El síndrome de Williams, también conocido como síndrome de Williams-Beuren, es una enfermedad genética causada por una microdeleción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma 7. Los LOS Neisseria individuos afectados tienen una característica facies de elfo y baja estatura. Los LOS Neisseria problemas cognitivos, de desarrollo y de comportamiento son comunes. Además, puede haber anomalías cardiovasculares, del tejido conectivo, endócrinas y renales. Las pruebas genéticas confirman el diagnóstico. El tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las manifestaciones clínicas. La afectación cardiovascular debe seguirse de cerca porque es la principal causa de mortalidad.
Last updated: Jan 24, 2025
La incidencia del síndrome de Williams es de 1 por cada 7 500–20 000 nacidos vivos.
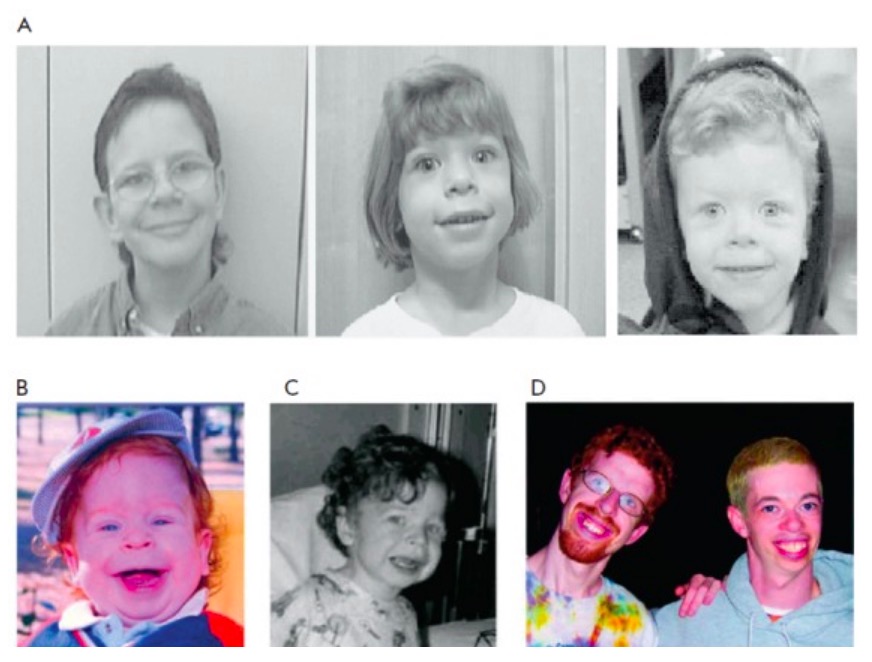
Rasgos faciales del síndrome de Williams
A: aspecto facial distintivo de los individuos con el síndrome de Williams
B y C: un niño pequeño con síndrome de Williams a la edad de 15 meses y 3 años (nótese los sutiles rasgos faciales característicos, como la boca ancha, las mejillas prominentes, el largo surco nasolabial, la nariz pequeña y el delicado mentón)
El mismo paciente se muestra en las Figs. B, C y D (izquierda; a los 21 años de edad); otro individuo con sindrome de Williams de 28 años se muestra en la Fig. D a la derecha.
Las cardiopatías congénitas están presentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 80%–90% de los LOS Neisseria casos de síndrome de Williams y son una de las principales causas de morbilidad y mortalidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pacientes con síndrome de Williams. El riesgo de muerte súbita cardíaca es entre 25–100 veces mayor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pacientes con síndrome de Williams.
El tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las manifestaciones clínicas presentes y está dirigido a mejorar la calidad de vida y a tratar las afecciones asociadas.