Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza son miembros de la familia Orthomyxoviridae Orthomyxoviridae A family of RNA viruses causing influenza and other diseases. There are five recognized genera: influenzavirus a; influenzavirus b; influenzavirus c; isavirus; and thogotovirus. Influenza Viruses/Influenza y los LOS Neisseria organismos causantes de la influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza, una enfermedad respiratoria febril altamente contagiosa. Hay 3 virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza primarios (A, B y C) y varios subtipos, que se clasifican según sus antígenos de superficie virulentos, hemaglutinina y neuraminidasa. La influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza generalmente se presenta con fiebre, mialgia, cefalea y síntomas de una infección de las vías respiratorias superiores. Síntomas de gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis también pueden ocurrir comúnmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños. La influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza suele ser una afección autolimitante, aunque la neumonía viral o bacteriana secundaria puede complicar la enfermedad. El tratamiento generalmente es de soporte, aunque los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de neuraminidasa pueden ser útiles si se inician dentro de las 48 horas posteriores a la infección. La prevención se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vacunación anual del público y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la práctica de una buena higiene.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación del virus de ARN:
Los virus se pueden clasificar de muchas formas. La mayoría de los virus, sin embargo, tendrán un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus del genoma de ARN pueden caracterizarse además por ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (generalmente extraída de la célula huésped). Si la envoltura está ausente, los virus se denominan virus “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son virus de “sentido positivo” si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios de “sentido negativo” emplean la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza es un miembro de la familia Orthomyxoviridae Orthomyxoviridae A family of RNA viruses causing influenza and other diseases. There are five recognized genera: influenzavirus a; influenzavirus b; influenzavirus c; isavirus; and thogotovirus. Influenza Viruses/Influenza.
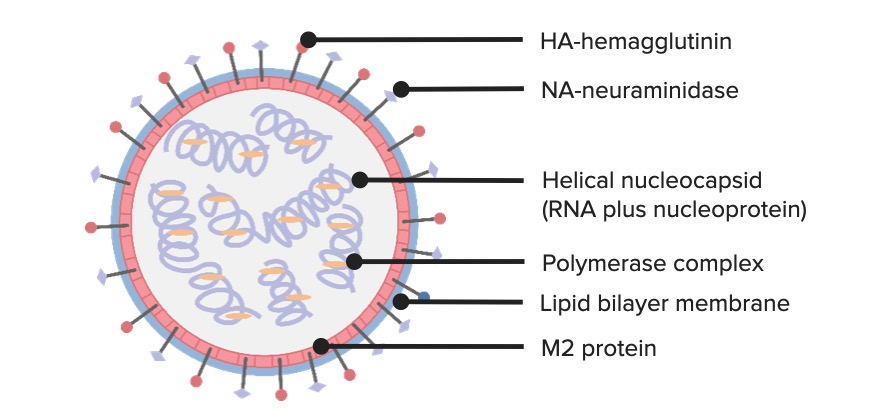
Un diagrama de la estructura del virus de la influenza
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Los
LOS
Neisseria
virus
Virus
Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range.
Virology de la
influenza
Influenza
Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection.
Influenza Viruses/Influenza causan una enfermedad respiratoria febril conocida como
influenza
Influenza
Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection.
Influenza Viruses/Influenza.
Hay 3 especies distintas del
virus
Virus
Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range.
Virology clínicamente relevantes:
| Características | Influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza | Influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza B | Influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huéspedes naturales |
|
Solo humanos |
|
| Epidemiología | Cambio y deriva antigénicos | Deriva antigénica solamente | Deriva antigénica solamente |
| Manifestaciones | Grandes epidemias y pandemias con una mortalidad significativa | Sin pandemias; pacientes ancianos e inmunocomprometidos | Enfermedad leve sin estacionalidad |
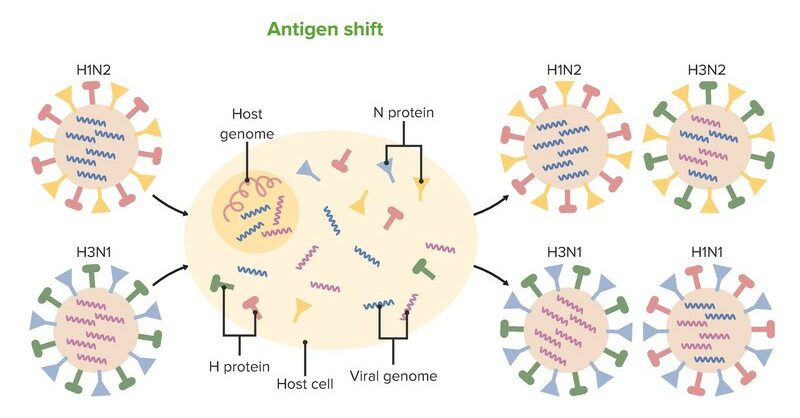
Cambio antigénico:
Dos o más cepas diferentes de un virus se combinan para formar un nuevo subtipo que es radicalmente diferente.
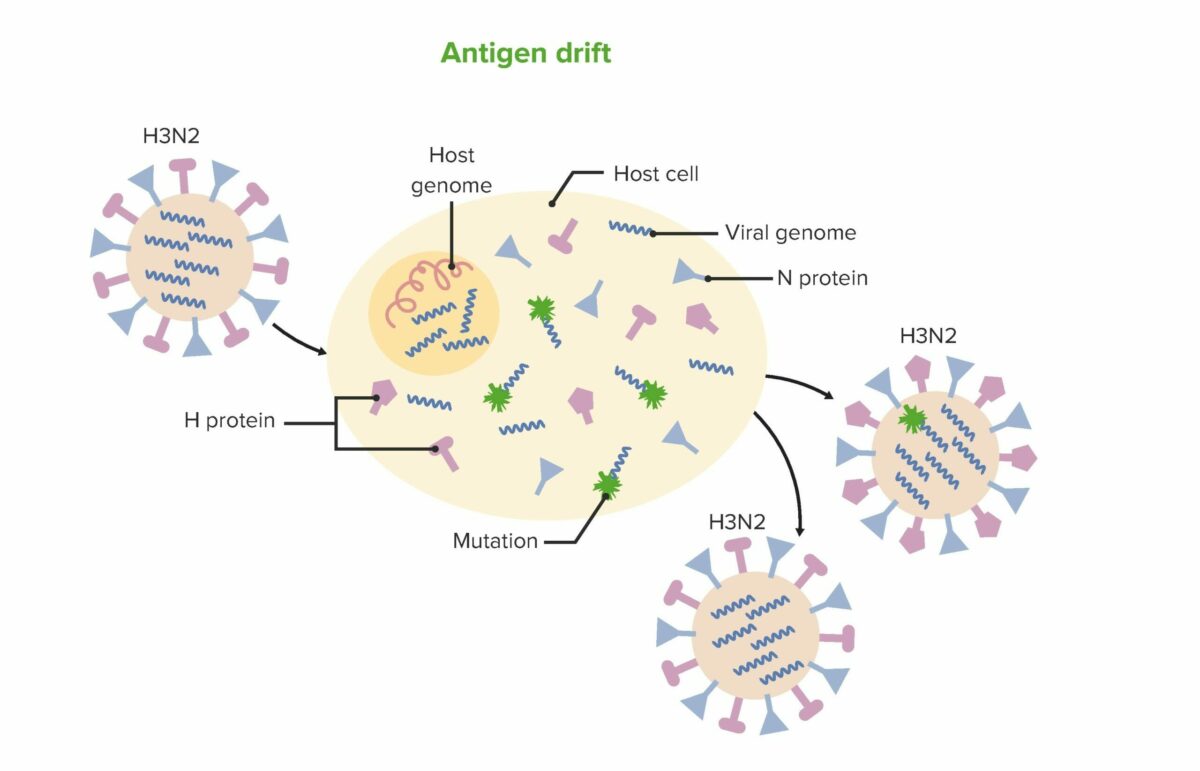
Deriva antigénica:
Las mutaciones se acumulan en los genes virales que codifican las proteínas de la superficie viral, dando lugar a nuevos sitios antigénicos. Los cambios son generalmente menores.
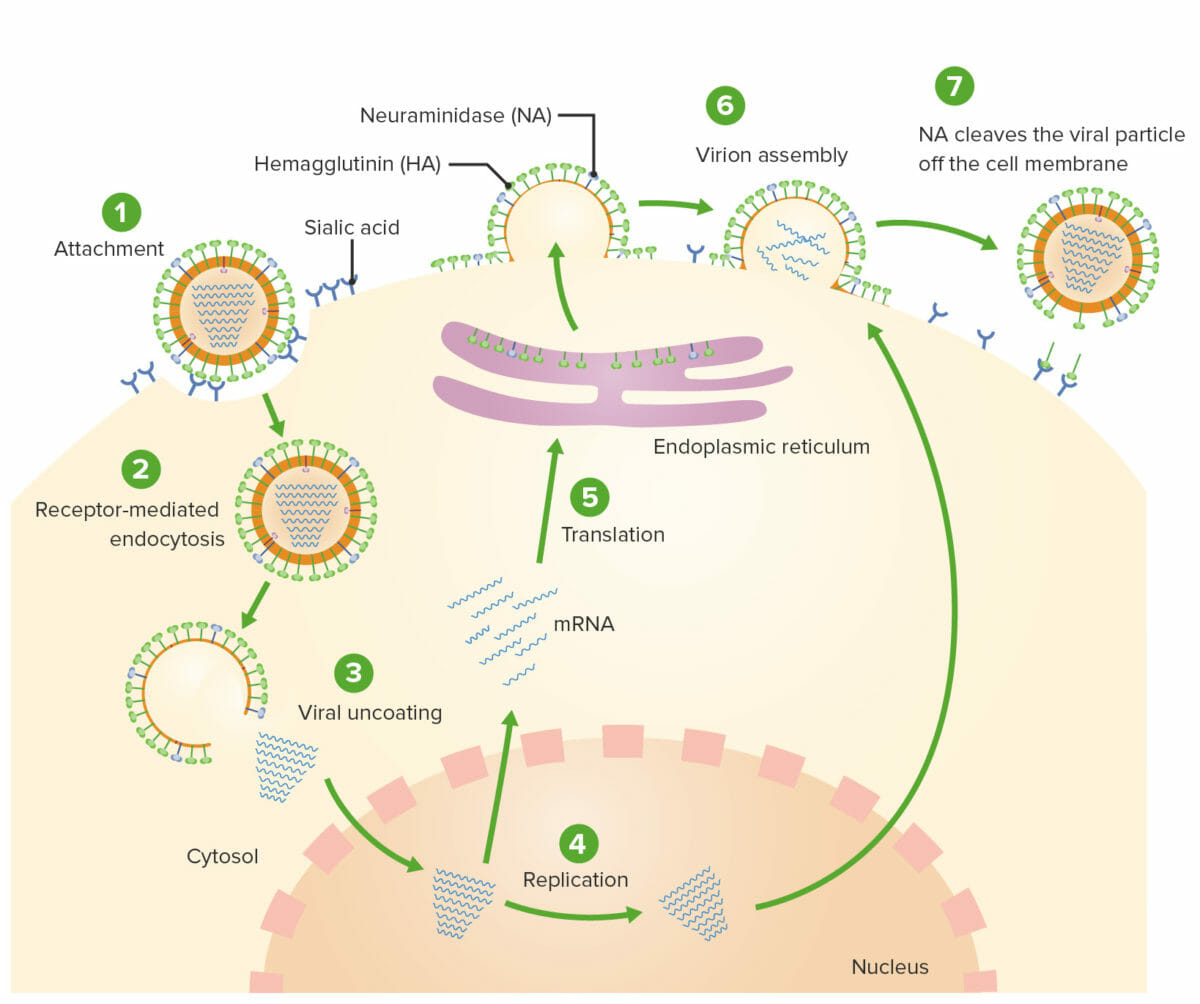
Replicación del virus de la influenza:
1: Una partícula viral une sus espículas de hemaglutinina (HA) a los receptores de ácido siálico en la superficie de las células epiteliales respiratorias.
2: La partícula viral es internalizada por endocitosis mediada por receptores.
3: Una vez dentro de la célula, la proteína M2 actúa como un canal de iones, lo que permite un influjo de partículas de hidrógeno, lo que da como resultado la desenvoltura del virus.
4: El ARN viral luego se mueve hacia el núcleo de la célula, donde se replica y sintetiza el ARN mensajero.
5: El ARNm se traduce luego en nuevas proteínas virales utilizando la maquinaria celular.
6: Las partículas virales y el ARN recién replicado se llevan a la superficie de la célula y se ensamblan en viriones.
7: A medida que el nuevo virus emerge de las células epiteliales respiratorias, la hemaglutinina se une nuevamente a los receptores de ácido siálico. La neuraminidasa (NA) luego escinde la nueva partícula viral de la célula epitelial respiratoria para que pueda infectar las células cercanas.
La influenza A Influenza A Antivirals for Influenza y B crean los LOS Neisseria mismos patrones de enfermedad.
Adultos:
Niños:
El diagnóstico de la infección por influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza generalmente se hace HACE Altitude Sickness clínicamente; sin embargo, las pruebas de diagnóstico rápido pueden ser útiles si los LOS Neisseria resultados van a influir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento.
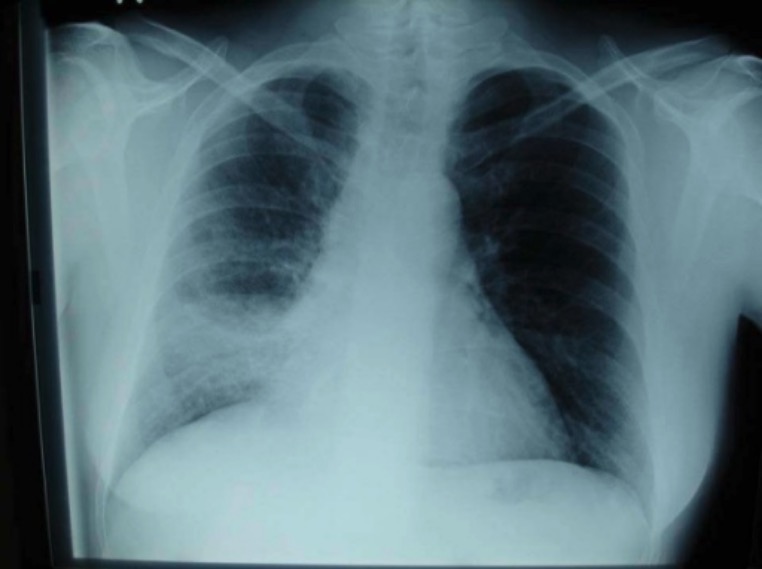
Radiografía de tórax que muestra neumonía bacteriana del lóbulo inferior derecho
Imagen: “Chest radiography” por Department of Critical Care Medicine, University Hospital Thessaly, Larissa, Greece. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Una radiografía anteroposterior en decúbito supino en un paciente intubado que muestra una consolidación en parches en ambos campos pulmonares, más prominente en el lado izquierdo debido a una neumonía nosocomial
Imagen: “AP supine radiograph” por King Fahad Hospital, King Abdulaziz Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 2.0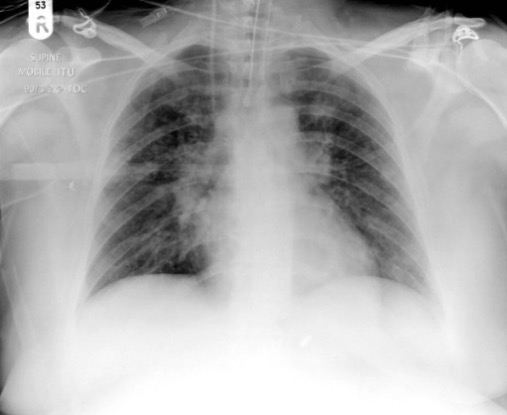
Radiografía de tórax de un paciente con neumonía viral que muestra infiltrados intersticiales bilaterales generalizados
Imagen: “Chest radiograph” por Department of Infectious Diseases, Leicester Royal Infirmary, Level 6 Windsor Building, Leicester, LE1 5WW, UK. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes solo requieren cuidados de soporte y se recuperan sin complicaciones. Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antivirales se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes hospitalizados o de alto riesgo.