O linfoma de Hodgkin ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) é uma neoplasia dos linfócitos B com origem nos gânglios linfáticos. O achado histológico patognomónico do LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle é uma célula de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg ( HRS HRS Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of hrs is hypovolemia, often as a result of forced diuresis or drainage of ascites. This leads to renal vasoconstriction resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Hepatorenal Syndrome) (células B gigantes multinucleadas com inclusões eosinofílicas). A doença apresenta-se mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente com linfadenopatias (o pescoço é o mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente envolvido), sudorese noturna, perda de peso, febre e, por vezes, esplenomegalia e hepatomegalia. Os exames complementares de diagnóstico incluem a análise histológica de gânglios linfáticos que mostram células HRS HRS Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of hrs is hypovolemia, often as a result of forced diuresis or drainage of ascites. This leads to renal vasoconstriction resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Hepatorenal Syndrome, análises sanguíneas, TAC e PET PET An imaging technique that combines a positron-emission tomography (PET) scanner and a ct X ray scanner. This establishes a precise anatomic localization in the same session. Nuclear Imaging. O LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle é tratado com quimioterapia e radioterapia. O prognóstico melhorou significativamente com o advento dos regimes de quimioterapia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
O linfoma de Hodgkin ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) é um linfoma monoclonal de células B (neoplasia) com origem nos gânglios linfáticos, nos quais as células malignas de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg ( HRS HRS Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of hrs is hypovolemia, often as a result of forced diuresis or drainage of ascites. This leads to renal vasoconstriction resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Hepatorenal Syndrome) estão misturadas com uma população heterogénea de células inflamatórias não neoplásicas.
