El aneurisma de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica es la dilatación anormal de un segmento de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica, generalmente la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy ascendente. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria aneurismas de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica se deben a trastornos aórticos degenerativos, comúnmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes> 65 años de edad. Los LOS Neisseria aneurismas de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica genéticos representan el 20% de los LOS Neisseria casos y se encuentran con frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes más jóvenes. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria aneurismas de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica son asintomáticos (se encuentran de forma incidental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología), pero pueden presentar síntomas debido a sus efectos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las estructuras circundantes. La ruptura aórtica es una emergencia potencialmente mortal. Entre los LOS Neisseria estudios de diagnóstico por imágenes, la angiografía por tomografía computarizada (TC) es la más utilizada. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos asintomáticos, se monitoriza la expansión aórtica. Se recomienda la reparación quirúrgica para aneurismas de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica sintomáticos y aumento del diámetro aórtico ( los LOS Neisseria criterios varían según la ubicación y la afección subyacente).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Aneurisma de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica
Tipos
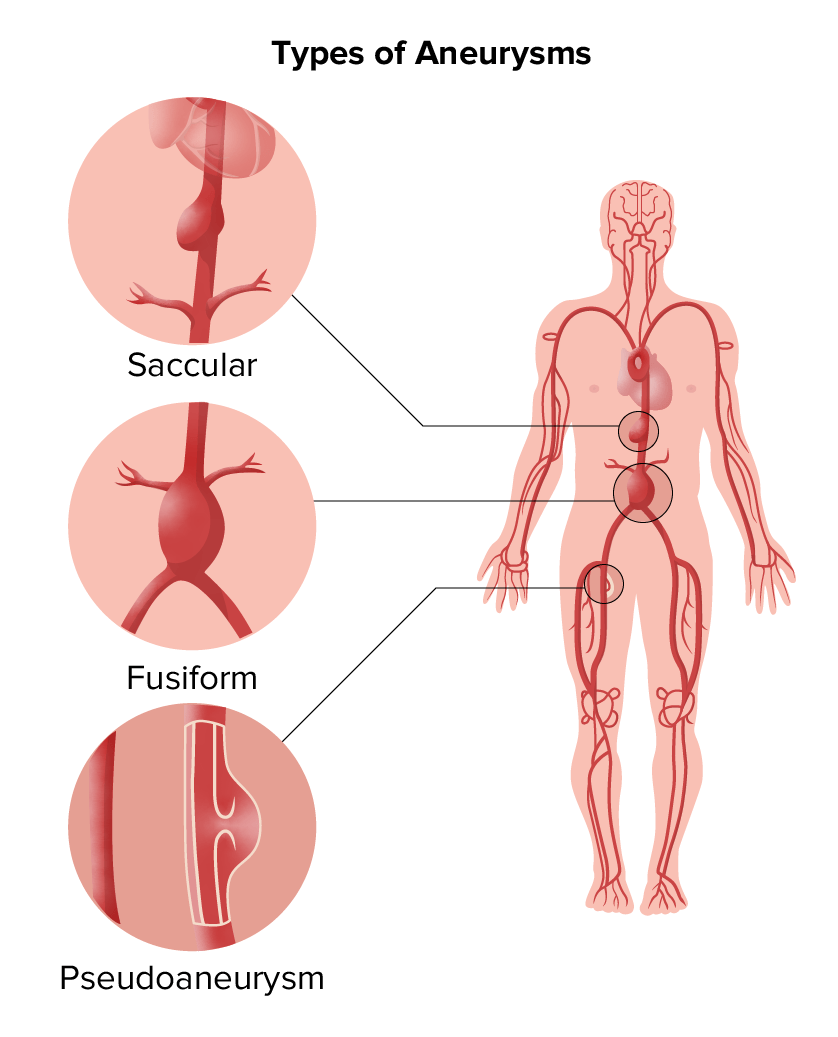
Tipos de aneurismas:
Los aneurismas saculares y fusiformes pertenecen a la categoría de aneurismas verdaderos; el pseudoaneurisma es otro tipo.
Localización
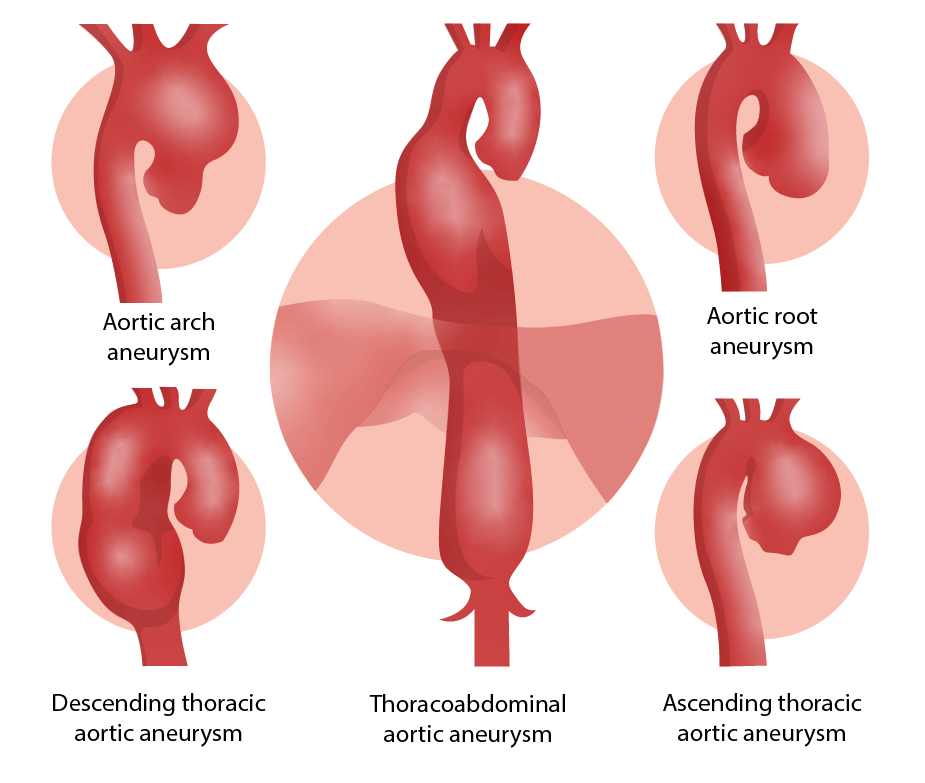
Localizaciones de aneurismas aórticos
Imagen por Lecturio.| Tratamiento de pacientes asintomáticos | Aneurisma degenerativo de raíz aórtica o aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy ascendente | Aneurisma de aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy descendente |
|---|---|---|
|
AngioTC/AngioRM anual
(ecocardiograma para seguimiento de la enfermedad valvular si es necesario) |
3,5–4,4 cm | 4–4,9 cm |
| Semestral (cada 6 meses) AngioTC/AngioRM
(ecocardiograma para seguimiento de la enfermedad valvular si es necesario) |
4–4,9 cm | 5–6 cm |
| Considerar la reparación electiva |
≥ 5,5 cm
Expansión rápida (> 0,5 cm/año) ≥ 4,5 cm si se necesita cirugía de válvula aórtica o derivación coronaria |
≥ 5,5 cm, considerar reparación endovascular torácica;
≥ 6 cm (la reparación endovascular torácica no es técnicamente posible) para cirugía abierta; Expansión rápida (> 0,5 cm/año) |
Indicaciones para la reparación quirúrgica
Opciones quirúrgicas
Los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos diferenciales de los LOS Neisseria aneurismas de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy torácica incluyen las siguientes condiciones: