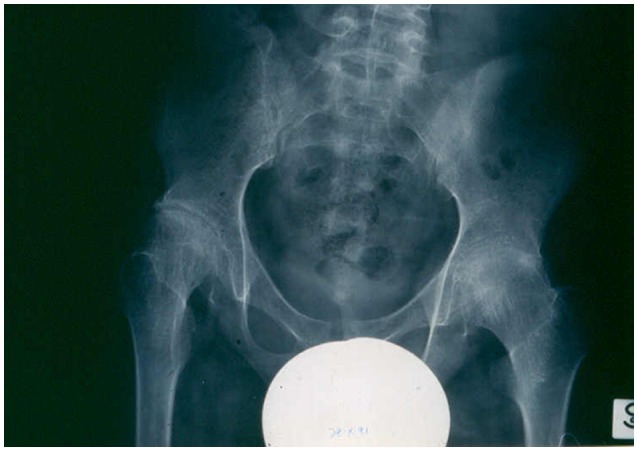
Radiografía que muestra cambios destructivos avanzados en las caderas de un paciente con artritis idiopática juvenil sistémica
Imagen: “X-ray showing advanced destructive changes in the hips of a systemic JIA patient” por Gabriella Giancane et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0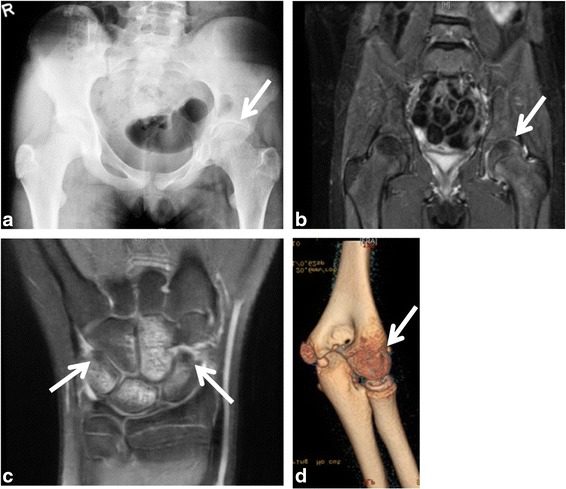
Imágenes representativas de monoartritis grave en niños con diagnóstico de artritis idiopática juvenil oligoarticular:
a) La radiografía de cadera muestra acortamiento del cuello femoral izquierdo y disminución del espacio articular.
b) La resonancia magnética con gadolinio revela un realce y leve engrosamiento de la membrana sinovial de la cadera izquierda en la imagen ponderada en T2.
c) La resonancia magnética de la muñeca derecha demuestra una sinovitis del carpo, edema de la médula ósea marcada, quistes óseos y erosiones en las imágenes ponderadas en T1.
d) La TC sin contraste del codo izquierdo muestra erosiones óseas, hiperostosis del complejo troclea-olécranon y reducción del espacio articular. Las flechas blancas apuntan hacia los hallazgos anormales.
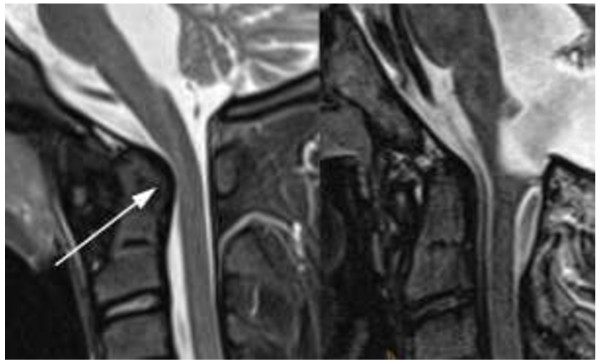
Imagenología de recuperación de inversión de tau corta con y sin artritis idiopática juvenil:
Izquierda: niña de 13 años con artritis idiopática juvenil, recuperación de inversión de tau corta de 3 mm sagital: fosas agrandadas con contorno dorsal abultado (flecha) y estrechamiento del canal espinal en la unión craneocervical (puntas de flecha)
Derecha: Imagen de control normal tomada de un niño de 13 años sin artritis idiopática juvenil y tamaño normal de sus fosas.
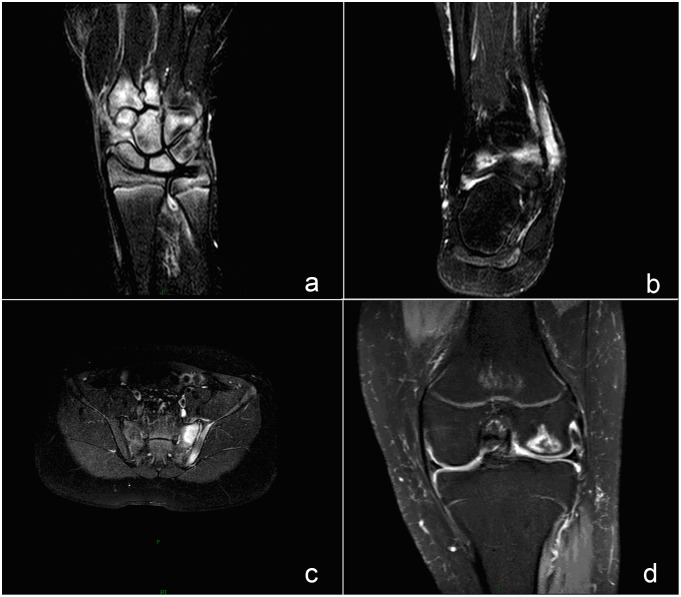
Hallazgos de la resonancia magnética de las articulaciones frecuentemente afectadas en la artritis idiopática juvenil:
El edema de médula ósea aparece como una señal hiperintensa en la secuencia de recuperación de la inversión espectral atenuada, lo que refleja una lesión inflamatoria activa.
a) Una imagen de recuperación de la inversión espectral atenuada de una muñeca muestra edema de médula ósea en el carpo.
b) Una imagen de recuperación de la inversión espectral atenuada de un tobillo muestra edema de médula ósea en la articulación tibiofibular.
c) Una imagen de recuperación de la inversión espectral atenuada de la articulación sacroilíaca muestra edema de médula ósea a la izquierda de una articulación sacroilíaca.
d) Una imagen de recuperación de la inversión espectral atenuada de una articulación de rodilla muestra edema de médula ósea en el fémur distal.
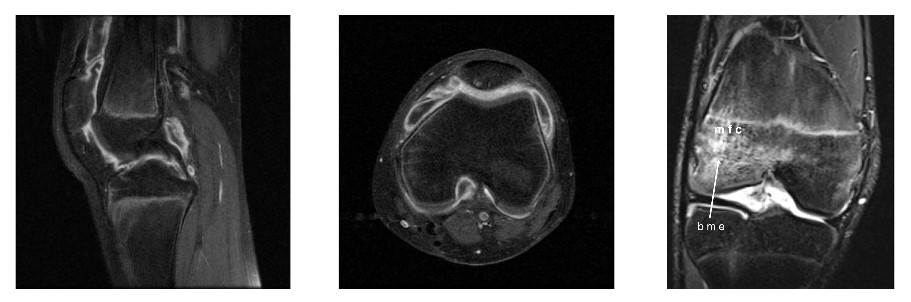
Resonancia magnética de una rodilla en un paciente con artritis idiopática juvenil:
Observe los cambios erosivos y la inflamación que se muestran aquí.
El objetivo principal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de la artritis idiopática juvenil es limitar la extensión del daño articular y restringir la pérdida de función. La artritis idiopática juvenil es una enfermedad crónica, y es esencial inducir la remisión con la menor cantidad de toxicidad.
Criterios del American College of Rheumatology para la remisión completa: