Os agentes alquilantes são fármacos antineoplásicos independentes do ciclo celular que atuam sobretudo pela ligação de grupos alquilo a várias partes do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure. Isto resulta na formação de ligações cruzadas no DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, levando à inibição da replicação e a danos no DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure. O efeito geral é a morte das células cancerígenas. Os subgrupos destes fármacos são as mostardas nitrogenadas, as nitrosureias, os alquilsulfonatos, os triazenos, as etileniminas e as metilmelaminas. Os complexos de coordenação de platina pertencem ao grupo dos agentes alquilantes por causarem o mesmo efeito, no entanto, o seu mecanismo de ação é através da formação de adutos metálicos covalentes com o DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure. As reações adversas mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comuns são a mielossupressão e a toxicidade para sistemas orgânicos como os rins, o fígado e os pulmões.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Os agentes alquilantes são fármacos antineoplásicos que ligam um grupo alquilo ao DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, resultando na morte das células cancerígenas.
Estrutura química da ciclofosfamida
Imagem: “Cyclophosphamide structure” de Mysid. Licença: Domínio Público
Estrutura química da carmustina
Imagem: “Carmustine” de Fvasconcellos. Licença: Domínio Público
Estrutura química da lomustina
Imagem: “Lomustine” de Fvasconcellos. Licença: Domínio Público
Estrutura química do bussulfano
Imagem: “Busulfan” de Fvasconcellos. Licença: Domínio Público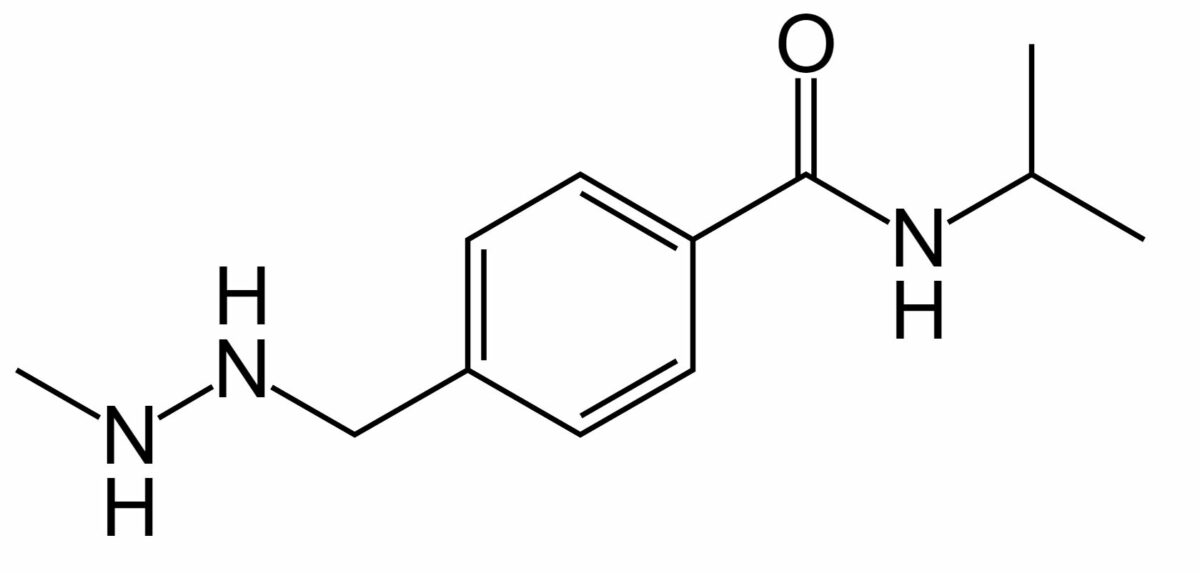
Estrutura química da procarbazina
Imagem: “Procarbazine” de Fvasconcellos. Licença: Domínio Público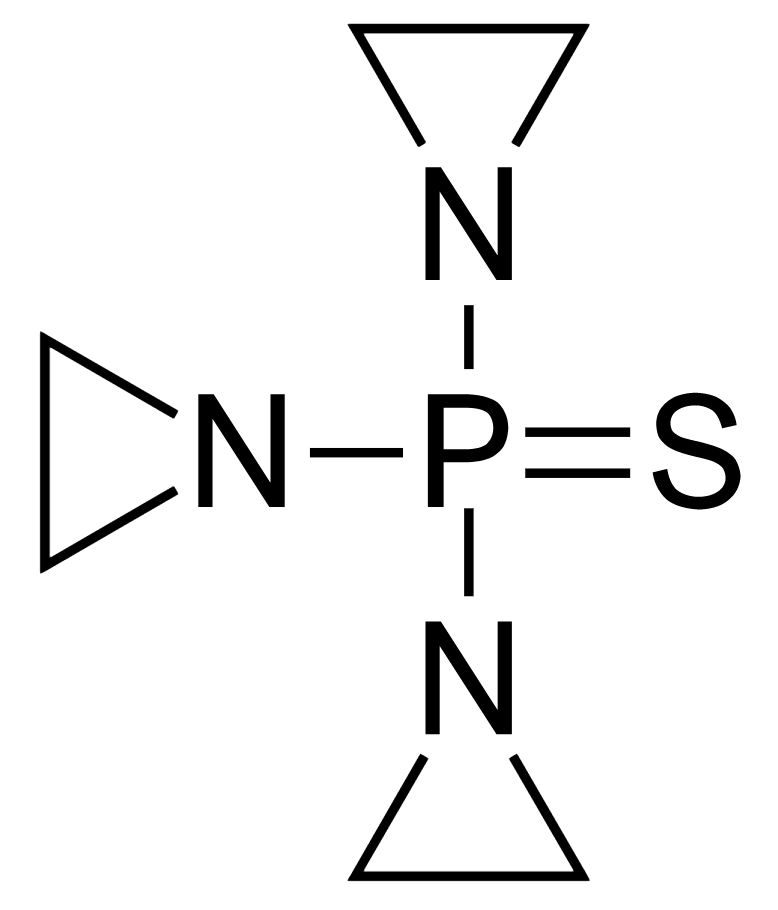
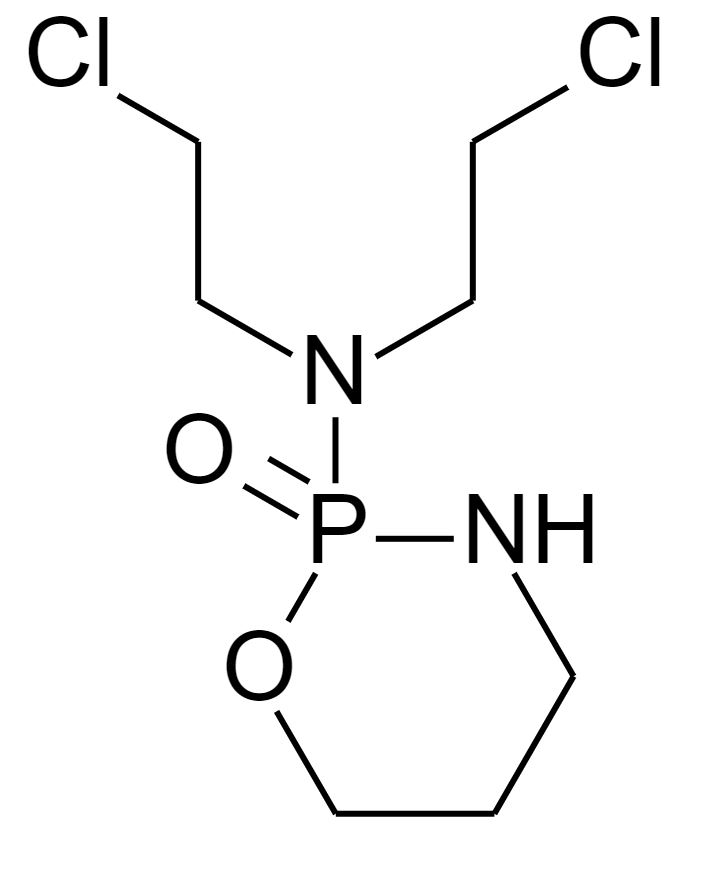
Estrutura química da tiotepa
Imagem: “ThioTEPA” de Fvasconcellos. Licença: Domínio Público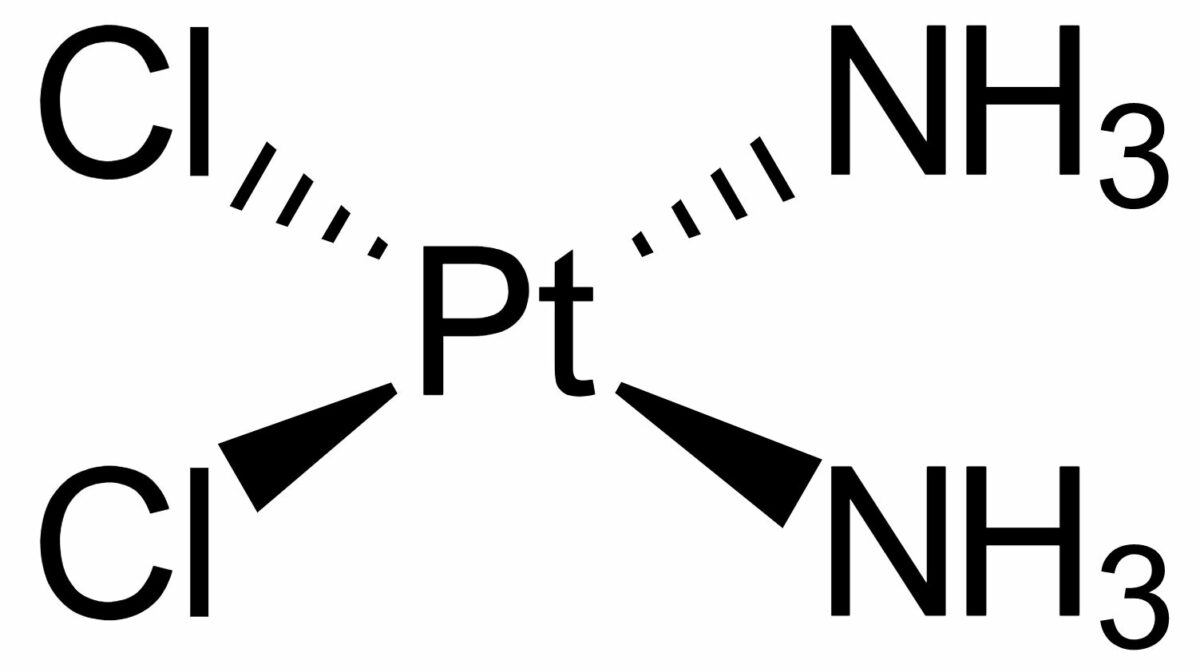
Estrutura química da cisplatina
Imagem: “Cisplatin-stereo” de Benrr101. Licença: Domínio Público
Estrutura química da carboplatina
Imagem: “Carboplatin-skeletal” de catclock. Licença: Domínio Público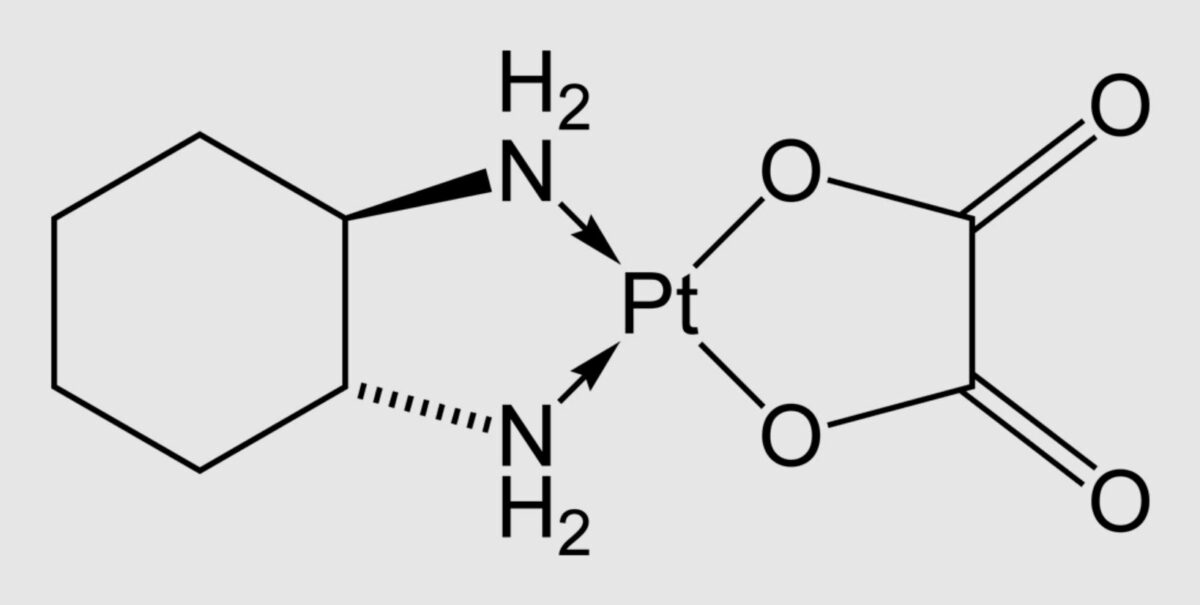
Estrutura química da oxaliplatina
Imagem: “Oxaliplatin-2D-skeletal” de Benjah-bmm27. Licença: Domínio Público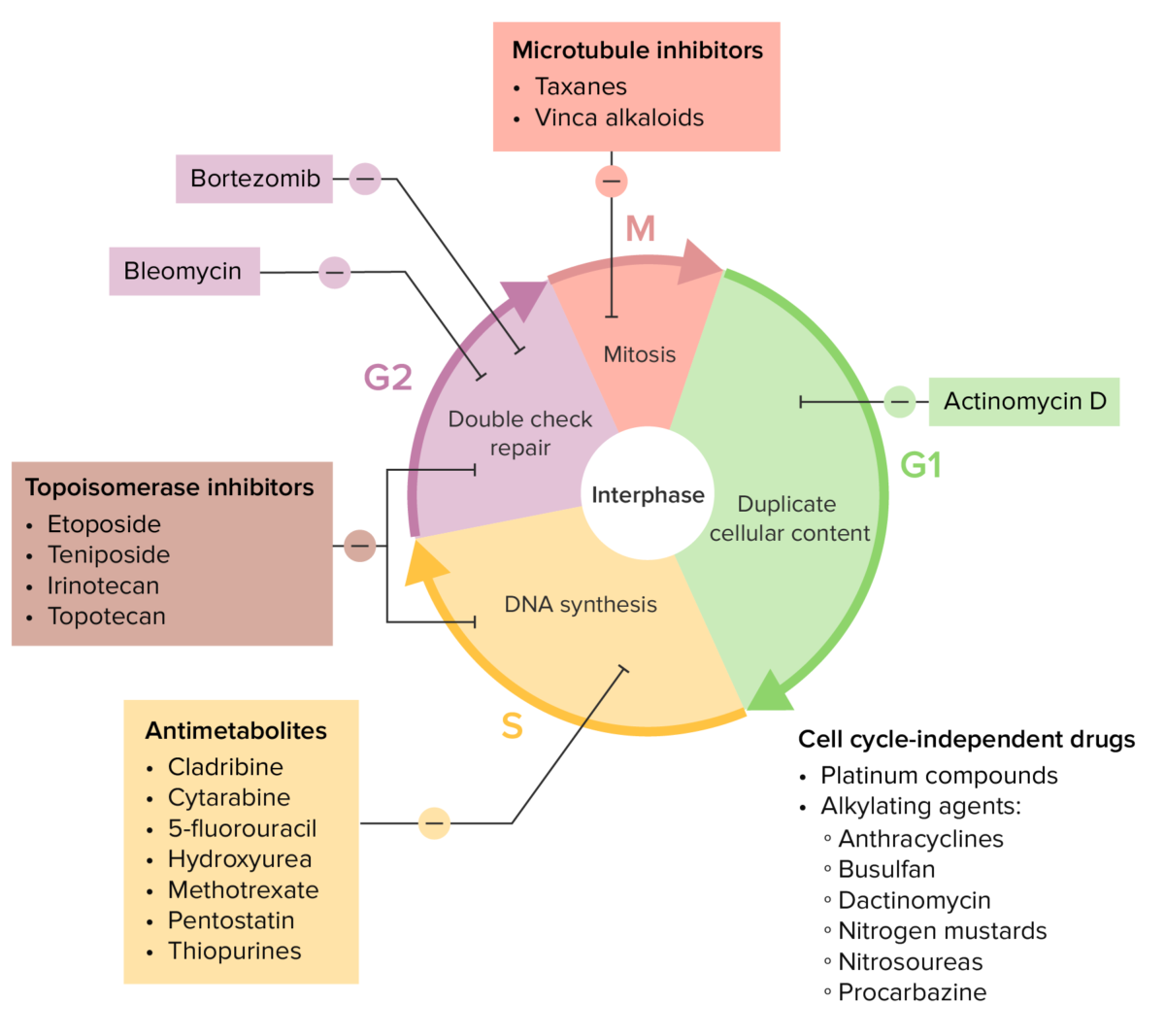
Vários fármacos de quimioterapia e os seus efeitos no ciclo celular
Imagem de Lecturio.| Classe do fármaco | Mecanismo |
|---|---|
Antibióticos antitumorais:
|
Intercalação entre bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance levando ao bloqueio da síntese de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure ou RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure e prevenção da replicação do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure |
| Antraciclinas |
|
| Agentes alquilantes |
|