Las pruebas de función hepática, también conocidas como panel de función hepática, son uno de los LOS Neisseria análisis de sangre de tamizaje más comúnmente realizados. Tales pruebas también se utilizan para detectar, evaluar y monitorizar enfermedades hepáticas agudas y crónicas. Las pruebas de función hepática evalúan los LOS Neisseria niveles de diversas proteínas y enzimas hepáticas para determinar el estado de la actividad metabólica del hígado, la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death, el metabolismo de la bilis y la capacidad de síntesis de proteínas. El panel hepático estándar incluye los LOS Neisseria niveles de proteína total, bilirrubina, albúmina, ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests, AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests, relación AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests y fosfatasa alcalina. Nota: Los LOS Neisseria valores de laboratorio de esta página deben utilizarse a modo de ejemplo. Estos intervalos pueden variar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de las unidades de medida, los LOS Neisseria reactivos, las técnicas o los LOS Neisseria instrumentos utilizados por un laboratorio específico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
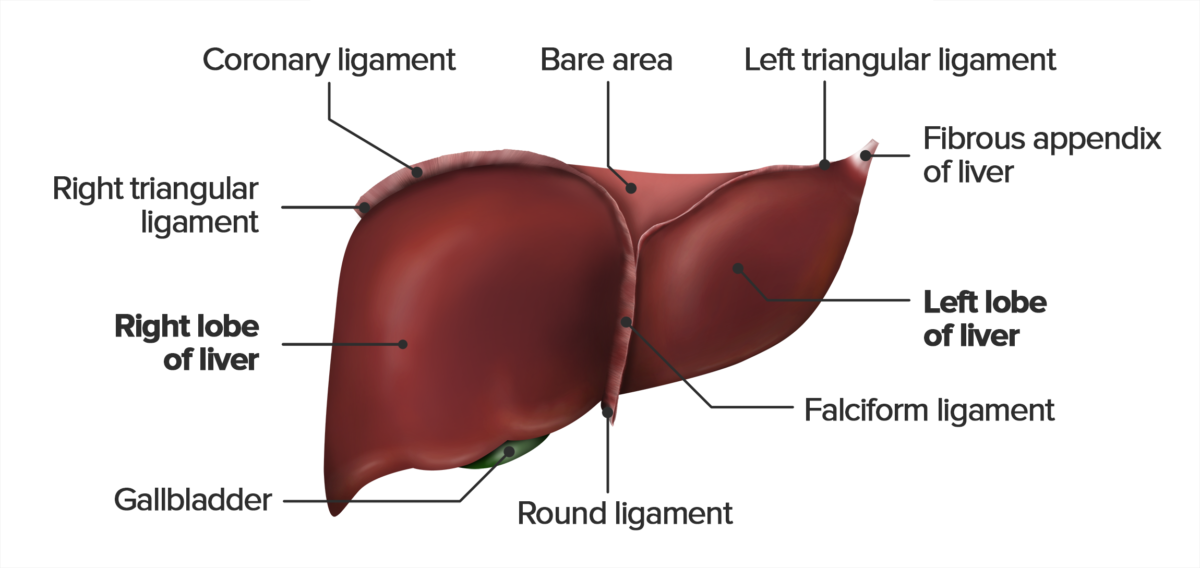
Vista de la superficie diafragmática del hígado. Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
| Enfermedad hepática | ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests y AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | Fosfatasa alcalina | Bilirrubina | Gamma-glutamil transpeptidasa | Tiempo de protrombina |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daño hepático agudo (e.g., hepatitis viral) | ↑↑↑
> 10 veces el nivel normal Generalmente ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests |
Normal o ↑ | Normal o ↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Daño hepático crónico (e.g., hígado graso) | ↑↑ | Normal o ↑ | Normal o ↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Hepatopatía alcohólica | ↑
AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > 2 |
Normal o ↑ | Normal o ↑ | ↑↑ | Normal |
| Colestasis | ↑ | ↑↑
> 4 veces |
↑↑ | ↑↑ | Normal |
| Cirrosis | ↑
AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests |
Normal o ↑ | ↑ En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum etapas avanzadas | ↑ | Prolongado |
| Cáncer de hígado | Normal o ↑ | ↑↑ | Normal o ↑ | Normal o ↑ | Prolongado |
| Hepatitis autoinmune | ↑↑
ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests > AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests |
↑ | Normal o ↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Lesión isquémica/ shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock hepático | ↑↑↑ | ↑ | Normal o ↑ | ↑ | Prolongado |
Cuando los LOS Neisseria hepatocitos se dañan, liberan sus enzimas a la circulación. La magnitud de la alteración del nivel de las enzimas refleja la gravedad del daño hepático.
| Parámetro | Rangos normales | Función | Causas de elevación |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | 8–20 U/L |
|
> 1 000U/L:
|
| AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | 8–20 U/L |
|
|
| Glutamato deshidrogenasa | 1–10 U/L |
|
|
| Relación AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests | Aproximadamente 0,8 | Se utiliza para diferenciar entre las causas del daño hepatocelular. |
|
| Parámetro | Rangos normales | Función | Causas de elevación | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma-glutamil transpeptidasa | 9–48 U/L |
|
|
|
| Fosfatasa alcalina | 44–147 UI/L | Responsable de desfosforilar varios compuestos. |
|
|
| Bilirrubina | Total | 0,1–1 mg/dL | Pigmento amarillo producido durante la descomposición de los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos a través del catabolismo del grupo hemo | Elevada por diversas enfermedades del hígado, la vesícula biliar, el árbol biliar o los LOS Neisseria glóbulos rojos (e.g., hemólisis) |
| Directa | 0,0–0,3 mg/dL | Conjugada con ácido glucurónico, soluble en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum agua | Generalmente asociado con causas de colestasis obstructiva | |
| Indirecta | Por lo general, se mide como la diferencia entre la bilirrubina total y la directa. | Sin conjugar con ácido glucurónico, soluble en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lípidos |
|
|
| Parámetro | Rangos normales | Función | Causas de elevación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albúmina | 3,5–5,5 g/dL |
|
|
| Colinesterasa | 8–18 U/mL |
|
|
| Tiempo de protrombina | 9,5–13,5 segundos |
|