Com base na classificação da OMS, os LHs apresentam os seguintes tipos e subtipos de acordo com o imunofenótipo e a morfologia.
LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle clássico (95%):
LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle com predominância de linfócitos nodulares (LLPHL, pela sigla em inglês):
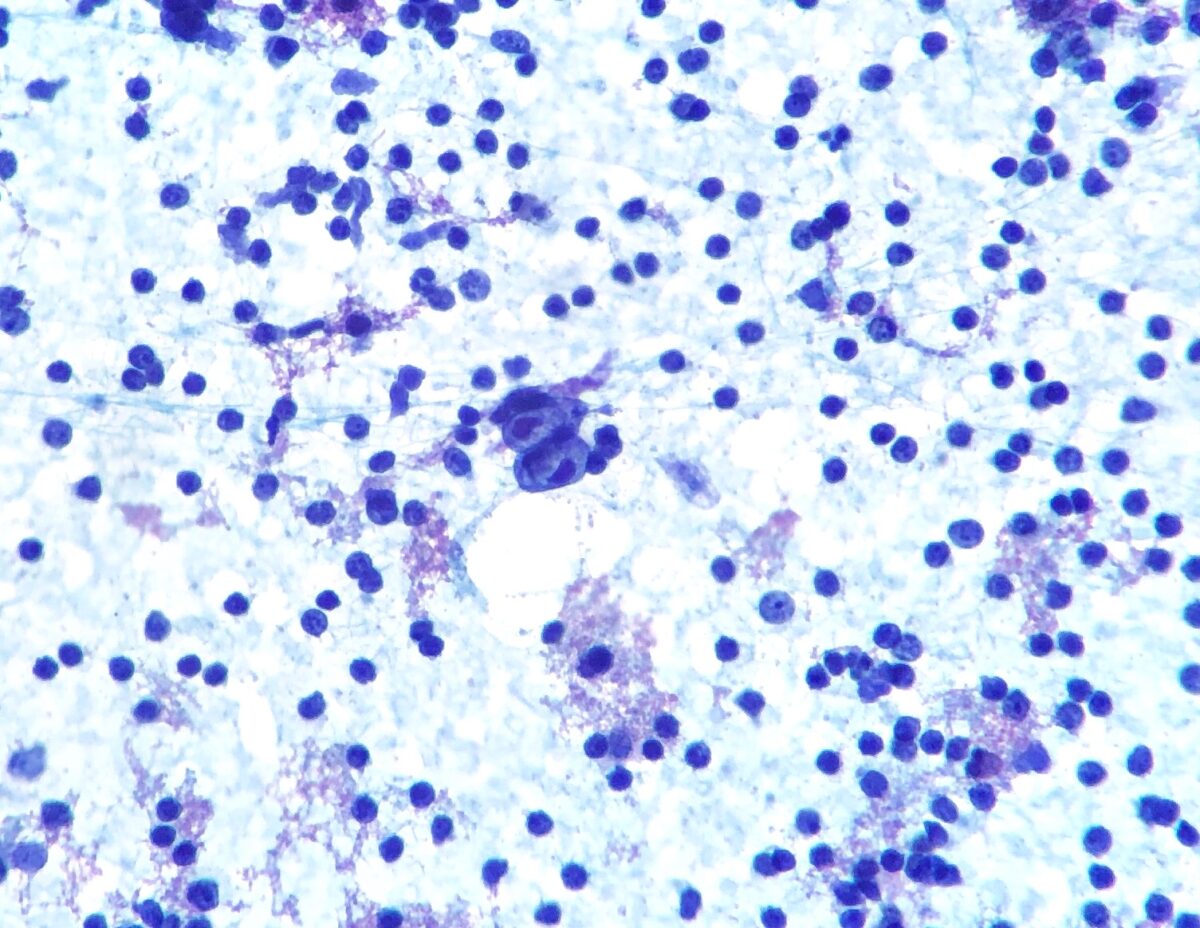
Linfoma de Hodgkin:
Aspiração por agulha fina de um gânglio que mostra uma célula de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (célula bilobada no centro)
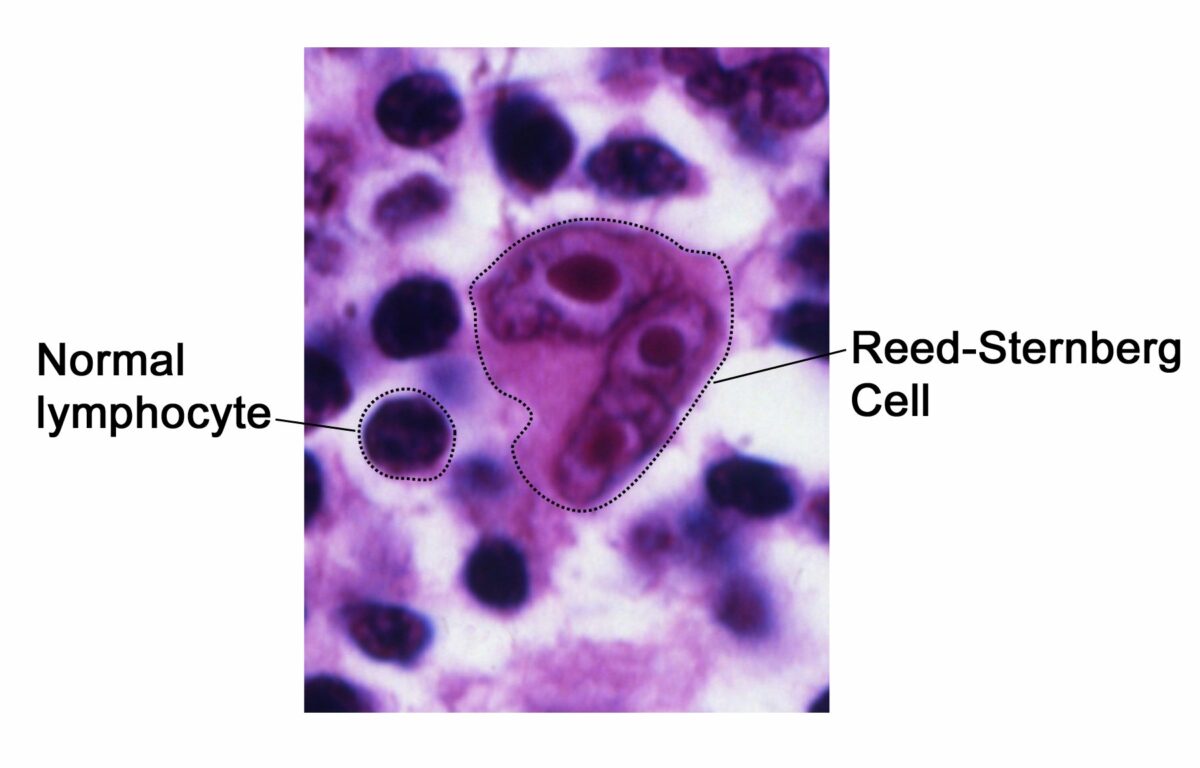
Achado histológico patognomónico de linfoma de Hodgkin:
A célula de Reed-Sternberg em “olhos de coruja”
Duração:
Apresentações mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comuns:
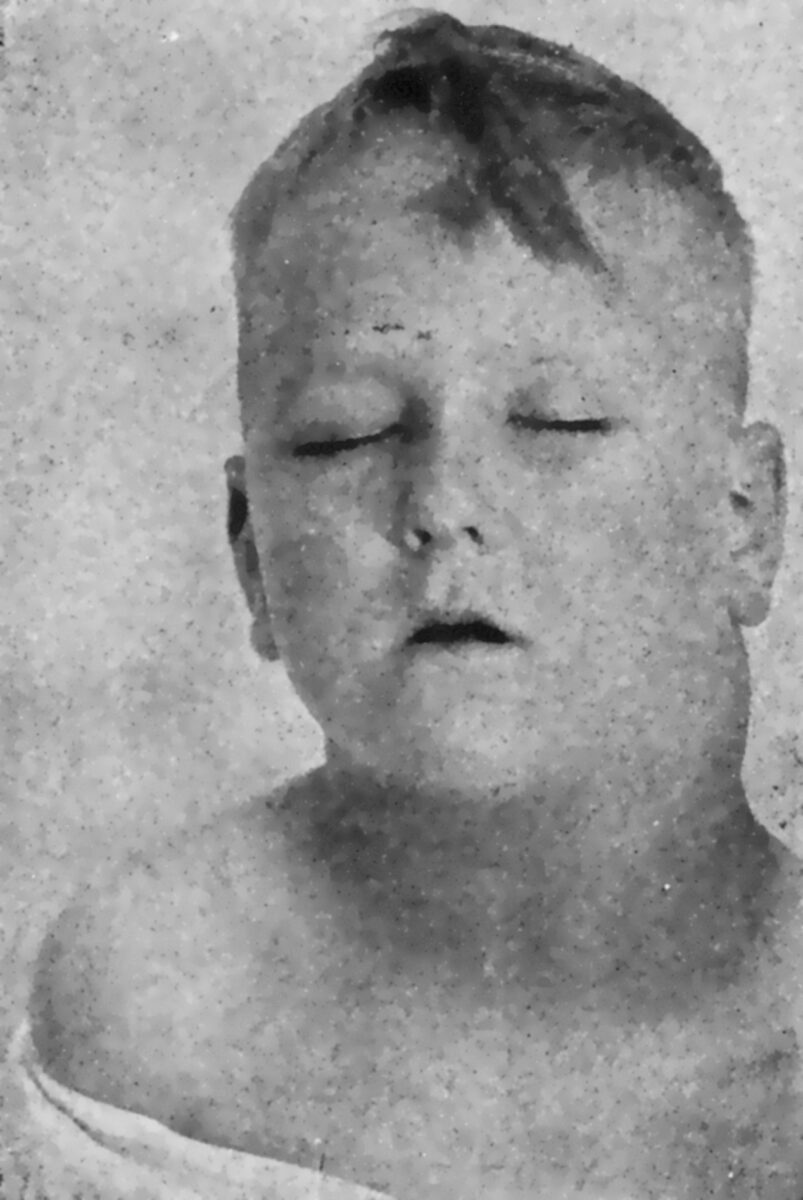
Linfoma de Hodgkin:
Linfadenopatia cervical proeminente
Sintomas “B” (constitucionais) presentes em 40% dos casos:
Outros sintomas:
Análises laboratoriais:
Imagiologia:
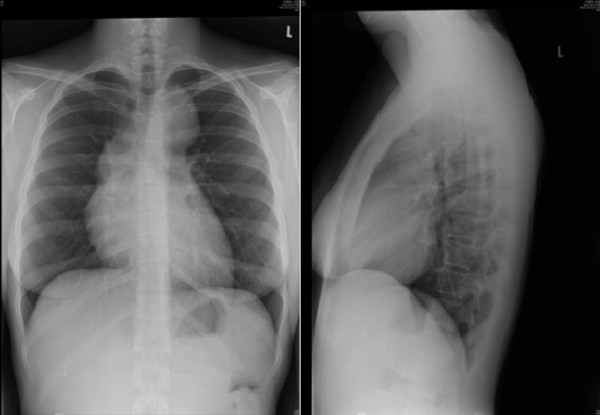
Linfoma de Hodgkin. O raio-X mostra linfadenopatia mediastínica.
