A deficiência do recetor de interleucina-12 (IL-12) é uma imunodeficiência primária autossómica recessiva causada por uma mutação nos genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure que codificam os recetores de IL-12 nas células T. A IL-12 promove a imunidade mediada por células induzindo a maturação das células T em células Th1 Th1 A subset of helper-inducer T-lymphocytes which synthesize and secrete interleukin-2; interferon-gamma; and interleukin-12. Due to their ability to kill antigen-presenting cells and their lymphokine-mediated effector activity, th1 cells are associated with vigorous delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. T cells: Types and Functions e estimulando a secreção de interferão-gama (IFN-γ). Este processo, por sua vez, ativa células natural killer (NK), macrófagos e células T citotóxicas. A deficiência do recetor de IL-12 resulta em deficiências em todas essas funções imunológicas; consequentemente, os doentes apresentam infeções disseminadas.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
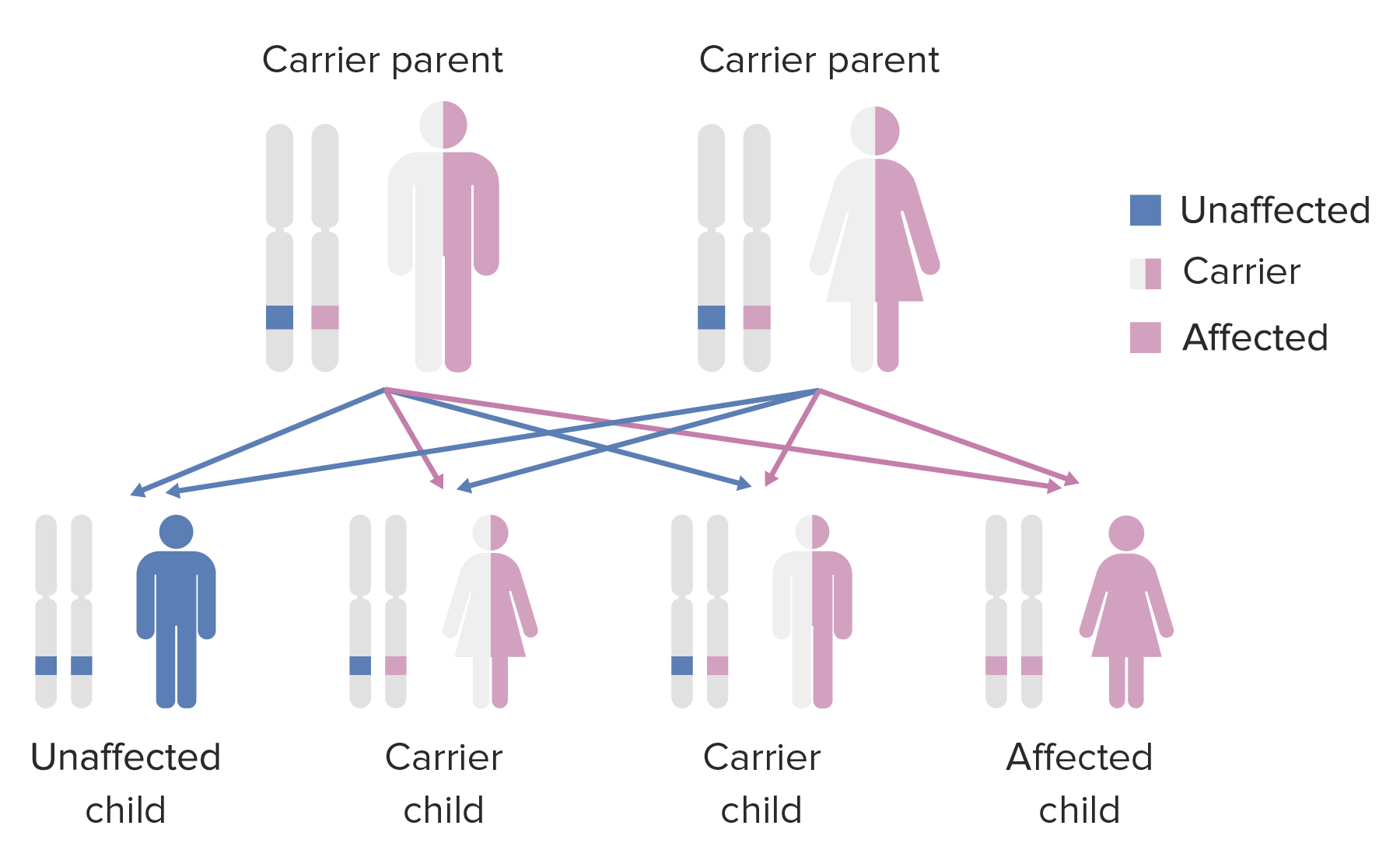
Diagrama do padrão de hereditariedade de condições autossómicas recessivas
Imagem por Lecturio.Diagnóstico
Tratamento
As seguintes condições são diagnósticos diferenciais da deficiência do recetor de IL-12: