As hormonas são moléculas sintetizadas numa parte do corpo que se movem através da corrente sanguínea para exercer efeitos de regulação específicos noutra parte do corpo. As hormonas desempenham um papel fundamental na coordenação das atividades celulares em todo o corpo em resposta às constantes mudanças tanto no ambiente interno quanto no externo. A ação das hormonas permite ao organismo manter a homeostasia e regular Regular Insulin o crescimento e desenvolvimento. As hormonas são normalmente compostas por aminoácidos ou derivados do colesterol (sendo este último grupo conhecido como hormonas esteroides). As hormonas exercem os seus efeitos através da ligação aos recetores quer na superfície celular (a maioria das hormonas à base de aminoácidos) quer no citosol (hormonas esteroides). Por fim, a ligação aos recetores desencadeia mudanças na expressão genética ou na atividade enzimática intracelular.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
As hormonas são moléculas sintetizadas numa parte do corpo que se movem através da corrente sanguínea para exercer efeitos de regulação específicos noutra parte do corpo.
As principais funções das hormonas incluem:
As principais glândulas endócrinas incluem:
| Glândula/órgão | Hormona segregada pela glândula/órgão | Efeito primário da hormona |
|---|---|---|
| Hipotálamo | Hormona libertadora de tirotropina (TRH) | Estimula os tireotrofos pituitários a libertarem a hormona estimulante da tiroide (TSH) |
| Hormona libertadora de corticotrofina (CRH) | Estimula os corticotrofos pituitários a libertarem a hormona adrenocorticotrófica (ACTH) | |
| Hormona libertadora de gonadotrofinas (GnRH) | Estimula os gonadotrofos pituitários a libertarem FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle e LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle | |
| Hormona libertadora da hormona do crescimento ( GHRH GHRH A peptide of 44 amino acids in most species that stimulates the release and synthesis of growth hormone. GHRF (or GRF) is synthesized by neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. After being released into the pituitary portal circulation, GHRF stimulates gh release by the somatotrophs in the pituitary gland. Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones) | Estimula o somatotrofo pituitário a libertar GH | |
| Somatostatina | Inibe a libertação de GH e TSH pela hipófise | |
| Dopamina | Inibe a libertação de prolactina pelos lactotrofos pituitários | |
| Hipófise Anterior | TSH | Estimula a secreção das hormonas da tiroide |
| Hormona adrenocorticotrópica (ACTH) | Estimula a secreção de hormonas pelo córtex adrenal | |
| Hormona folículo-estimulante ( FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle, pela sigla em inglês) | Estimula a produção de gâmetas nas gônadas | |
| Hormona luteinizante ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle, pela sigla em inglês) | Estimula a produção de androgénio a nível das gónadas | |
| Hormona do crescimento (GH) | Promove o crescimento dos tecidos corporais | |
| Prolactina (PRL) | Promove a produção de leite pelas glândulas mamárias | |
| Hipófise posterior | Hormona antidiurética (ADH) | Estimula a reabsorção de água pelos rins |
| Oxitocina | Estimula:
|
|
| Glândula pineal | Melatonina | Regula os ciclos de sono |
| Glândula tiroideia | Hormonas da tiroide:
|
Estimula o metabolismo celular |
| Calcitonina | ↓ Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ sérico | |
| Paratiróide | Hormona da paratiroide (PTH, pela sigla em inglês) | ↑ Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ sérico |
| Córtex adrenal | Mineralocorticóides: aldosterona |
