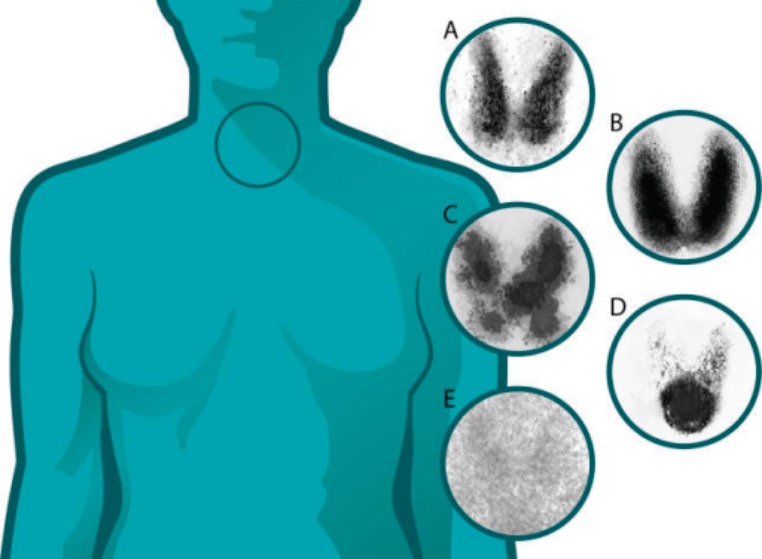
La tiroiditis de Hashimoto, o tiroiditis linfocítica crónica, es la causa más común de hipotiroidismo en las regiones donde el aporte de yodo es suficiente. Se trata de un trastorno autoinmune que conduce a la destrucción de las células tiroideas y a la insuficiencia tiroidea. El curso clínico progresivo de la tiroiditis de Hashimoto comienza con un estado hipertiroideo transitorio ("hashitoxicosis") seguido de hipotiroidismo subclínico. Con el tiempo, se produce una progresión hacia el hipotiroidismo clínico, que es permanente. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden tener un bocio indoloro, pero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum etapas posteriores, la glándula es atrófica. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante pruebas de laboratorio que muestran una elevación de la hormona estimulante del tiroides (TSH), un nivel bajo de tiroxina libre ( T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones) y anticuerpos positivos contra la tiroglobulina y la peroxidasa tiroidea. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos dudosos, se requiere la realización de imágenes. La captación de yodo radiactivo mostrará una baja captación de yodo y el ultrasonido demuestra un agrandamiento simétrico difuso. La biopsia muestra una infiltración linfocítica con células de Hurthle. El tratamiento es la sustitución de la hormona tiroidea de por vida.
Last updated: Jan 18, 2026
La tiroiditis de Hashimoto es una enfermedad tiroidea autoinmune que provoca la destrucción y el fallo de la glándula tiroidea.
Se desconoce la causa exacta, aunque los LOS Neisseria factores genéticos y ambientales desempeñan un papel importante:
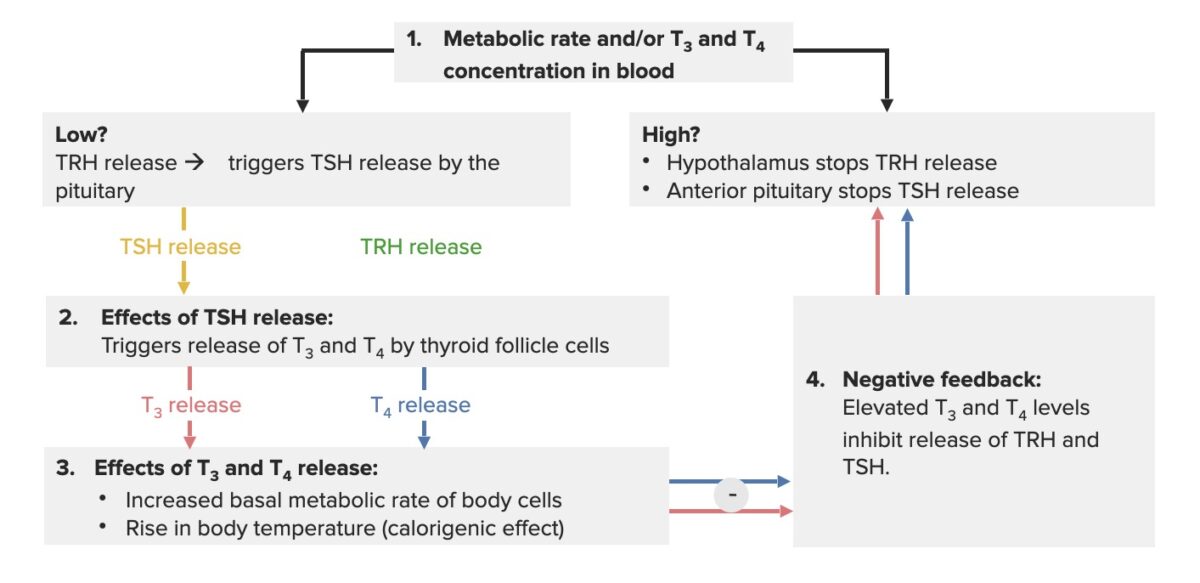
Cuando se induce la autoinmunidad tiroidea, se produce un agotamiento progresivo de las células epiteliales tiroideas.
Destrucción de células tiroideas mediada por:
Infiltración linfocítica y fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans de las células tiroideas → los LOS Neisseria folículos se rompen y liberan hormonas tiroideas:
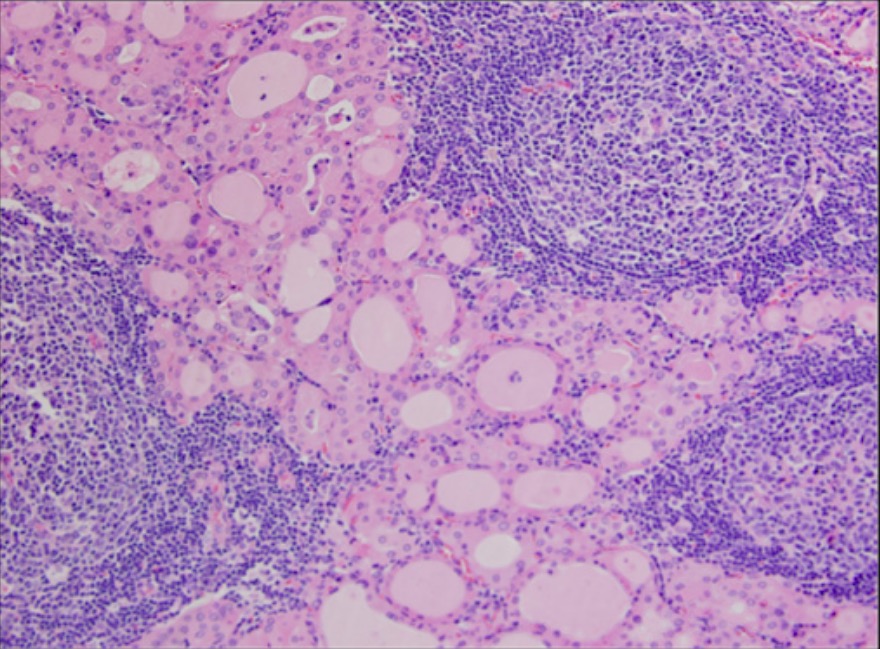
Respuesta inmunológica vista histológicamente como:
Destrucción de células tiroideas:
Síntomas comunes del hipotiroidismo:
Signos comunes del hipotiroidismo: