Las pruebas de coagulación son un grupo de estudios de laboratorio hematológicos que reflejan la función de los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos, plaquetas y factores de coagulación, que interactúan entre sí para lograr la hemostasia. Las pruebas de coagulación generalmente se solicitan para evaluar pacientes con trastornos hemorrágicos o de hipercoagulación.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las pruebas de coagulación son un grupo de estudios hematológicos que reflejan la función de los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos, plaquetas y factores de coagulación, que funcionan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum armonía para lograr la hemostasia.
A continuación un resumen del proceso hemostático:
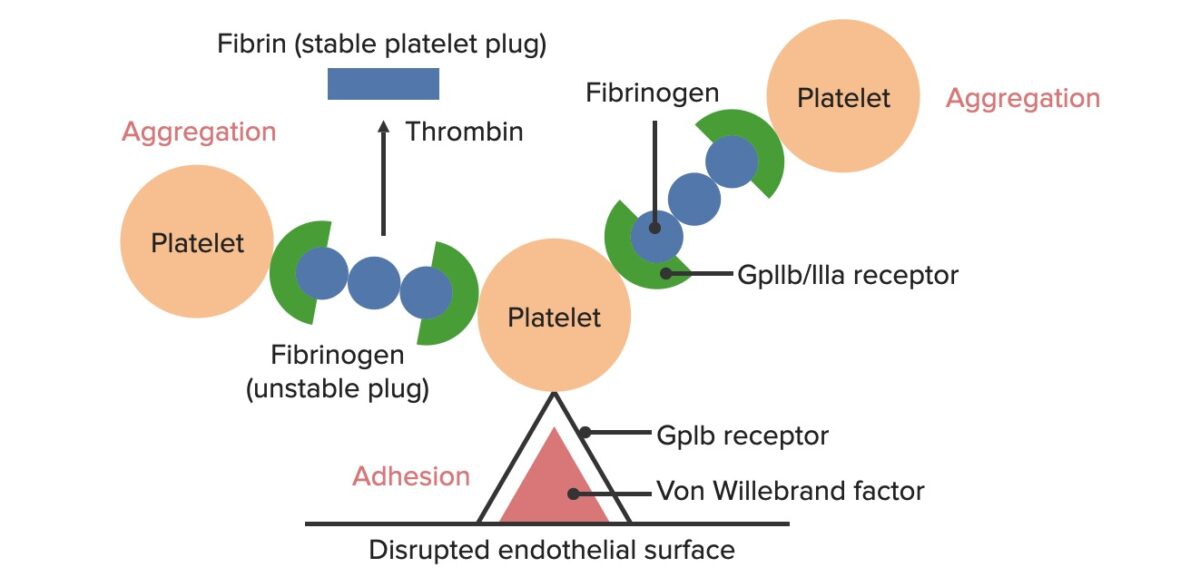
Formación del tapón hemostático temporal:
La superficie endotelial rota expone el factor de von Willebrand a la sangre circulante. Las plaquetas se unen al factor de von Willebrand a través de sus receptores GpIb y se activan. La activación de las plaquetas hace que secreten difosfato de adenosina (ADP, por sus siglas en inglés), que estimula la expresión de los receptores GpIIb/IIIa en las plaquetas. Los receptores GpIIb/IIIa se unen al fibrinógeno, que puede unirse a una plaqueta en cada extremo, lo que hace que las plaquetas se agreguen. A medida que se unen más plaquetas entre sí, se genera el tapón plaquetario. A medida que se activa la cascada de coagulación, la trombina convierte el fibrinógeno más débil en fibrina más fuerte, creando un coágulo mucho más estable.
Descripción general de la cascada de la coagulación
a: forma activada
PF3: factor plaquetario 3 (fosfolípidos)
Las siguientes pruebas pueden ayudar a diagnosticar problemas relacionados con la hemostasia.
Recuento plaquetario:
Tiempo de sangrado:
Estos estudios se utilizan para evaluar la cantidad de tiempo que tarda el plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum coagularse cuando se agregan varias sustancias.
Evaluación de la cascada de la coagulación
Imagen por Lecturio.
Factores involucrados en las vías intrínseca, extrínseca y común
Las pruebas de los LOS Neisseria factores de la coagulación se utilizan principalmente para diagnosticar deficiencias de factores específicos. Las pruebas se utilizan para evaluar la concentración o el nivel de actividad de factores individuales.
Los LOS Neisseria estudios mezclados se utilizan para evaluar más a fondo una prolongación inexplicable de una prueba de coagulación, incluidos un TP, TTPa o TT prolongados.
Las condiciones hipocoagulables son un grupo de enfermedades que resultan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una hemostasia anormal. Se manifiestan con hemorragia menor (petequias, hemorragia mucocutánea) o hemorragia interna más severa (hemartrosis, hemorragia intracraneal).
Lo más probable es que los LOS Neisseria pacientes con estos trastornos tengan un mayor tiempo de sangrado, pero un TP y un TTPa normales.
Hemofilia: un raro trastorno de la coagulación de la sangre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que el cuerpo carece de factores de coagulación ( factor VIII Factor VIII Factor VIII of blood coagulation. Antihemophilic factor that is part of the factor viii/von Willebrand factor complex. Factor VIII is produced in the liver and acts in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. It serves as a cofactor in factor X activation and this action is markedly enhanced by small amounts of thrombin. Hemostasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hemofilia A y factor IX Factor IX Storage-stable blood coagulation factor acting in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Its activated form, ixa, forms a complex with factor VIII and calcium on platelet factor 3 to activate factor X to Xa. Hemostasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hemofilia B). Los LOS Neisseria individuos afectados presentan hemorragia anormal que ocurre espontáneamente o después de un traumatismo menor. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden presentar sangrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria espacios articulares y desarrollar una hemorragia interna potencialmente mortal. Los LOS Neisseria estudios de coagulación típicamente revelan un TTPa prolongado debido a anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vía intrínseca, pero el TP y los LOS Neisseria recuentos plaquetarios son normales. Los LOS Neisseria estudios mezclados corregirán, y el nivel de actividad del factor específico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que el paciente es deficiente será bajo.