Un absceso es una acumulación de pus en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions o tejido subcutáneo. Los LOS Neisseria abscesos son una de las infecciones más frecuentes de la piel y los LOS Neisseria tejidos blandos. Aunque los LOS Neisseria abscesos pueden ocurrir de forma espontánea, a menudo se identifican factores predisponentes como abrasiones y pinchazos. Un paciente con un absceso cutáneo suele presentarse con una masa sensible, fluctuante y localizada que parece enrojecida y cálida. La incisión y el drenaje son los LOS Neisseria pilares del tratamiento, pero se pueden usar antibióticos según el tamaño del absceso y los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo del paciente para una infección grave.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El absceso de tejidos blandos es una acumulación de pus en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dermis Dermis A layer of vascularized connective tissue underneath the epidermis. The surface of the dermis contains innervated papillae. Embedded in or beneath the dermis are sweat glands; hair follicles; and sebaceous glands. Skin: Structure and Functions o tejido subcutáneo.
Agentes causales:
Factores de riesgo:
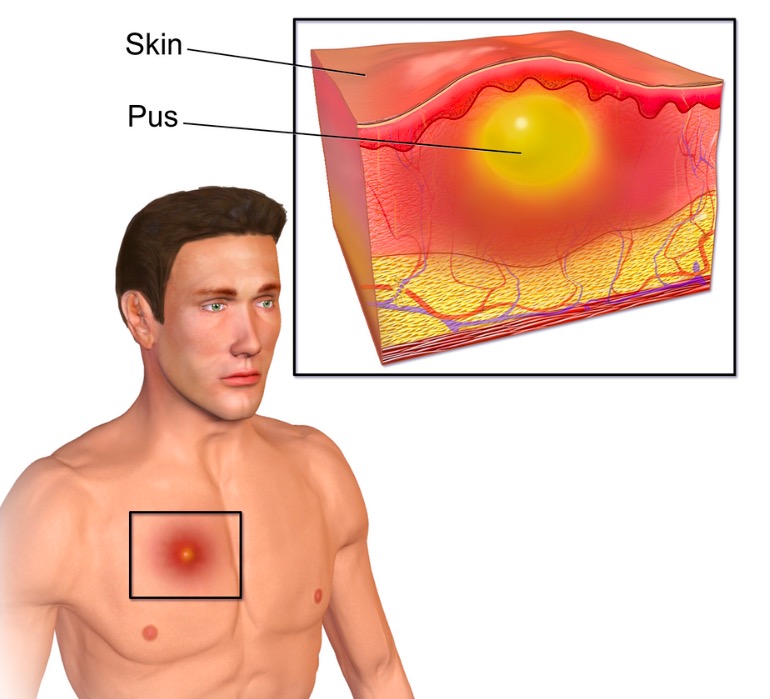
Una ilustración de un absceso cutáneo.
Imagen: “Abscess” por BruceBlaus. Licencia: CC BY 3.0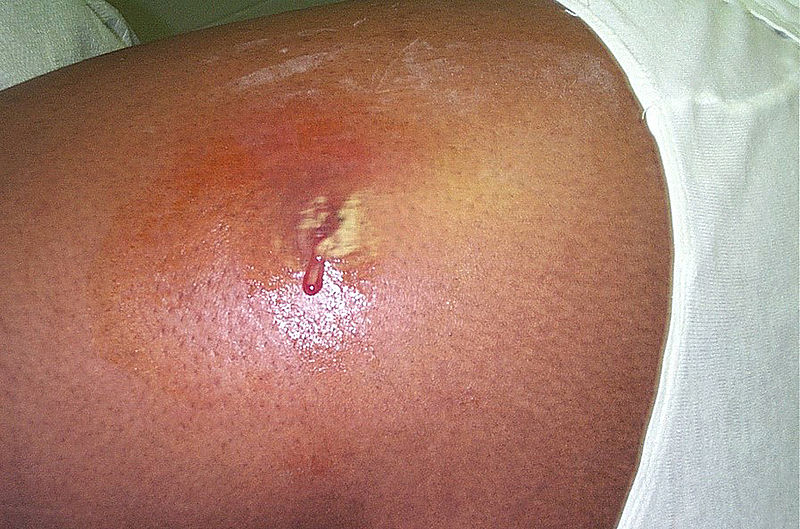
Un absceso cutáneo localizado en la cadera con algún drenaje purulento espontáneo.
Imagen: “Cutaneous abscess MRSA” por CDC/Bruno Coignard, M.D. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria abscesos de tejidos blandos generalmente se diagnostican según el examen físico y el antecedente clínico.

Un ultrasonido que muestra un área hipoecoica rodeada por una inflamación de los tejidos blandos compatible con un absceso.
Imagen: “Abscess” por Section of Emergency Medicine, Department of Medicine, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, LA 70112, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0