La regurgitación aórtica (RA) es una afección cardíaca que se caracteriza por el reflujo de sangre desde la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy hacia el ventrículo izquierdo durante la diástole. La regurgitación aórtica esta asociada con una válvula aórtica y/o una raíz aórtica anormales originadas por múltiples causas, principalmente la cardiopatía reumática, así como trastornos valvulares congénitos y degenerativos. La insuficiencia valvular aguda, la cual rápidamente progresa a shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock cardiogénico, es una emergencia que requiere cirugía valvular aórtica inmediata. La RA crónica evoluciona de forma gradual, permitiendo que el ventrículo izquierdo se adapte al AL Amyloidosis aumento del volumen sistólico. De esta manera, el ecocardiograma muestra hipertrofia y dilatación del ventrículo izquierdo acompañado de anomalías valvulares. Eventualmente, ocurre una insuficiencia cardíaca cuando el ventrículo izquierdo no es capaz de soportar la sobrecarga hemodinámica. El reemplazo de la válvula aórtica es el pilar del tratamiento para la RA con disfunción ventricular izquierda.
Last updated: Jan 16, 2024
Regurgitación aórtica (RA) o insuficiencia aórtica:
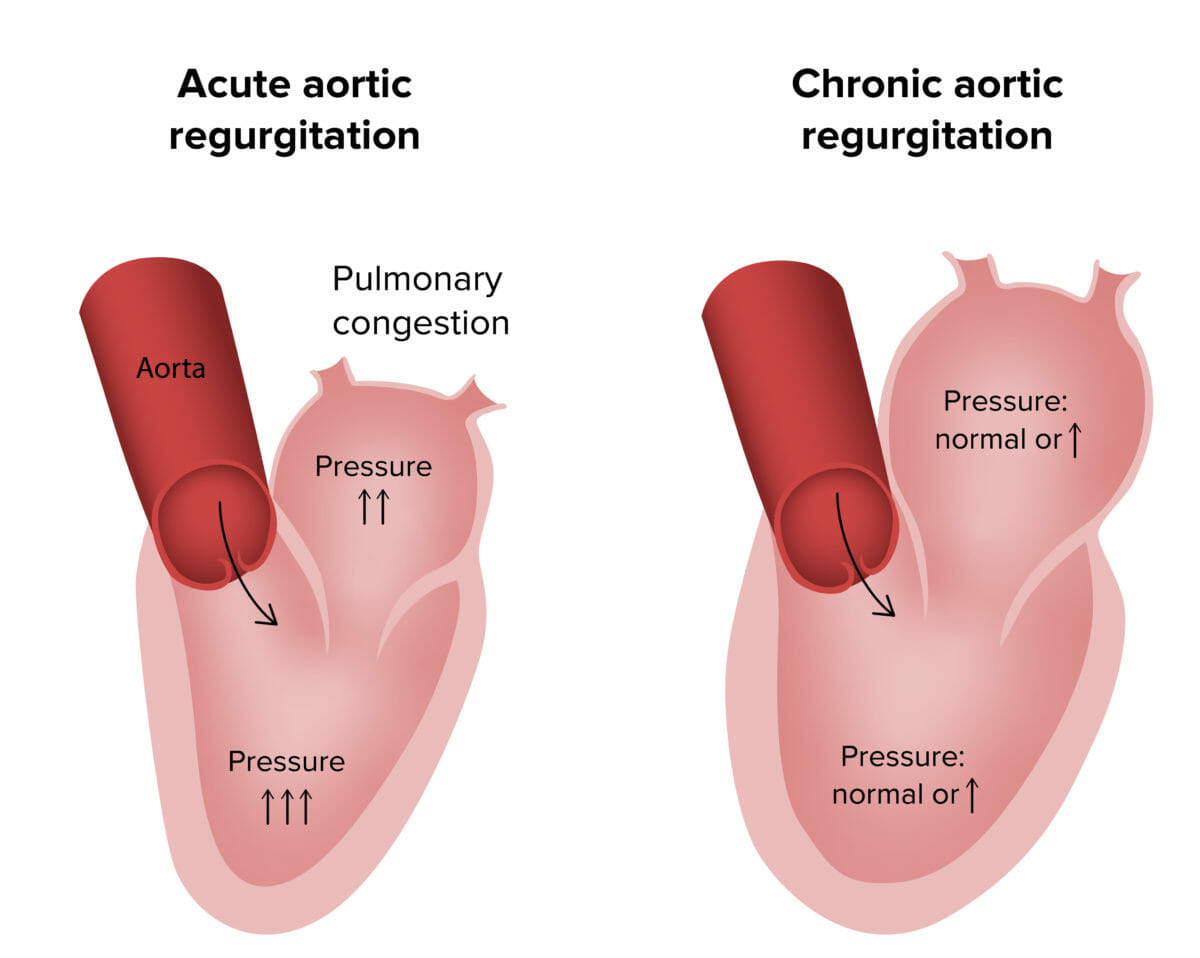
Fisiopatología de la regurgitación aórtica aguda y crónica
Imagen por Lecturio.Síntomas:
Signos:
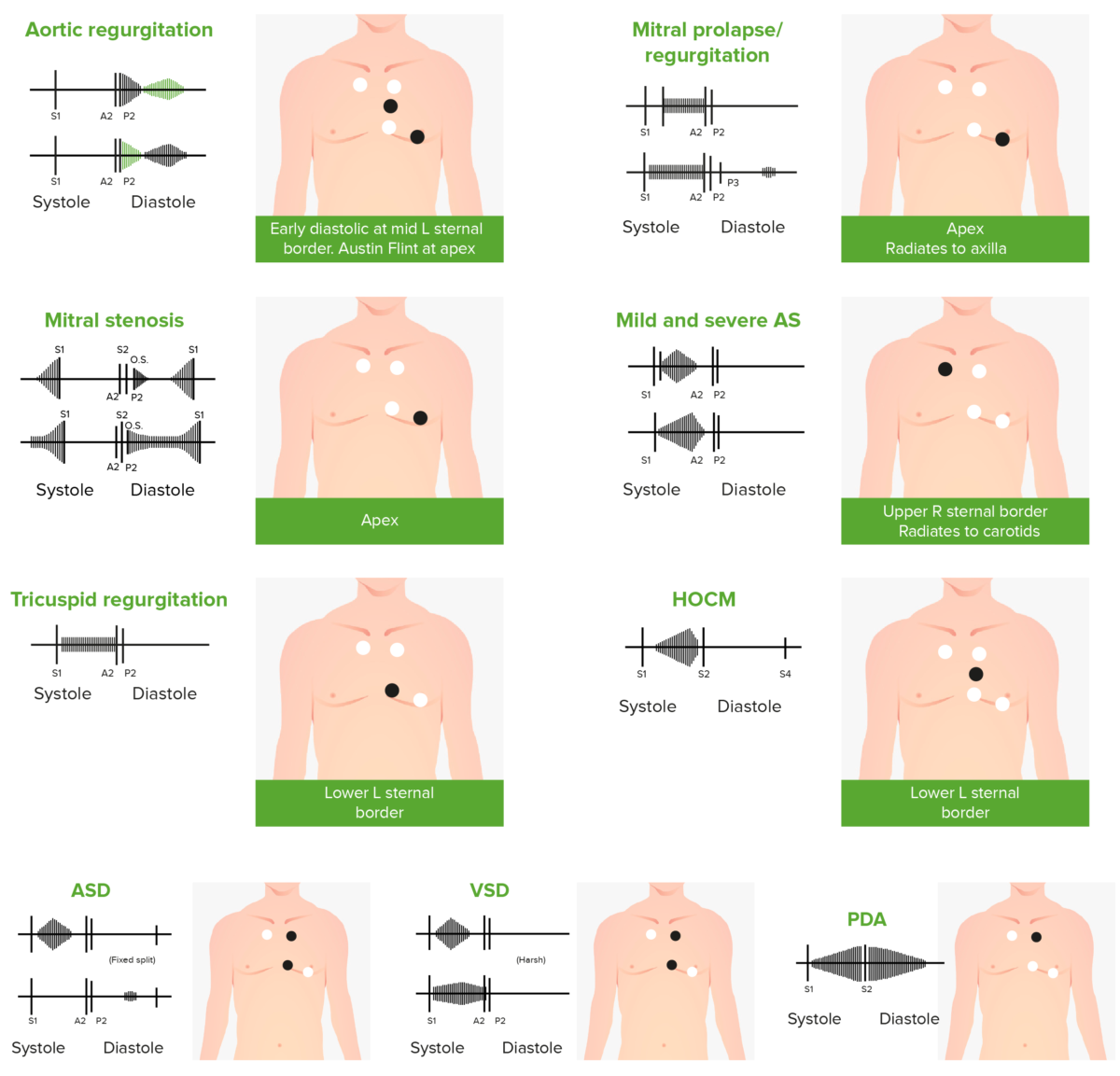
Fonocardiogramas de sonidos cardíacos anormales causados por los siguientes defectos cardíacos:
insuficiencia aórtica, prolapso de la válvula mitral, estenosis mitral (EM), estenosis aórtica (EA), insuficiencia tricuspídea, miocardiopatía hipertrófica obstructiva (MHTO), comunicación interauricular (CIA), comunicación interventricular (CIV) y conducto arterioso persistente (CAP)
Audio:
Este clip de audio es un ejemplo de insuficiencia aórtica. La cual se caracteriza por un soplo decrescendo que aparece justo después de S2 S2 Heart Sounds.
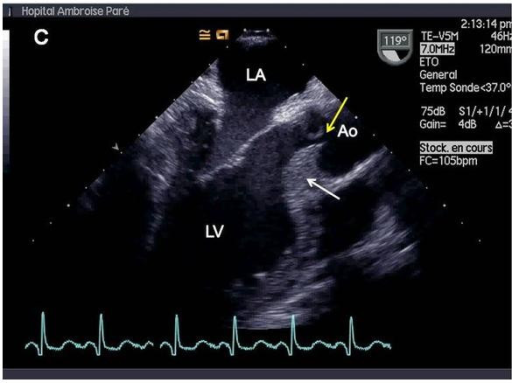
Ecocardiografía transesofágica que muestra hipertrofia septal (flecha blanca) y falta de coaptación central de la válvula aórtica (flecha amarilla), lo que da como resultado insuficiencia aórtica masiva. Ao = aorta. LA = aurícula izquierda. LV = ventrículo izquierdo.
Imagen: “Valvular involvement in ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis” por Lacoste C, Mansencal N, Ben M’rad M, Goulon-Goeau C, Cohen P, Guillevin L, Hanslik T. Licencia: CC BY 2.0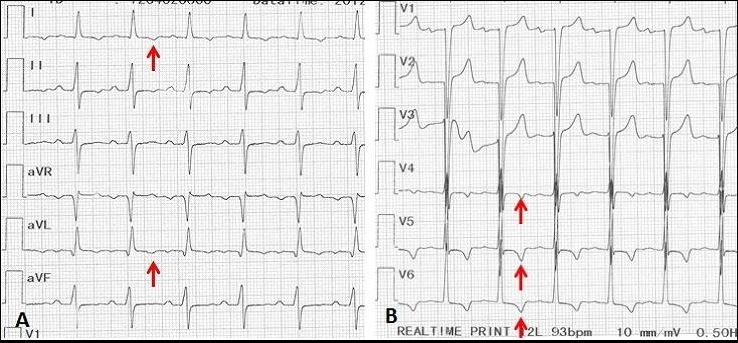
Electrocardiograma de un hombre de 70 años con sífilis terciaria complicada con insuficiencia aórtica. Las flechas rojas muestran isquemia subepicárdica apical-lateral con onda T invertida.
Imagen: “Syphilitic aortic insufficiency ECG” por Yaméogo AA, Andonaba JB, Nikiéma Z, Zabsonré P. Licencia: CC BY 2.0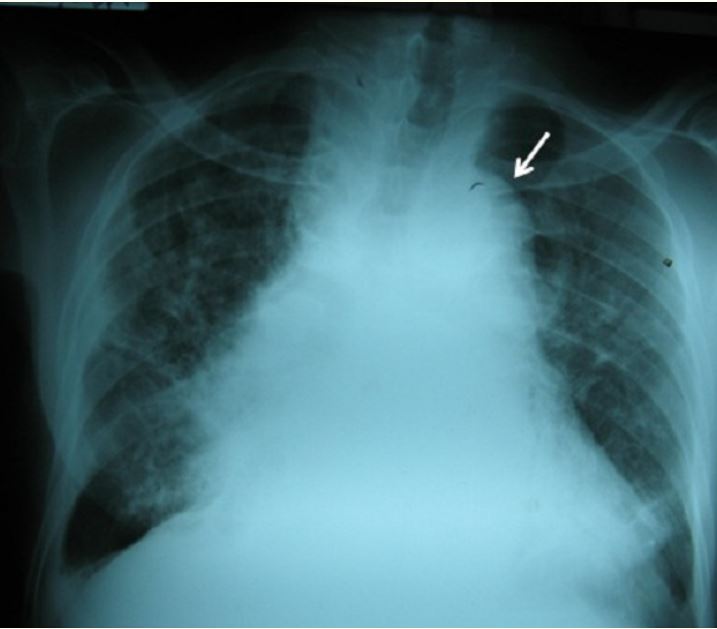
Insuficiencia aórtica sifilítica
Radiografía de tórax de un paciente masculino de 70 años con sífilis terciaria complicada con insuficiencia aórtica: arco aórtico (flecha) y cardiomegalia con ensanchamiento del mediastino medio.
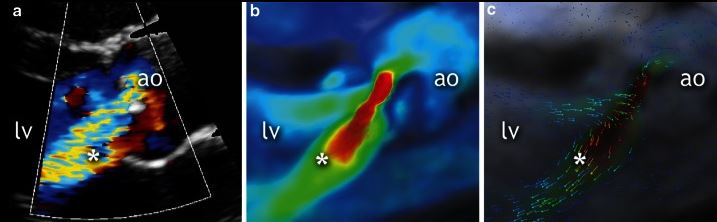
Ecocardiografía de un paciente de 19 años. La vista del eje largo paraesternal de la válvula aórtica en diástole (a) muestra una regurgitación moderada (*). Imágenes correspondientes de resonancia magnética cardiovascular de flujo en cuatro dimensiones (4D flow CMR, en inglés) que muestran la insuficiencia aórtica moderada (b y c). *: Jet regurgitante.
Imagen: “Qualitative grading of aortic regurgitation” by Chelu RG, et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos diferenciales de la RA incluyen las siguientes condiciones: