A babesiose é uma infeção causada por um protozoário pertencente ao género Babesia Babesia Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body's immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis. A Babesia Babesia Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body's immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comum observada nos Estados Unidos é a B. microti B. microti A species of protozoa infecting humans via the intermediate tick vector ixodes scapularis. The other hosts are the mouse peromyscus leucopus and meadow vole microtus pennsylvanicus, which are fed on by the tick. Other primates can be experimentally infected with babesia microti. Babesia/Babesiosis, transmitida pela carraça Ixodes. Os protozoários prosperam e replicam-se dentro dos eritrócitos do hospedeiro. A lise dos eritrócitos e a resposta imune do corpo resulta em sintomas clínicos. Os doentes geralmente apresentam uma doença semelhante à gripe e icterícia. Em casos graves, podem ocorrer danos nos órgãos. O diagnóstico é confirmado pela presença visual de parasitas dentro das hemácias, que são frequentemente observadas em configuração de “Cruz de Malta”. Os testes Testes Gonadal Hormones serológicos e PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) também são usados no diagnóstico. A azitromicina e atovaquona são frequentemente usadas no tratamento. A coinfecção com Borrelia Borrelia Borrelia are gram-negative microaerophilic spirochetes. Owing to their small size, they are not easily seen on Gram stain but can be visualized using dark-field microscopy, Giemsa, or Wright stain. Spirochetes are motile and move in a characteristic spinning fashion due to axial filaments in the periplasmic space. Borrelia e Anaplasma é comum.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Para babesiose:
Para doença grave:
Fora de um hospedeiro humano:
Dentro de um hospedeiro humano:
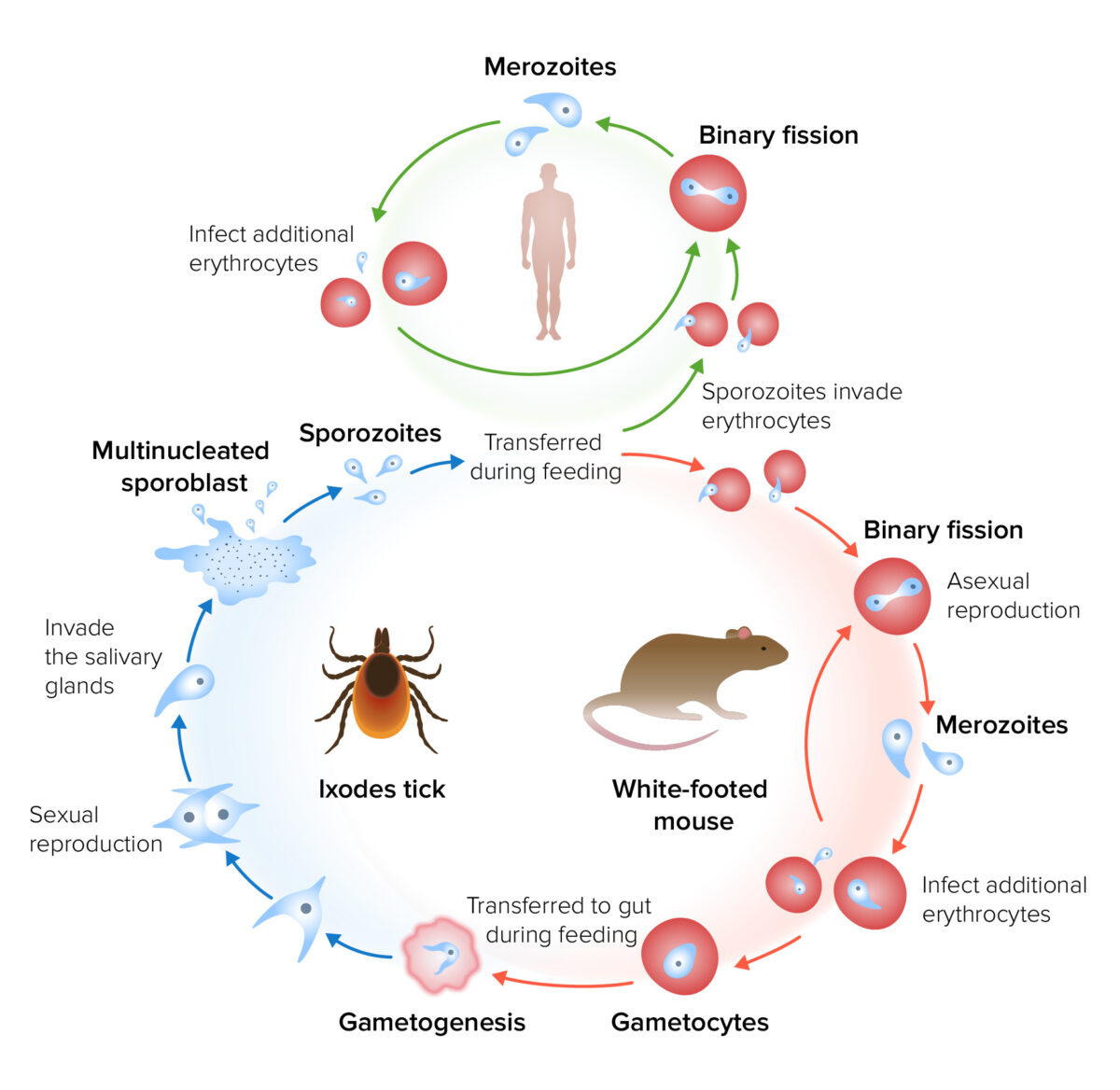
Ciclo de vida e transmissão da Babesia
Imagem por Lecturio.O período de incubação da babesiose é de 1 a 4 semanas.
Doença ligeira a moderada:
Doença grave:
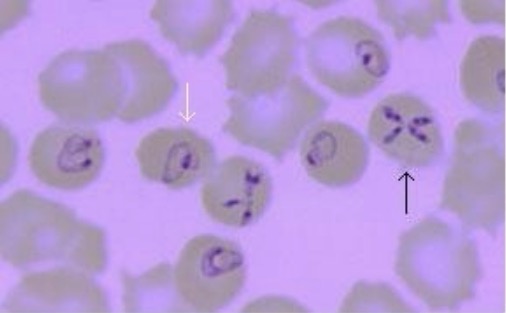
Esfregaço de sangue periférico demonstra infeção por Babesia:
A seta branca indica estruturas pleomórficas, semelhantes a anéis, frequentemente encontradas em infeções por Babesia. A seta preta mostra a clássica “Cruz de Malta”, patognomónica da babesiose.
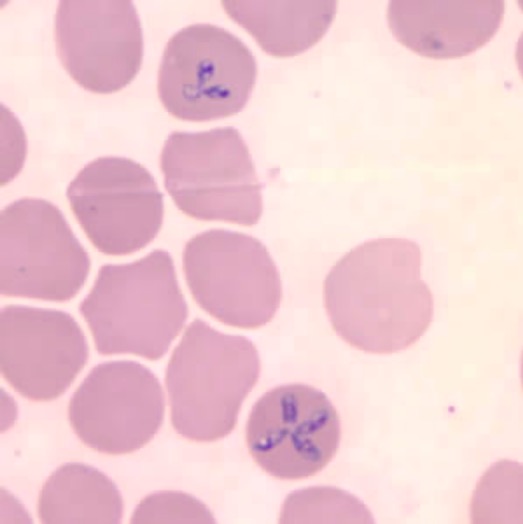
Esfregaço de sangue mostra hemácias infetadas com Babesia microti
Imagem : “Babesia microti” por U.S. Centers for Disease Control. Licença: Public DomainA base do tratamento são os antibióticos e a educação dos indivíduos acerca de métodos preventivos para evitar picadas de carraças.
Devem ser tomadas precauções em áreas endémicas, particularmente em indivíduos com risco de doença grave e complicações.
A tabela abaixo resume as características dos parasitas que infetam as hemácias.
| Organismo | Babesia Babesia Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body’s immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis | Plasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs |
|---|---|---|
| Doença | Babesiose | Malária |
| Aparência microscópica |
|
|
| Reservatório | Rato de patas brancas |
|
| Transmissão | Carraça Ixodes | Mosquito Anopheles Anopheles A genus of mosquitoes (culicidae) that are known vectors of malaria. Plasmodium/Malaria |
| Regiões comuns |
|
|
| Clínica |
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
| Tratamento |
|
Depende da espécie, gravidade e padrões de resistência, mas pode incluir uma combinação de:
|