|
Glucocorticoides:
|
|
|
| Androgénios | Estimula os caracteres sexuais secundários | |
| Medula da suprarrenal | Catecolaminas:
|
Estimula a reação de luta ou fuga |
| Gónadas | Testosterona | Estimula:
|
| Estrogénios e progesterona |
|
|
| Inibina | Inibe de forma seletiva a libertação de FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle | |
| Placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity | Estrogénio | Sustenta a fisiologia materna durante a gravidez |
| Progesterona |
|
|
| Gonadotrofina coriónica humana (hCG) | Mantém a atividade endócrina do corpo lúteo | |
| Lactogénio placentário humano (hPL) | Altera a secreção materna de insulina de modo a ↑ glicose para o feto | |
| Fator de crescimento semelhante à insulina | Regula o crescimento fetal | |
| CRH e glucocorticóides placentários | Regulam o desenvolvimento e a maturação dos órgãos |
| Glândula/órgão | Hormona segregada pela glândula/órgão | Efeito primário da hormona |
|---|---|---|
| Estômago | Gastrina, histamina | Estimula a secreção de HCl HCL Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare, chronic, B-cell leukemia characterized by the accumulation of small mature B lymphocytes that have “hair-like projections” visible on microscopy. The abnormal cells accumulate in the peripheral blood, bone marrow (causing fibrosis), and red pulp of the spleen, leading to cytopenias. Hairy Cell Leukemia no estômago |
| Serotonina | Estimula a motilidade gástrica | |
| Pâncreas | Insulina | ↓ os níveis de glicemia movendo a glicose para o espaço intracelular através das membranas celulares |
| Glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions | ↑ níveis de glicemia estimulando a gliconeogénese e a glicogenólise | |
| Intestino | Secretina |
|
| Colecistoquinina |
|
|
| Peptído inibidor gástrico ( GIP GIP A gastrointestinal peptide hormone of about 43-amino acids. It is found to be a potent stimulator of insulin secretion and a relatively poor inhibitor of gatsric acid secretion. Gastrointestinal Neural and Hormonal Signaling) | Estimula a produção de insulina | |
| Timo | Timopoietina | Regula a função imunológica |
| Tecido adiposo | Leptina | Diminui a ingestão de alimentos |
| Coração | Peptído natriurético auricular (ANP) | Reduz o volume de plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products ao estimular a diurese |
| Fígado | Angiotensinogénio | Precursor da angiotensina II, um potente vasoconstritor que estimula a aldosterona |
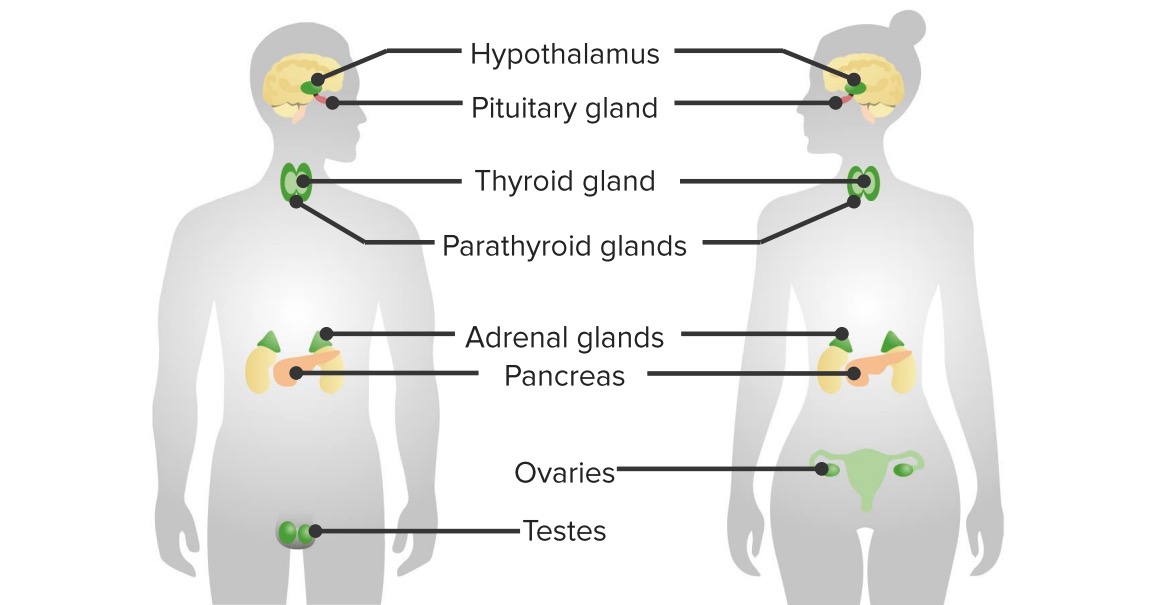
Principais órgãos do sistema endócrino
Imagem por Lecturio.A maioria das hormonas são à base de aminoácidos.
A maioria das hormonas liga-se aos recetores, que transmitem depois a mensagem através de mensageiros secundários e/ou de cascatas de sinalização. As hormonas esteróides, quando ligadas aos seus recetores, conseguem ligar-se diretamente ao DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure e afetar a expressão genética.
Há várias maneiras através das quais as hormonas enviam mensagens para todo o corpo:
Os recetores de membrana plasmática são, por norma, necessários para hormonas à base de aminoácidos e utilizam sistemas de 2.º mensageiro e cascatas de sinalização:
Os recetores intracelulares habitualmente provocam a ativação direta do gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics:
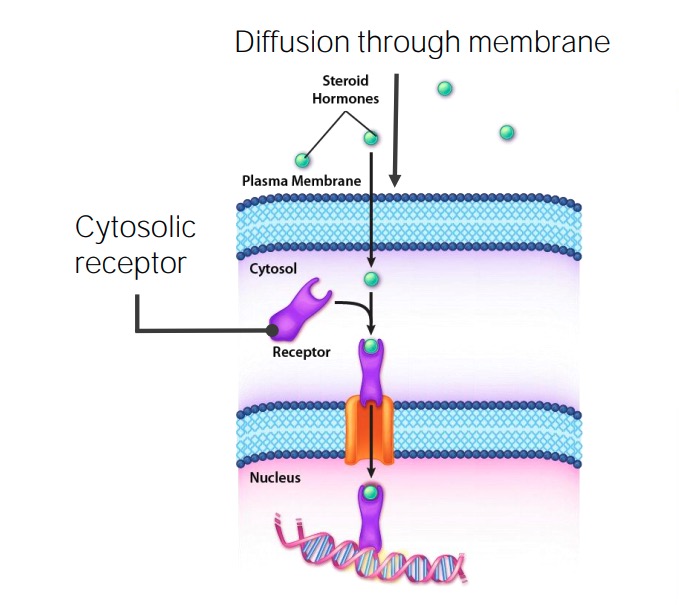
Sinalização das hormonas esteróides
Imagem por Kevin Ahern, MD.Quase todas as hormonas enumeradas nas tabelas podem ser produzidas em níveis anormais, resultando numa vasta gama de patologias clínicas. Algumas destas patologias incluem: