El síndrome de Edwards, o trisomía 18, es un síndrome genético causado por la presencia de un cromosoma 18 adicional. El cromosoma extra proviene de 3 copias completas del cromosoma 18 o de un segmento adicional del cromosoma 18. Siendo la 2da trisomía más común, el síndrome de Edwards se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 1 de cada 5 500 nacidos vivos y aumenta con la edad materna. Muchos casos se detectan prenatalmente con el tamizaje materno y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ultrasonido. Entre las anomalías se encuentran la restricción del crecimiento intrauterino (RCIU), los LOS Neisseria dedos superpuestos, los LOS Neisseria rasgos craneofaciales típicos, los LOS Neisseria pies en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de balancín y los LOS Neisseria defectos cardíacos congénitos. La trisomía 18 suele provocar la pérdida del feto. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria embarazos a término, la mayoría de las muertes se producen durante los LOS Neisseria 1os 6 meses de vida. Se recomienda el parto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un centro especializado para los LOS Neisseria embarazos a término y la intervención se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las anomalías asociadas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome de Edwards, o trisomía 18, se define como la presencia de 3 copias del cromosoma 18.
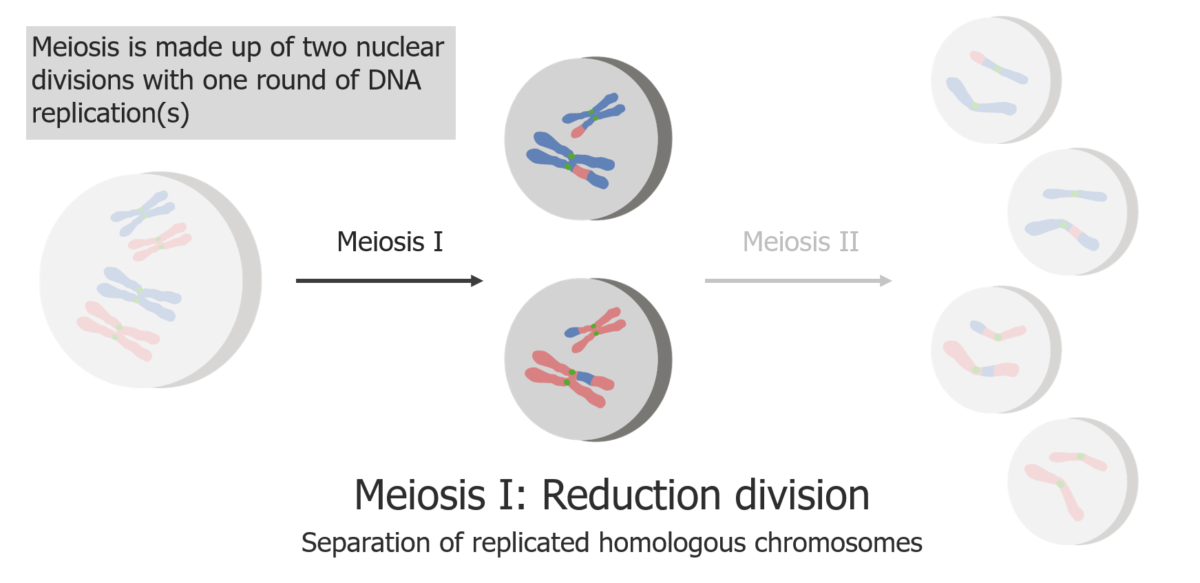
La meiosis I consiste en la separación de las cromátidas hermanas replicadas.
Imagen por Lecturio.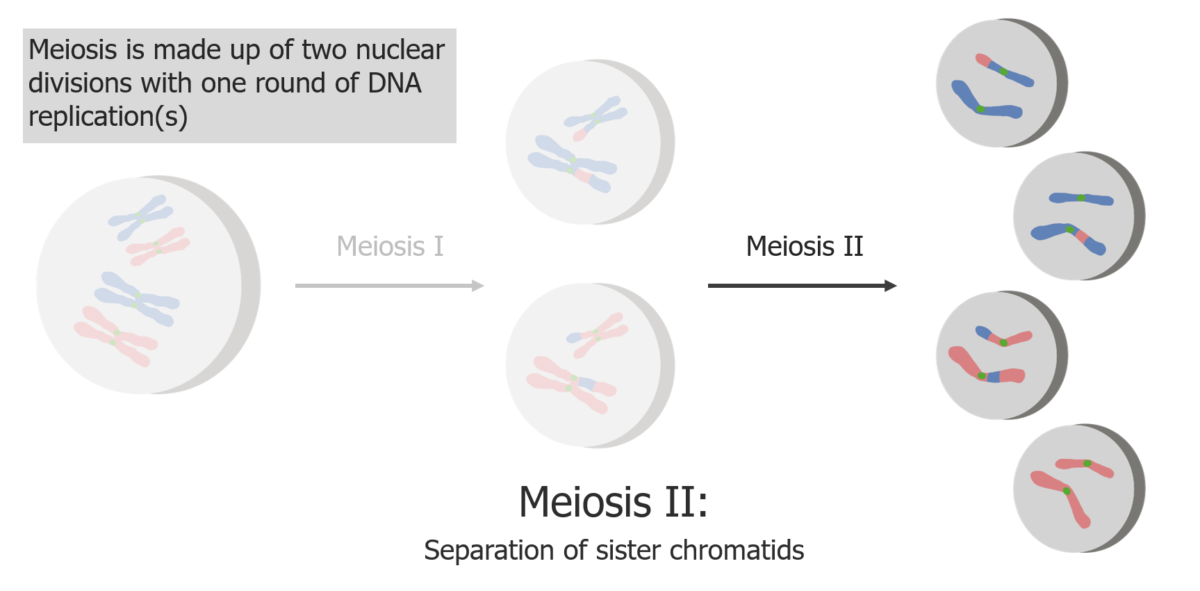
La meiosis II consiste en la separación de las cromátidas hermanas, produciendo 4 células/gametos haploides.
Imagen por Lecturio.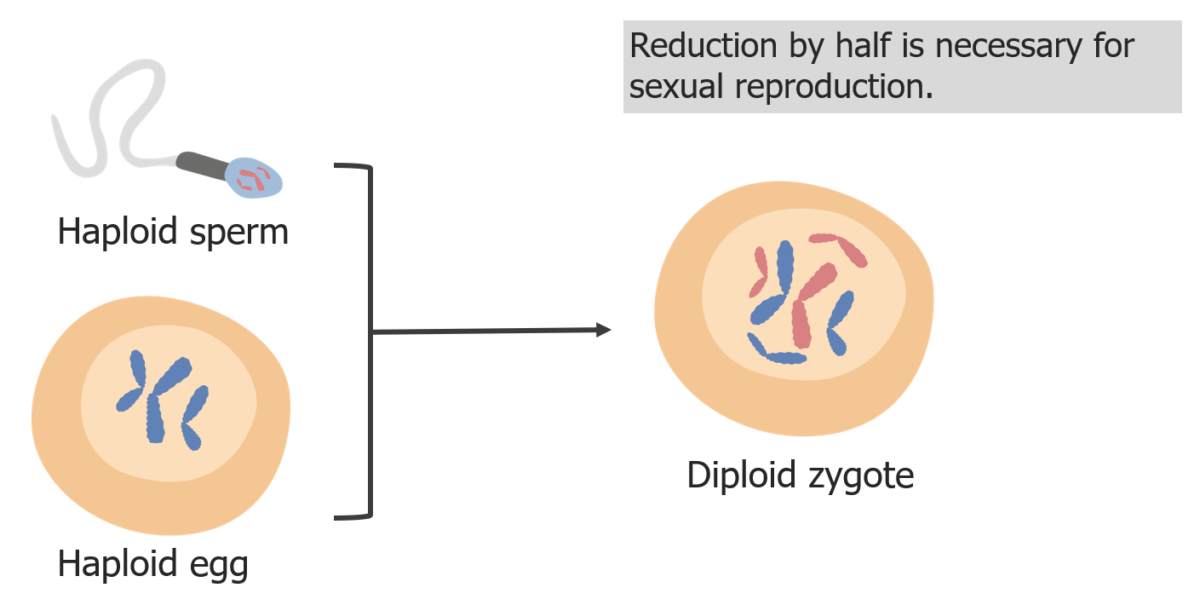
La reducción de los cromosomas es necesaria para que el cigoto sea diploide en la fecundación.
Imagen por Lecturio.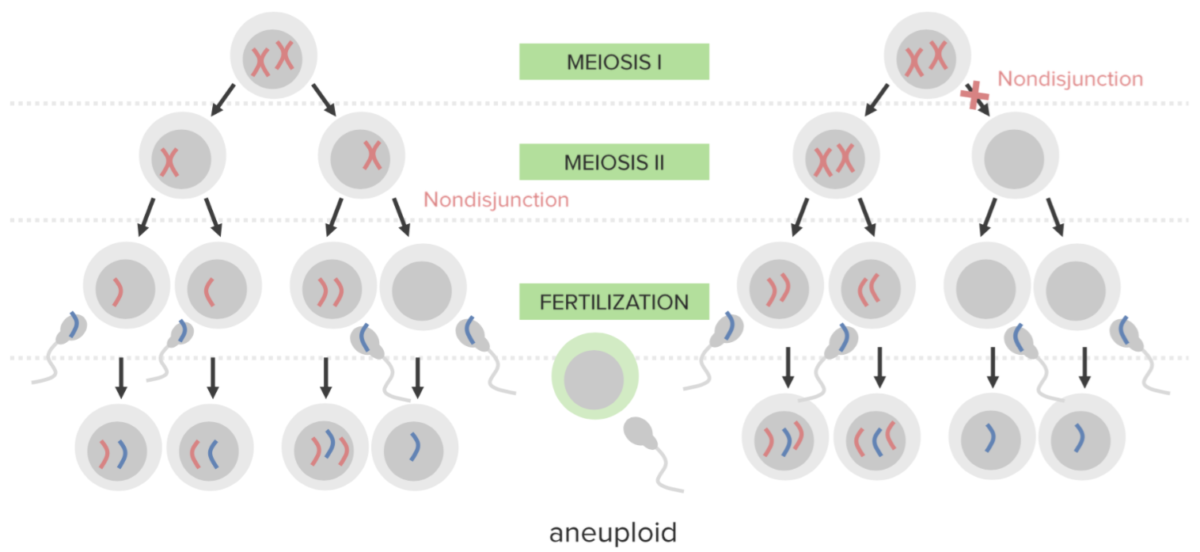
La no disyunción:
La falta de separación adecuada de 2 cromosomas homólogos o cromátidas hermanas durante la división celular. La no disyunción da lugar a la aneuploidía (un estado de desequilibrio cromosómico).
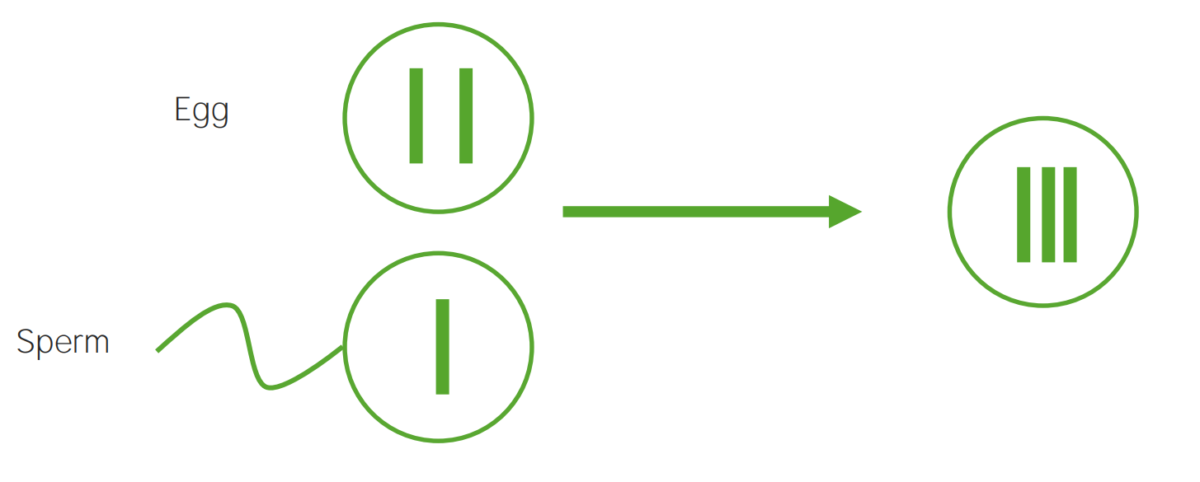
Diagrama que ilustra el mecanismo etiológico de la no disyunción en la trisomía:
Un óvulo que lleva 2 copias del mismo cromosoma adquiere otro al ser fecundado, lo que da lugar a 3 copias.
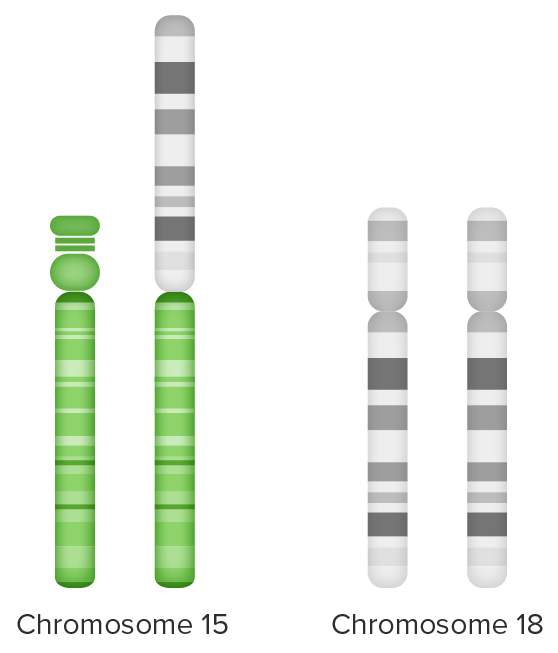
Translocación desequilibrada:
Material extra del cromosoma 18 (brazo largo) unido al cromosoma 15 (a la izquierda) y
trisomía parcial 18 de 2 juegos de cromosomas 18 + brazo extra largo del cromosoma 18 (a la derecha)
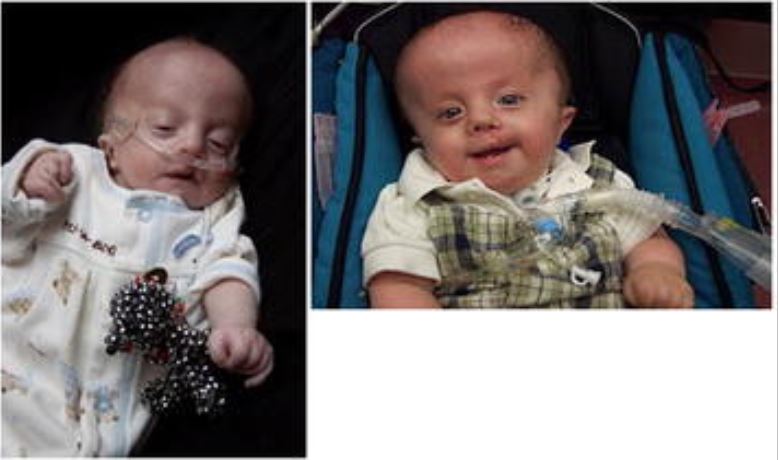
Niño con trisomía 18 en la primera infancia y al año de edad:
Obsérvese el rasgo característico de la mano, con los dedos cabalgados y la traqueotomía en su sitio.
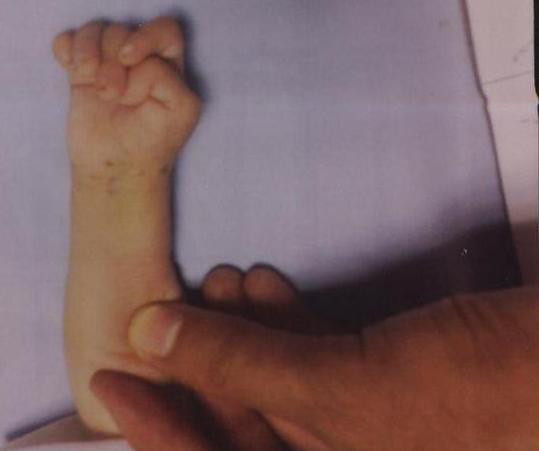
Bebé con trisomía 18 y dedos superpuestos
Imagen: “Congenital hydrocephalus in an Egyptian baby with trisomy 18: a case report” por Metwalley KA, Farghalley HS, Abd-Elsayed AA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0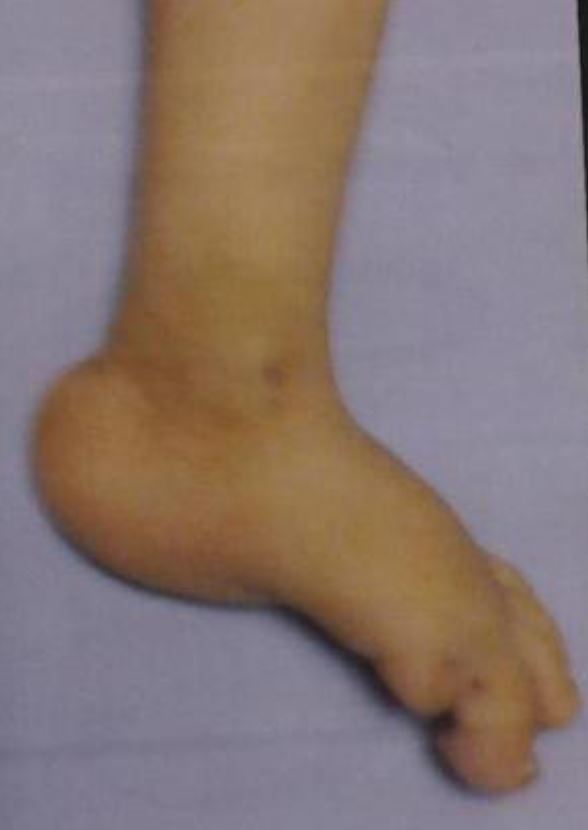
Bebé con trisomía 18 y pies de balancín (un hallazgo común)
Imagen: “Congenital hydrocephalus in an Egyptian baby with trisomy 18: a case report” por Metwalley KA, Farghalley HS, Abd-Elsayed AA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0| 1er trimestre | 2do trimestre | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | PAPP-A | hCG | AFP AFP The first alpha-globulins to appear in mammalian sera during fetal development and the dominant serum proteins in early embryonic life. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases | Estriol Estriol A hydroxylated metabolite of estradiol or estrogen that has a hydroxyl group at C3, 16-alpha, and 17-beta position. Estriol is a major urinary estrogen. During pregnancy, a large amount of estriol is produced by the placenta. Isomers with inversion of the hydroxyl group or groups are called epiestriol. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins | hCG | Inhibina A | |
| Trisomía 13 | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | Sin cambios | Sin cambios | Sin cambios | Sin cambios |
| Trisomía 18 | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | Sin cambios |
| Trisomía 21 | ↑↑ | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
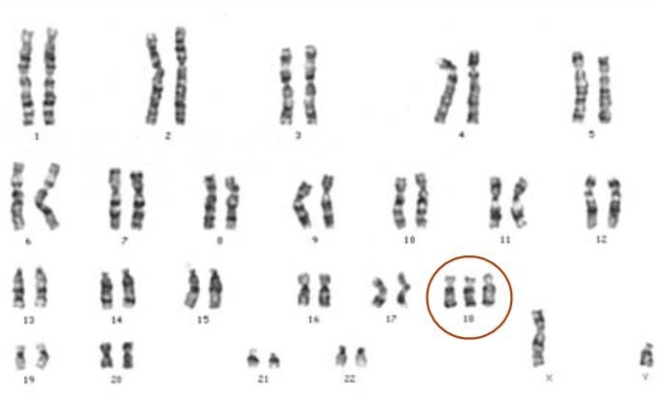
Cariotipo de una persona afectada por el síndrome de Edward:
Se observan tres copias del cromosoma 18