El politraumatismo se produce cuando ocurren 2 o más lesiones traumáticas en al menos 2 áreas del cuerpo. Es necesario un abordaje terapéutico sistemático para los pacientes que han sufrido un traumatismo para maximizar los resultados y reducir el riesgo de lesiones ocultas. La evaluación del politraumatismo comienza con una evaluación primaria seguida del esquema "ABCDE" ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), que implica asegurar la vía aérea (A) y evaluar la respiración (B), la circulación (C), el reconocimiento de déficits neurológicos o discapacidad (D) y exposición al AL Amyloidosis control ambiental (E). Una vez que se completa la evaluación primaria, se realiza una evaluación secundaria para obtener los LOS Neisseria antecedentes pertinentes y la naturaleza del traumatismo basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un examen completo y estudios diagnósticos. El abordaje ABCDE es crucial para la estabilización general, el tratamiento y la identificación de cualquier lesión oculta.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El traumatismo múltiple o politraumatismo se define como 2 o más lesiones graves en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum al AL Amyloidosis menos 2 áreas del cuerpo (con al AL Amyloidosis menos 1 lesión potencialmente mortal).
Un traumatismo es una de las principales causas de mortalidad y morbilidad a nivel mundial.
La hemorragia es la causa de mortalidad prevenible más frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria traumatismos.
Factores asociados con malos pronósticos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria traumatismos:
La evaluación primaria es la evaluación inicial que se utiliza para identificar y tratar las lesiones potencialmente mortales en un paciente con traumatismos. La valoración consta de 5 evaluaciones realizadas en forma escalonada (“ABCDE”, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés): airway (vía aérea), breathing (respiración), circulation (circulación), disability (discapacidad) y exposure (exposición).
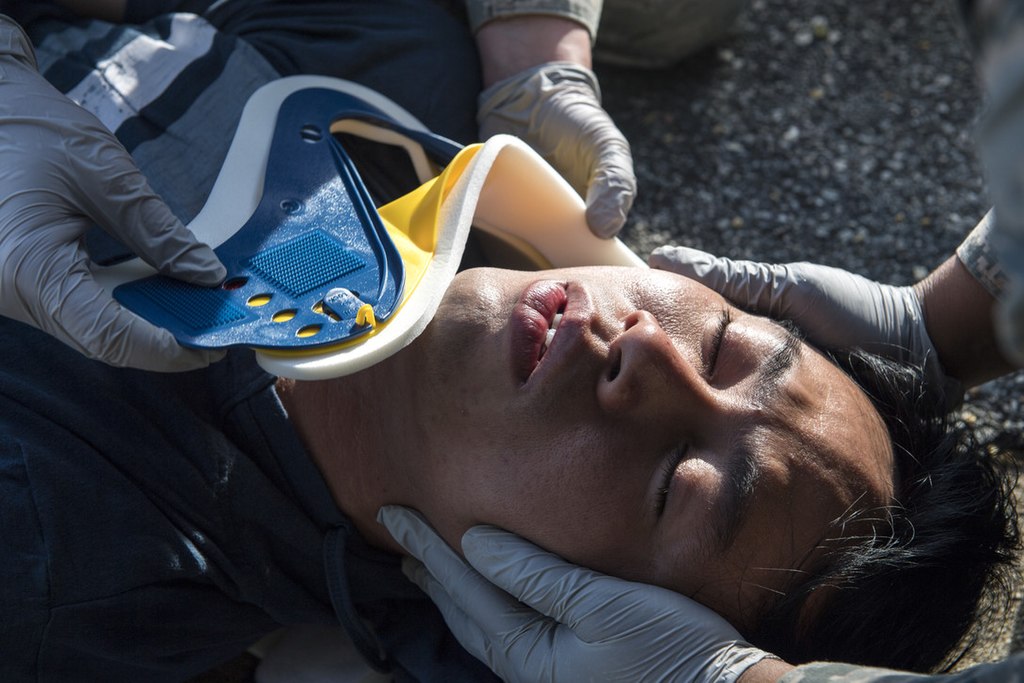

Aplicación de la tabla y el collarín cervical por parte de los servicios médicos de emergencia en el campo:
Si el paciente afectado llega en un vehículo personal, se coloca el collarín C durante la parte de la vía aérea (A) de la evaluación primaria.
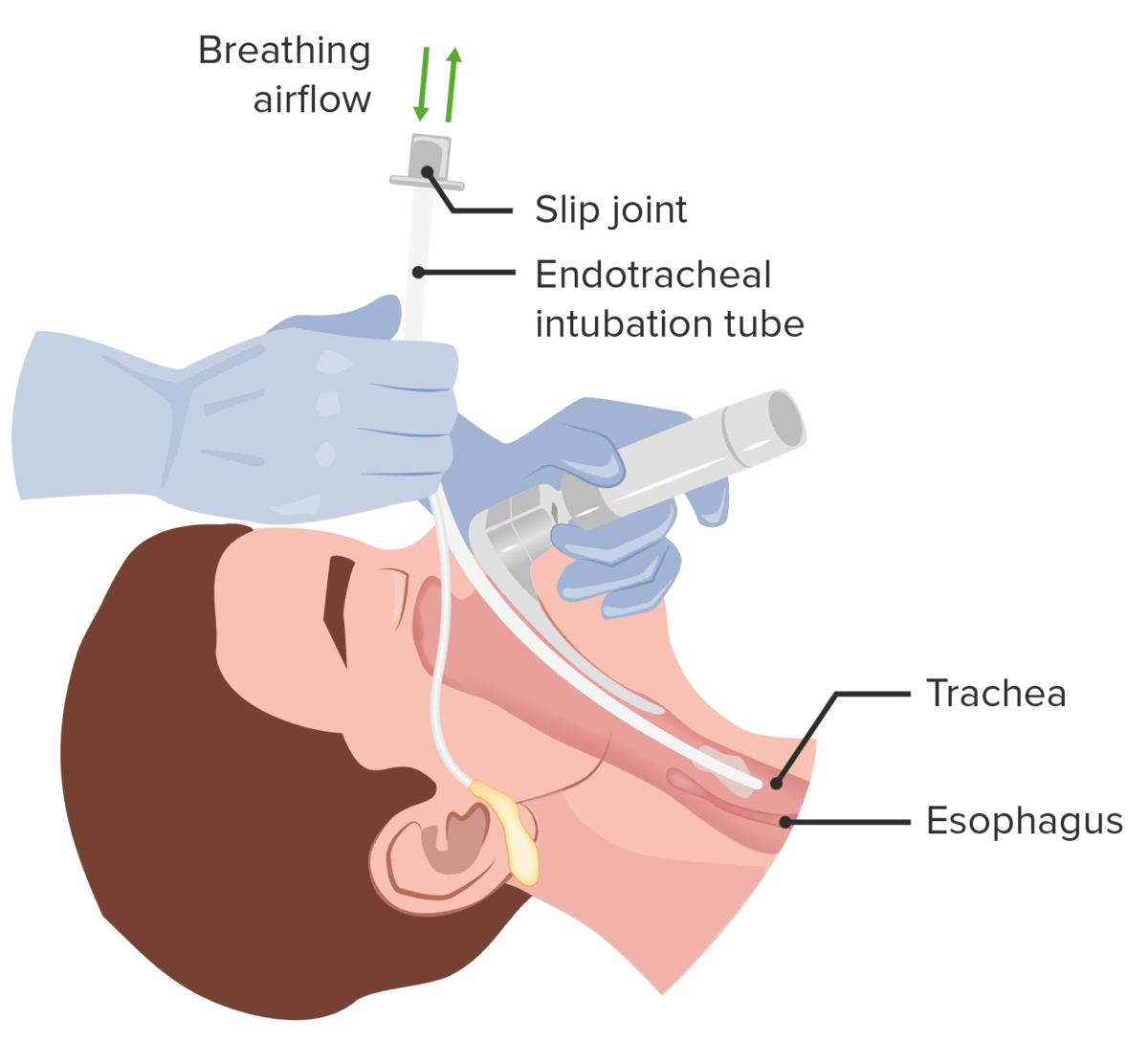
Manejo de la vía aérea: establecimiento de una vía aérea definitiva mediante la inserción de un tubo endotraqueal
Imagen por Lecturio.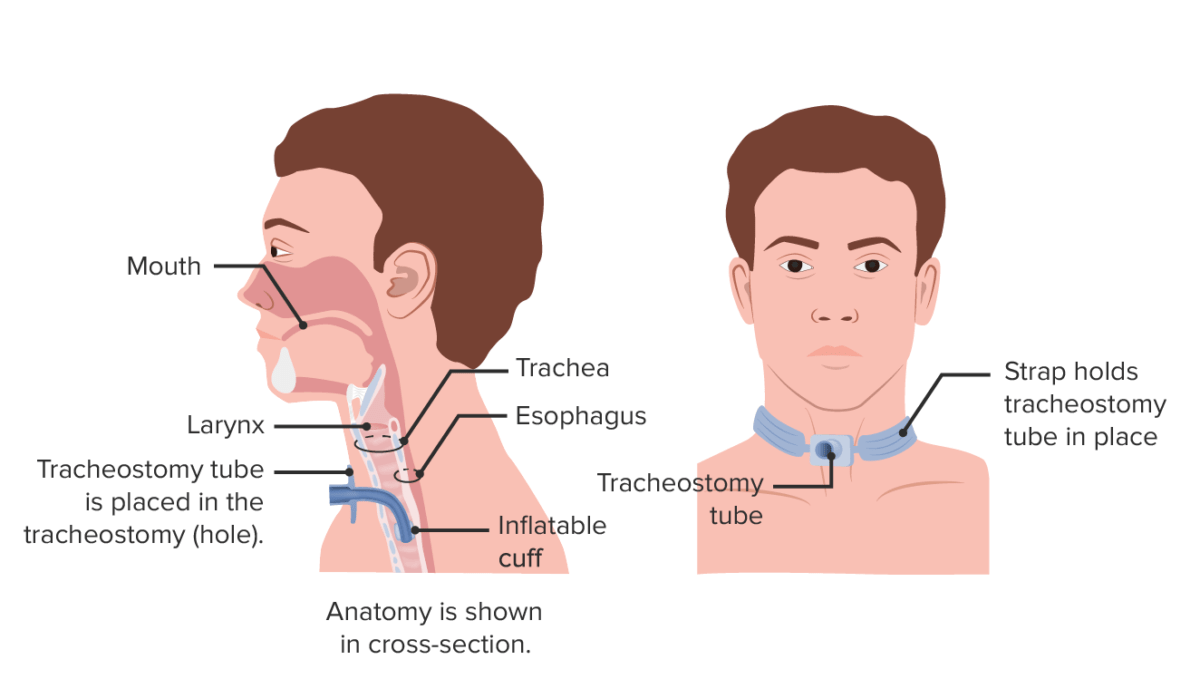
Traqueostomía:
La Figura A muestra una vista lateral del cuello y la colocación correcta de un tubo de traqueostomía en la tráquea. La Figura B muestra una vista externa de un indiviuo con un tubo de traqueostomía.
Evaluación de la discapacidad:
| Característica | Respuesta | Puntuación |
|---|---|---|
| Apertura ocular | Apertura espontánea | 4 |
| Apertura a las órdenes verbales | 3 | |
| Apertura al AL Amyloidosis dolor Dolor Inflammation | 2 | |
| Sin apertura ocular | 1 | |
| Respuesta verbal | Orientada y apropiada | 5 |
| Desorientada pero conversa | 4 | |
| Palabras sin sentido | 3 | |
| Quejidos | 2 | |
| Silencio | 1 | |
| Respuesta motora | Sigue órdenes | 6 |
| Localiza el dolor Dolor Inflammation | 5 | |
| Se retira del dolor Dolor Inflammation | 4 | |
| Postura flexora | 3 | |
| Postura extensora | 2 | |
| Flacidez | 1 |
El objetivo de este paso es evaluar y tratar los LOS Neisseria efectos ambientales negativos:
El objetivo de la evaluación secundaria es examinar rápida y minuciosamente al AL Amyloidosis paciente afectado de la cabeza a los LOS Neisseria pies e identificar todas las lesiones potencialmente significativas.
Para obtener los antecedentes importantes, podemos obtenerlos utilizando la mnemotecnia “AMPLE” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés es):
Los LOS Neisseria antecedentes pertinentes, el examen físico completo y los LOS Neisseria estudios diagnósticos apropiados ayudan a evitar lesiones ocultas como:
Las siguientes tablas resumen los LOS Neisseria diferentes mecanismos de traumatismo y sus lesiones específicas asociadas.
| Mecanismo de lesión | Lesiones potencialmente asociadas |
|---|---|
| Colisión frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy |
|
| Colisión trasera |
|
| Expulsión del vehículo | Lesiones de la columna vertebral |
| Daños contra el parabrisas |
|
| Daños contra el volante | Lesiones torácicas |
| Involucramiento/daños contra el tablero |
|
| Mecanismo de lesión | Lesiones potencialmente asociadas |
|---|---|
| Baja velocidad (automóvil en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proceso de frenado) |
|
| Alta velocidad | Triada de Waddle (
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum peatones pediátricos):
|
| Mecanismo de lesión | Lesiones potencialmente asociadas |
|---|---|
| Relacionadas con automóviles |
|
| No relacionadas con automóviles |
|
| Mecanismo de lesión | Lesiones potencialmente asociadas |
|---|---|
| Impacto vertical |
|
| Impacto horizontal |
|