Imagem: “Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting with markedly elevated IgE: a case report” por Ellis AK, Waserman S. Licença: CC BY 2.0Biópsia:
O estadiamento é baseado na classificação de Ann Arbor.
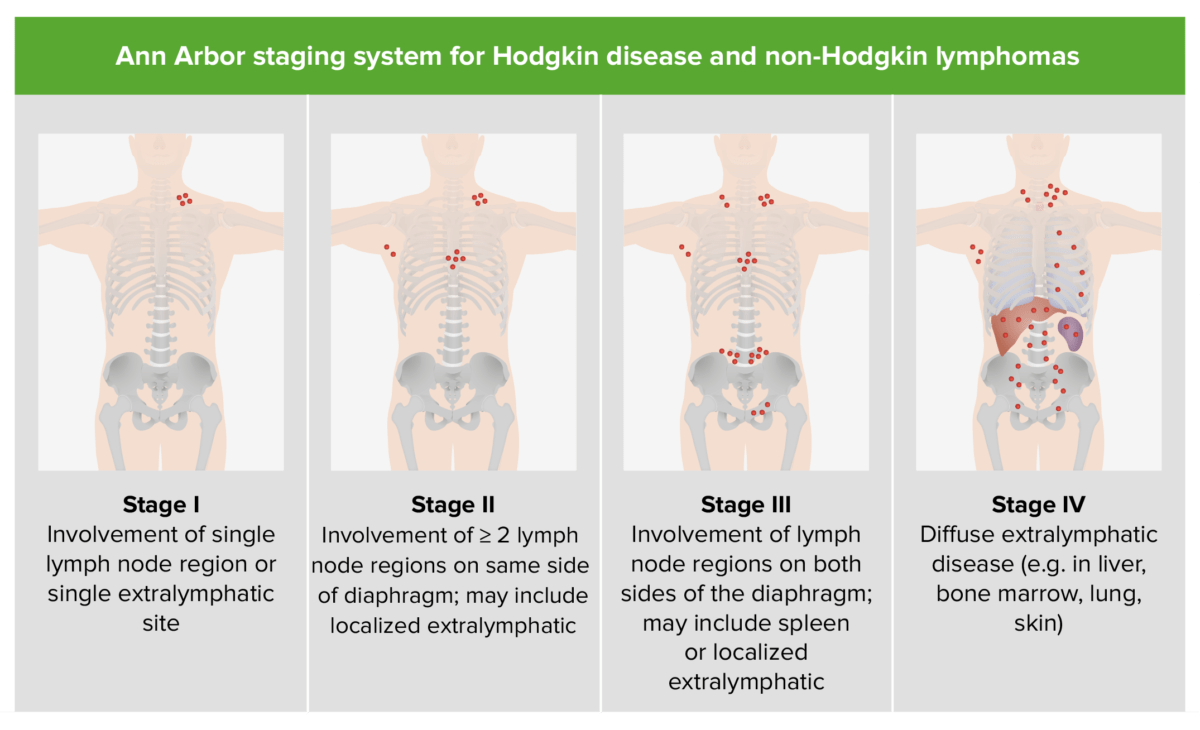
Estadiamento da doença de Hodgkin e do LNH
Imagem por Lecturio.