Staphylococcus Staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a medically important genera of Gram-positive, aerobic cocci. These bacteria form clusters resembling grapes on culture plates. Staphylococci are ubiquitous for humans, and many strains compose the normal skin flora. Staphylococcus es un género de cocos anaeróbicos facultativos y grampositivos de importancia médica. Estas bacterias forman racimos que se asemejan a las uvas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las placas de cultivo. Los LOS Neisseria estafilococos son ubicuos para los LOS Neisseria humanos y muchas cepas componen la flora cutánea normal. Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess es la especie más virulenta; S. epidermidis S. epidermidis A species of staphylococcus that is a spherical, non-motile, gram-positive, chemoorganotrophic, facultative anaerobe. Mainly found on the skin and mucous membrane of warm-blooded animals, it can be primary pathogen or secondary invader. Staphylococcus y S. saprophyticus S. saprophyticus A species of gram-positive bacteria in the family staphylococcaceae. It commonly causes urinary tract infections in humans. Staphylococcus son menos virulentos, pero también clínicamente significativos. La infección por Staphylococcus Staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a medically important genera of Gram-positive, aerobic cocci. These bacteria form clusters resembling grapes on culture plates. Staphylococci are ubiquitous for humans, and many strains compose the normal skin flora. Staphylococcus puede causar una amplia gama de enfermedades, que incluyen celulitis, abscesos, endocarditis Endocarditis Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease involving the inner lining (endometrium) of the heart, most commonly affecting the cardiac valves. Both infectious and noninfectious etiologies lead to vegetations on the valve leaflets. Patients may present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever and fatigue. Endocarditis, osteomielitis e infecciones por dispositivos médicos. Las toxinas formadas por S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus pueden causar gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis, síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos y síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico. El tratamiento con antibióticos varía según el tipo de infección, la gravedad y los LOS Neisseria datos sobre la sensibilidad.
Last updated: Jan 29, 2026
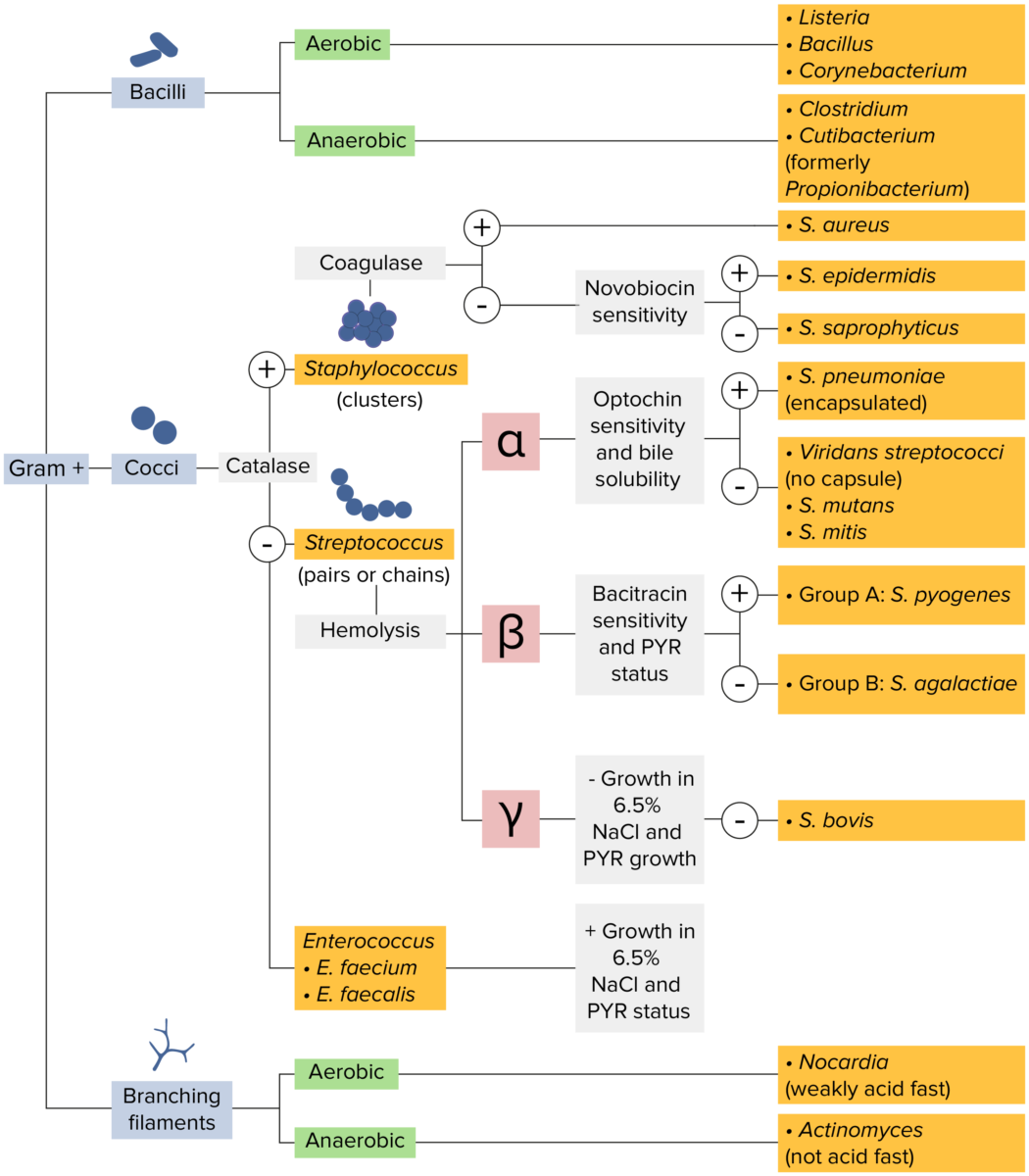
Bacterias gram-positivas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo con un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa gruesa de peptidoglicano retienen la tinción cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram, pero no se ven afectadas por la contratinción de safranina. Estas bacterias aparecen como azul púrpura en la tinción, lo que indica que son gram-positivas. Las bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (filamentos ramificados, bacilos y cocos en grupos o cadenas) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos versus anaeróbicos). Los cocos también pueden identificarse con mayor profundidad. Los estafilococos pueden reducirse en función de la presencia de la enzima coagulasa y de su sensibilidad al antibiótico novobiocina. Los estreptococos se cultivan en agar sangre y se clasifican según la forma de hemólisis que emplean (α, β o γ). Los estreptococos se reducen aún más en función de su respuesta a la prueba de pirrolidonil-β-naftilamida, su sensibilidad a antimicrobianos específicos (optoquina y bacitracina) y su capacidad para crecer en medios de cloruro de sodio (NaCl).
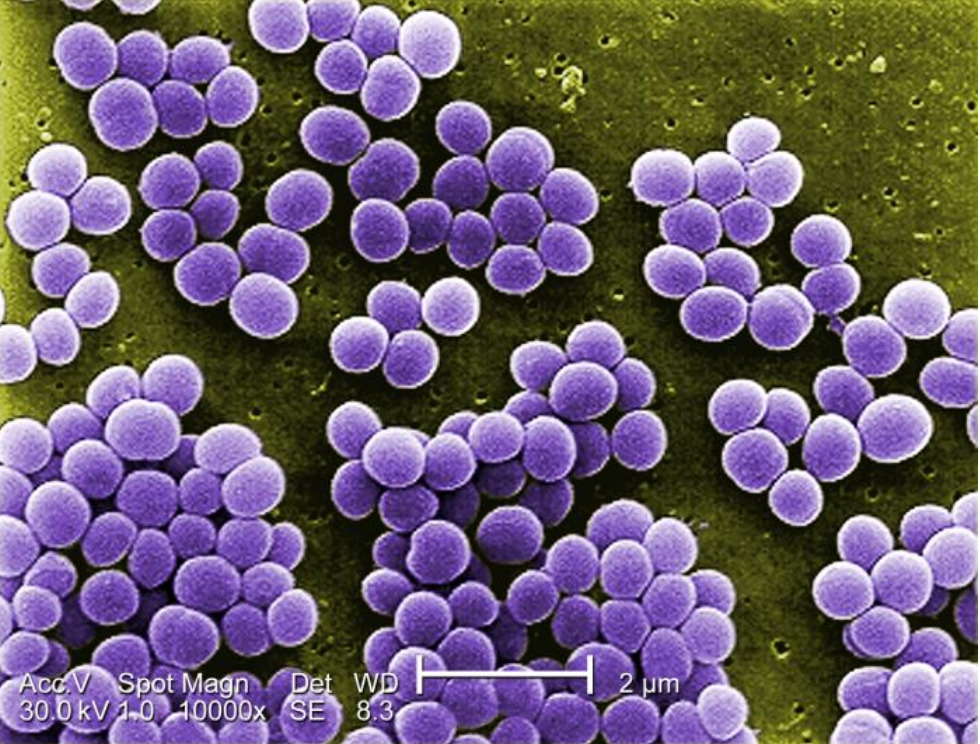
Imagen de microscopio electrónico de barrido coloreada digitalmente con un aumento de 10 000X de Staphylococcus aureus:
Obsérvese que estos cocos se asemejan a un “racimo de uvas”.
Las especies clínicamente relevantes se pueden clasificar según la presencia (o ausencia) de coagulasa:
| Especies | Coagulasa | Agar sangre | Agar manitol salado | Novobiocina * sensibilidad |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus | Positivo | Beta-hemólisis | Colonias amarillas | Sensible |
| S. epidermidis S. epidermidis A species of staphylococcus that is a spherical, non-motile, gram-positive, chemoorganotrophic, facultative anaerobe. Mainly found on the skin and mucous membrane of warm-blooded animals, it can be primary pathogen or secondary invader. Staphylococcus | Negativo | No hemolítico | Colonias rosadas o rojas | Sensible |
| S. saprophyticus S. saprophyticus A species of gram-positive bacteria in the family staphylococcaceae. It commonly causes urinary tract infections in humans. Staphylococcus | Negativo | No hemolítico | Colonias amarillas o rojas (dependiendo de la cepa) | Resistente |
Staphylococcus aureus resistente a la meticilina (MRSA, por sus siglas en inglés):
El S. aureus coagulasa positivo fermenta manitol (rojo), produciendo colonias amarillas en placas de agar con sal de manitol.
Las especies de Staphylococcus Staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a medically important genera of Gram-positive, aerobic cocci. These bacteria form clusters resembling grapes on culture plates. Staphylococci are ubiquitous for humans, and many strains compose the normal skin flora. Staphylococcus forman parte de la flora humana normal:
Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess se puede transmitir a través de aerosoles y el contacto con:
Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo de infección grave por Staphylococcus Staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a medically important genera of Gram-positive, aerobic cocci. These bacteria form clusters resembling grapes on culture plates. Staphylococci are ubiquitous for humans, and many strains compose the normal skin flora. Staphylococcus incluyen:
Comunes a la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria estafilococos:
Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess:
Estafilococos coagulasa negativos:
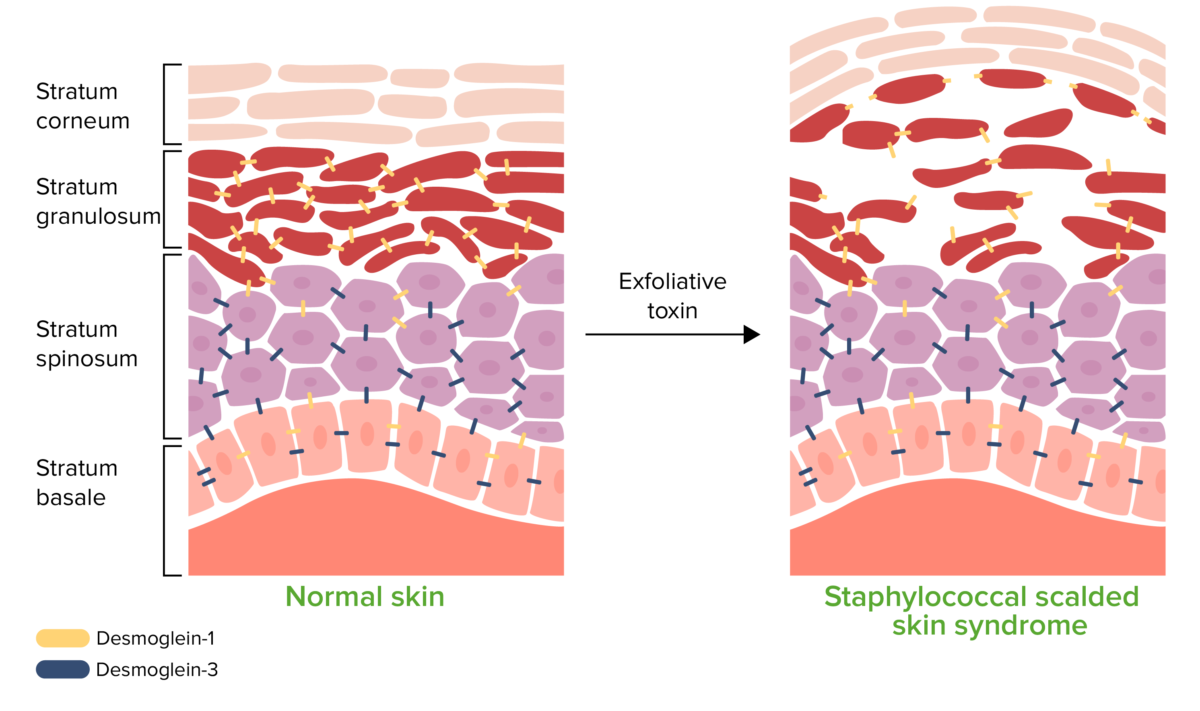
Fisiopatología del síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos:
La toxina exfoliativa escinde la desmogleína (Dsg) 1, interrumpiendo la adhesión de célula a célula del estrato granuloso. Este desprendimiento de la epidermis superficial provoca la formación de ampollas y descamación.
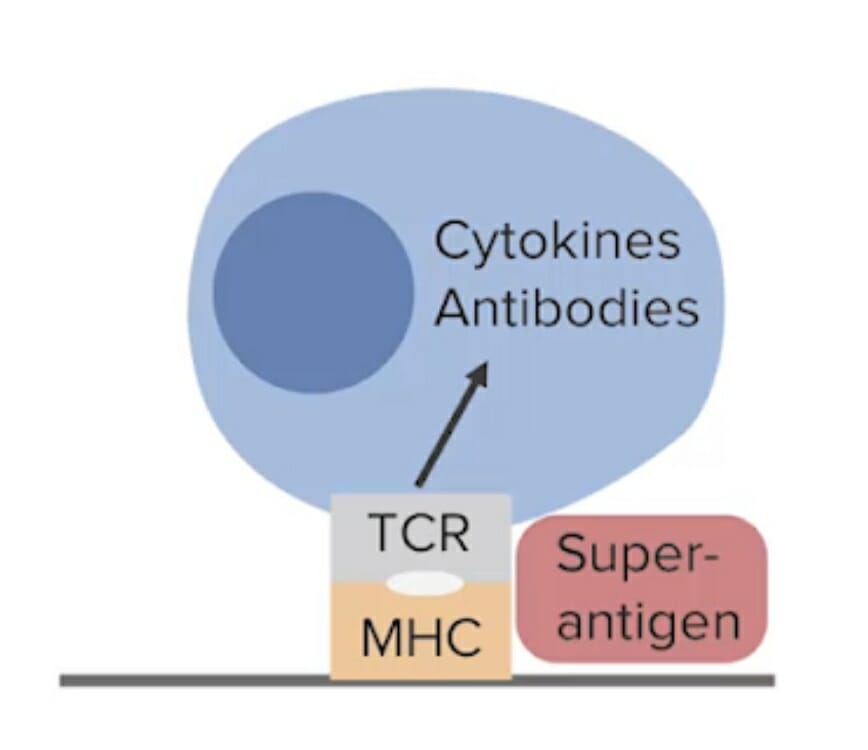
Los superantígenos se unen a los receptores de linfocitos T del complejo mayor de histocompatibilidad (CMH) de clase II, que estimulan una exagerada liberación de citocinas y respuesta inflamatoria. Esto incluye la toxina del síndrome de shock tóxico tipo 1, que puede ser producida por Staphylococcus aureus.
Imagen por Lecturio.Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess puede causar una amplia gama de infecciones, que incluyen (pero no se limitan a):
Impétigo no ampolloso con costra en la extremidad superior de un paciente pediátrico
Imagen: “Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis: Mimics, Overlaps, and Complications” por Siegfried EC, Hebert AA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0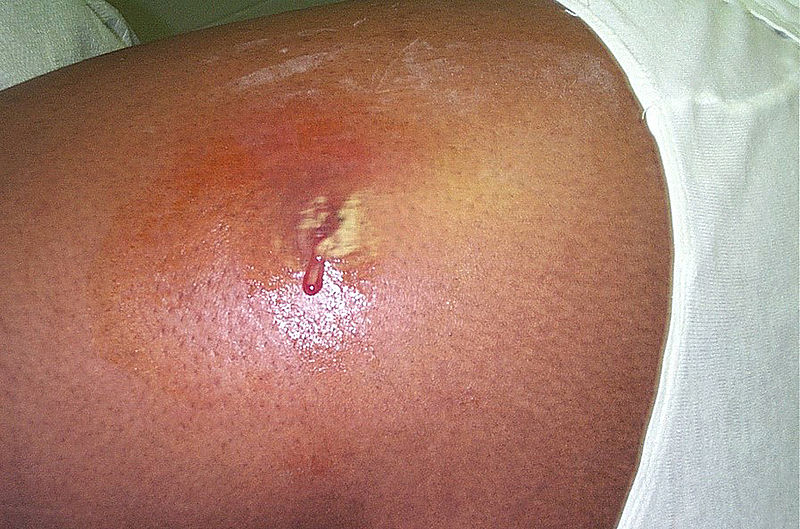
Absceso cutáneo causado por MRSA
Imagen: “Cutaneous abscess MRSA” por CDC/Bruno Coignard, MD Licencia: Dominio Público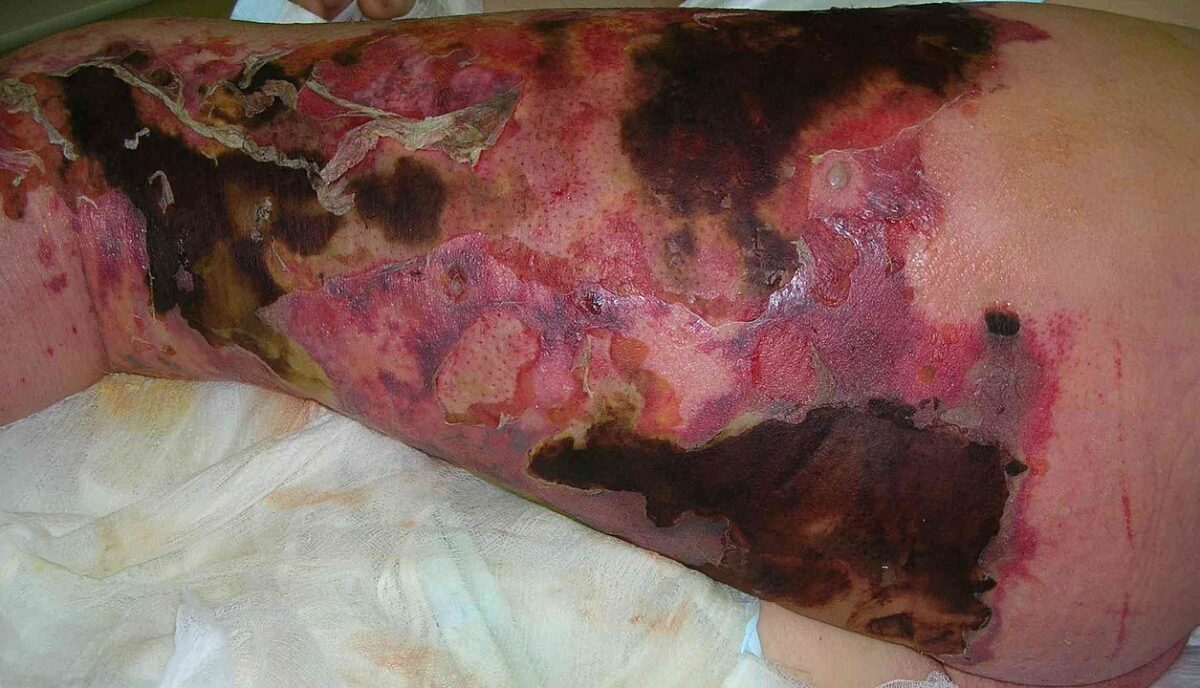
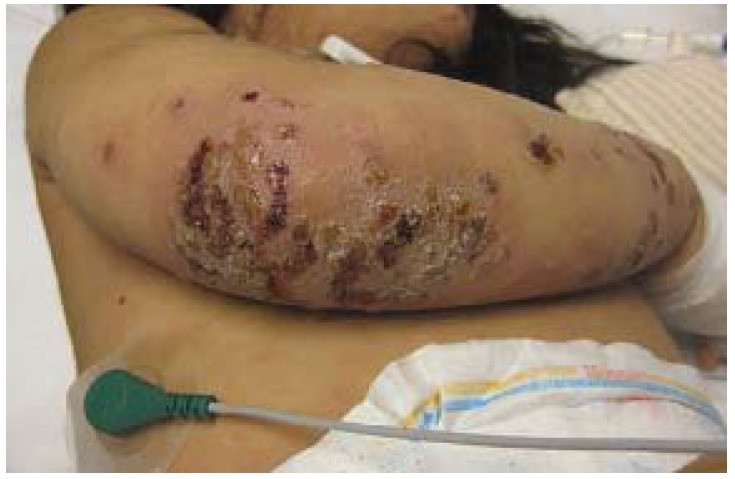
Extremidad inferior con áreas de necrosis, eritema y cambios ampollosos, que se observan comúnmente en la fascitis necrosante.
Imagen: “Necrotizing fasciitis left leg” por Piotr Smuszkiewicz, Iwona Trojanowska y Hanna Tomczak. Licencia: CC BY 2.0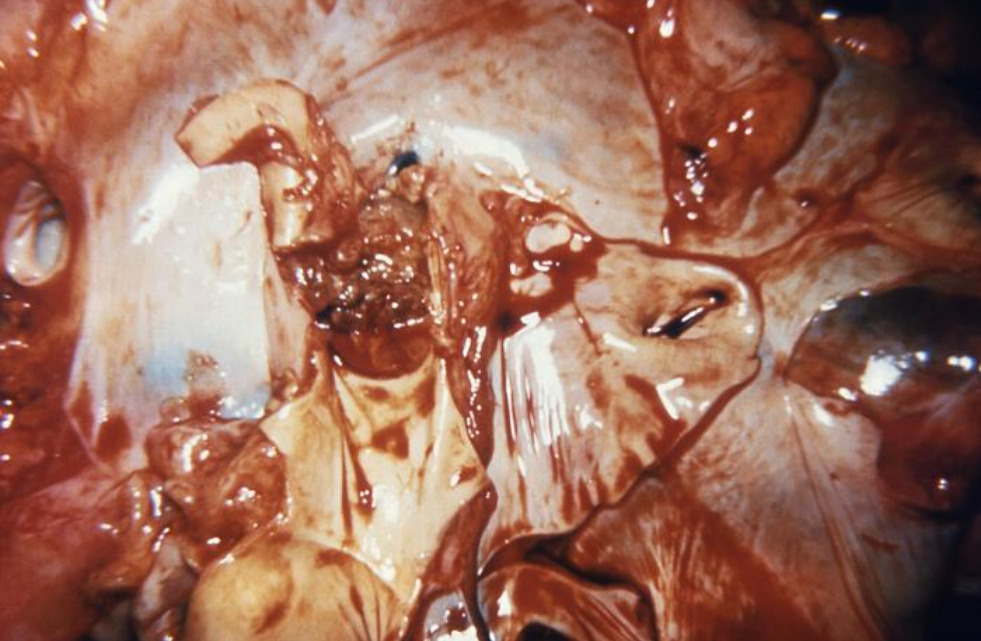
Endocarditis bacteriana: obstrucción de la válvula pulmonar de un corazón por una vegetación bacteriana, que se observa aquí durante la autopsia
Imagen: “Bacterial endocarditis” por CDC/Dr. Sellers. Licencia: Dominio Público| Enfermedad | Exotoxina | Presentación clínica |
|---|---|---|
| Síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos | Toxinas exfoliativas A y B |
|
| Síndrome de shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock tóxico | Toxina del síndrome de
shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed.
Types of Shock tóxico tipo 1 Enterotoxina B |
|
| Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the stomach and intestines, commonly caused by infections from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Transmission may be foodborne, fecal-oral, or through animal contact. Common clinical features include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis | Enterotoxinas |
|
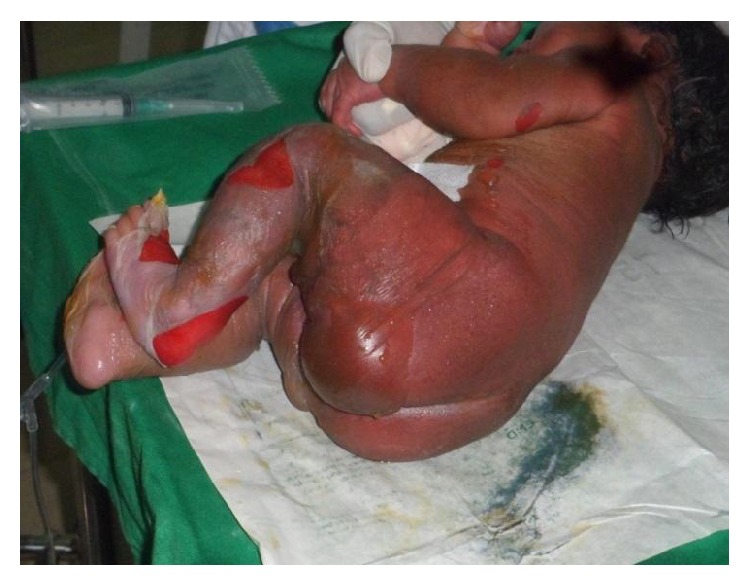
Síndrome de piel escaldada por estafilococos en un recién nacido:
Esta imagen muestra eritema difuso, formación de ampollas y descamación de la piel.
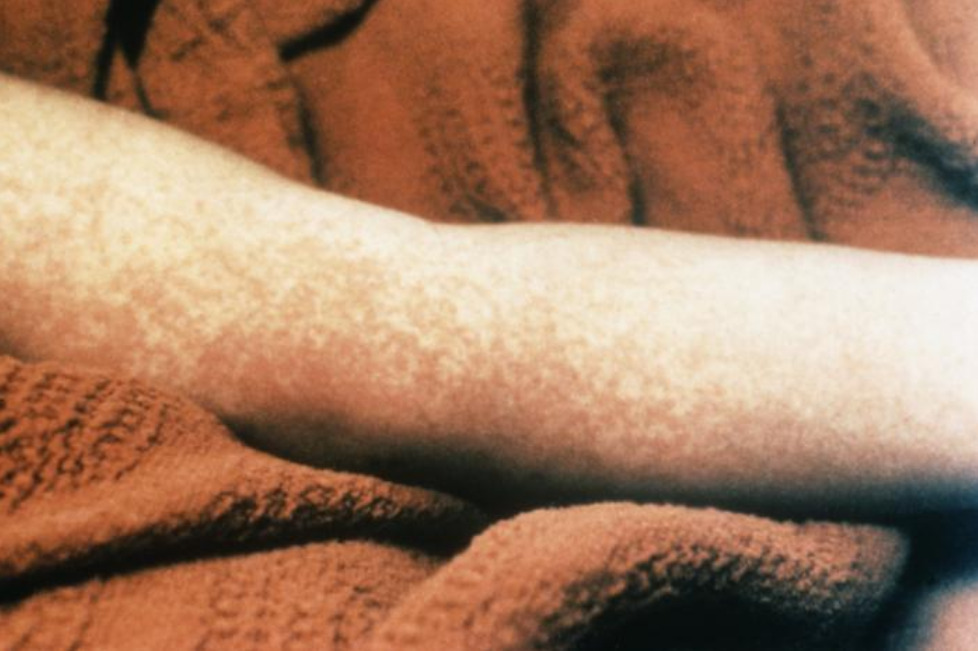
Erupción morbiliforme por síndrome de shock tóxico
Imagen: “Morbilliform rash (resembling measles) resulting from toxic shock syndrome” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria estafilococos coagulasa negativos pueden causar muchas de las mismas afecciones que S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus. Las infecciones notables incluyen:
Las especies de Staphylococcus Staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a medically important genera of Gram-positive, aerobic cocci. These bacteria form clusters resembling grapes on culture plates. Staphylococci are ubiquitous for humans, and many strains compose the normal skin flora. Staphylococcus pueden desarrollar resistencia a los LOS Neisseria antibióticos y la identificación de la susceptibilidad es necesaria para un tratamiento adecuado. Las especies a menudo se designan como:

La proteína de unión a penicilina forma puentes entrecruzados entre cadenas de peptidoglicano adyacentes durante la síntesis de la pared celular bacteriana. Un antibiótico beta-lactámico se une e inhibe irreversiblemente la proteína de unión de penicilina, evitando que forme nuevos enlaces cruzados. Esto inhibe eficazmente una mayor síntesis de la pared celular, lo que finalmente conduce a la muerte celular. Las alteraciones en las proteínas de unión de penicilina son las que confieren resistencia estafilocócica a los antibióticos de penicilinas, como la meticilina.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0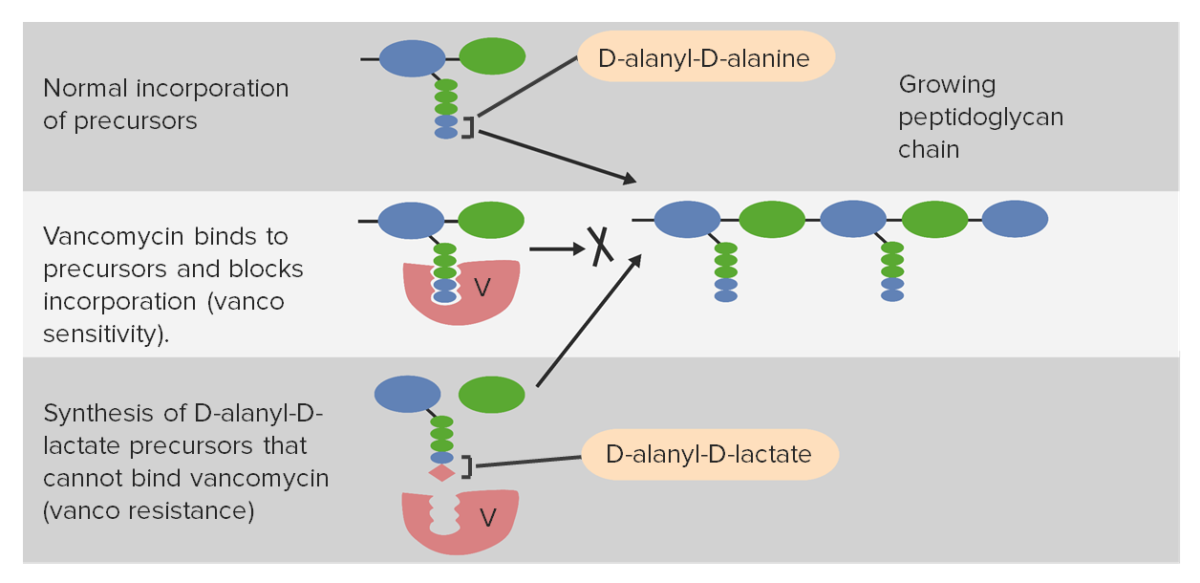
Resistencia a la vancomicina:
La síntesis de D-alanil-D-lactato en precursores de peptidoglicano en la pared celular provoca una unión deficiente con la vancomicina, lo que reduce la eficacia del antibiótico.
El agente de elección y la duración del tratamiento para la infección por Staphylococcus Staphylococcus Staphylococcus is a medically important genera of Gram-positive, aerobic cocci. These bacteria form clusters resembling grapes on culture plates. Staphylococci are ubiquitous for humans, and many strains compose the normal skin flora. Staphylococcus dependen del área del cuerpo afectada, la gravedad de la infección y la sensibilidad a los LOS Neisseria antibióticos de la cepa.
| Cepa | Antibiótico |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess sensible a la meticilina (MSSA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y estafilococos coagulasa negativos |
|
| MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus |
|
| Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess resistente a la vancomicina |
|