El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis D Hepatitis D Inflammation of the liver in humans caused by hepatitis delta virus, a defective RNA virus that can only infect hepatitis B patients. For its viral coating, hepatitis delta virus requires the hepatitis B surface antigens produced by these patients. Hepatitis d can occur either concomitantly with (coinfection) or subsequent to (superinfection) hepatitis B infection. Similar to hepatitis b, it is primarily transmitted by parenteral exposure, such as transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products, but can also be transmitted via sexual or intimate personal contact. Hepatitis D Virus ( HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology pequeño de ARN monocatenario, envuelto. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis D Hepatitis D Inflammation of the liver in humans caused by hepatitis delta virus, a defective RNA virus that can only infect hepatitis B patients. For its viral coating, hepatitis delta virus requires the hepatitis B surface antigens produced by these patients. Hepatitis d can occur either concomitantly with (coinfection) or subsequent to (superinfection) hepatitis B infection. Similar to hepatitis b, it is primarily transmitted by parenteral exposure, such as transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products, but can also be transmitted via sexual or intimate personal contact. Hepatitis D Virus se considera un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology satélite, ya que requiere la presencia del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus ( HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) para su ensamblaje y secreción. Por lo tanto, para que un individuo contraiga la hepatitis D Hepatitis D Inflammation of the liver in humans caused by hepatitis delta virus, a defective RNA virus that can only infect hepatitis B patients. For its viral coating, hepatitis delta virus requires the hepatitis B surface antigens produced by these patients. Hepatitis d can occur either concomitantly with (coinfection) or subsequent to (superinfection) hepatitis B infection. Similar to hepatitis b, it is primarily transmitted by parenteral exposure, such as transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products, but can also be transmitted via sexual or intimate personal contact. Hepatitis D Virus, se requiere la coinfección o sobreinfección con el HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus. Al AL Amyloidosis igual que el HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus, el HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus se transmite por vía parenteral, a través de relaciones sexuales sin protección, o por vía perinatal. La presentación clínica es la de una hepatitis vírica clásica, incluida la coinfección por el HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus y el HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus, que se considera la forma más grave de hepatitis debido a la elevada tasa de mortalidad. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos agudos, el tratamiento es de apoyo, mientras que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos crónicos se necesita interferón alfa pegilado.
Last updated: Jan 17, 2024

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son positivos si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARNm.
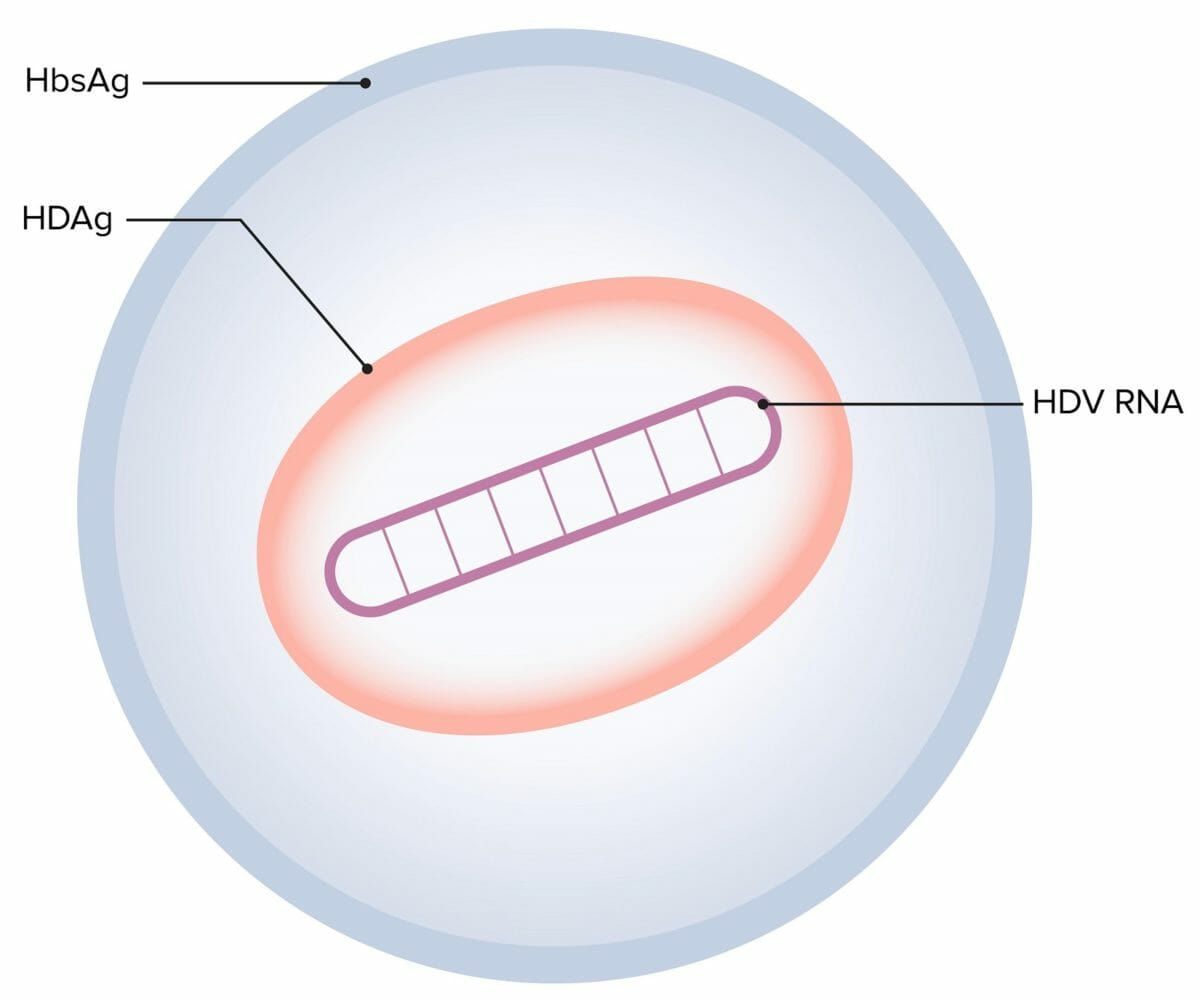
Virus de la hepatitis D (HDV):
El virión de la hepatitis D está formado por un ARN circular monocatenario (ARN del HDV), un único antígeno codificado por el HDV (HDAg) y una envoltura lipoproteica (HbsAg), que proviene del virus de la hepatitis B (HBV).
La transmisión de la hepatitis D Hepatitis D Inflammation of the liver in humans caused by hepatitis delta virus, a defective RNA virus that can only infect hepatitis B patients. For its viral coating, hepatitis delta virus requires the hepatitis B surface antigens produced by these patients. Hepatitis d can occur either concomitantly with (coinfection) or subsequent to (superinfection) hepatitis B infection. Similar to hepatitis b, it is primarily transmitted by parenteral exposure, such as transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products, but can also be transmitted via sexual or intimate personal contact. Hepatitis D Virus es similar a la de la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus.
| Marcadores séricos | Coinfección por HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus/ HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus aguda | Superinfección aguda por HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus | Infección crónica por HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg | Positivo | Positivo | Positivo |
| Anti-HBc anti-HBc Hepatitis B Virus IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | Positivo | Negativo | Negativo |
| RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure HDV HDV Hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a small enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus. Hepatitis D virus is considered a satellite virus, as it requires the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) for assembly and secretion. Therefore, in order for an individual to contract hepatitis D, coinfection or superinfection with HBV is required. Hepatitis D Virus sérico | Temprano, transitorio | Temprano, persistente | Positivo |
| HDAg sérico* | Positivo (transitorio) | Positivo (transitorio) | Negativo |
| Anti-HDV IgM Anti-HDV IgM Hepatitis D Virus | Positivo (transitorio) | Positivo (persistente y títulos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum incremento) | Positivo (títulos altos) |
| Anti-HDV IgG Anti-HDV IgG Hepatitis D Virus | Positivo (tardío) | Positivo (tardío) | Positivo (títulos altos) |
Anti-HBc antibodies: anticuerpos del núcleo de la hepatitis B
Anti-HBs antibodies: anticuerpos de superficie contra la hepatitis B
HBcAg: antígeno del núcleo de la hepatitis B
HBsAg: antígeno de superficie de la hepatitis B
HBV: virus de la hepatitis B
HCC: carcinoma hepatocelular
HCV: virus de la hepatitis C
HDV: virus de la hepatitis D