El paludismo es una enfermedad parasitaria infecciosa que afecta a los LOS Neisseria seres humanos y a otros animales. El paludismo, que se transmite sobre todo por la picadura de un mosquito Anopheles Anopheles A genus of mosquitoes (culicidae) that are known vectors of malaria. Plasmodium/Malaria hembra infectado, es causado por microorganismos unicelulares del género Plasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes se presentan con fiebre, escalofríos, mialgia, cefalea y diaforesis después de un antecedente de exposición en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una zona endémica de paludismo, que suele ser cíclica. La profilaxis es de suma importancia. Existe un tratamiento con medicamentos orales, pero el paludismo puede ser grave y mortal si no se diagnostica a tiempo, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños pequeños.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El paludismo es una enfermedad parasitaria causada por parásitos unicelulares del género Plasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs y es transmitida por mosquitos del género Anopheles Anopheles A genus of mosquitoes (culicidae) that are known vectors of malaria. Plasmodium/Malaria.
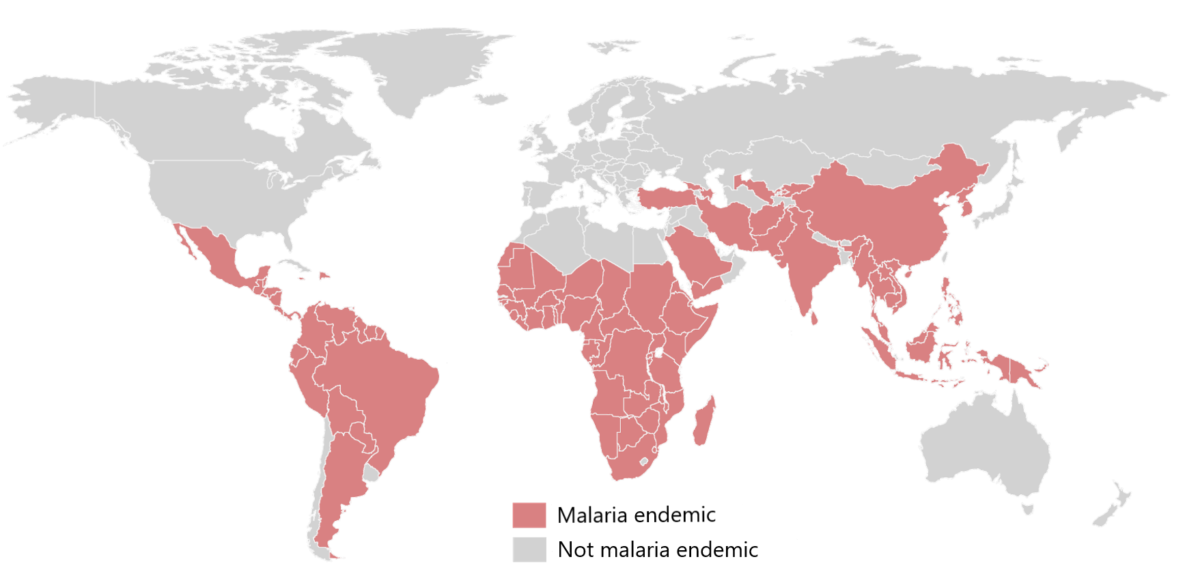
Distribución endémica a nivel mundial del paludismo
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0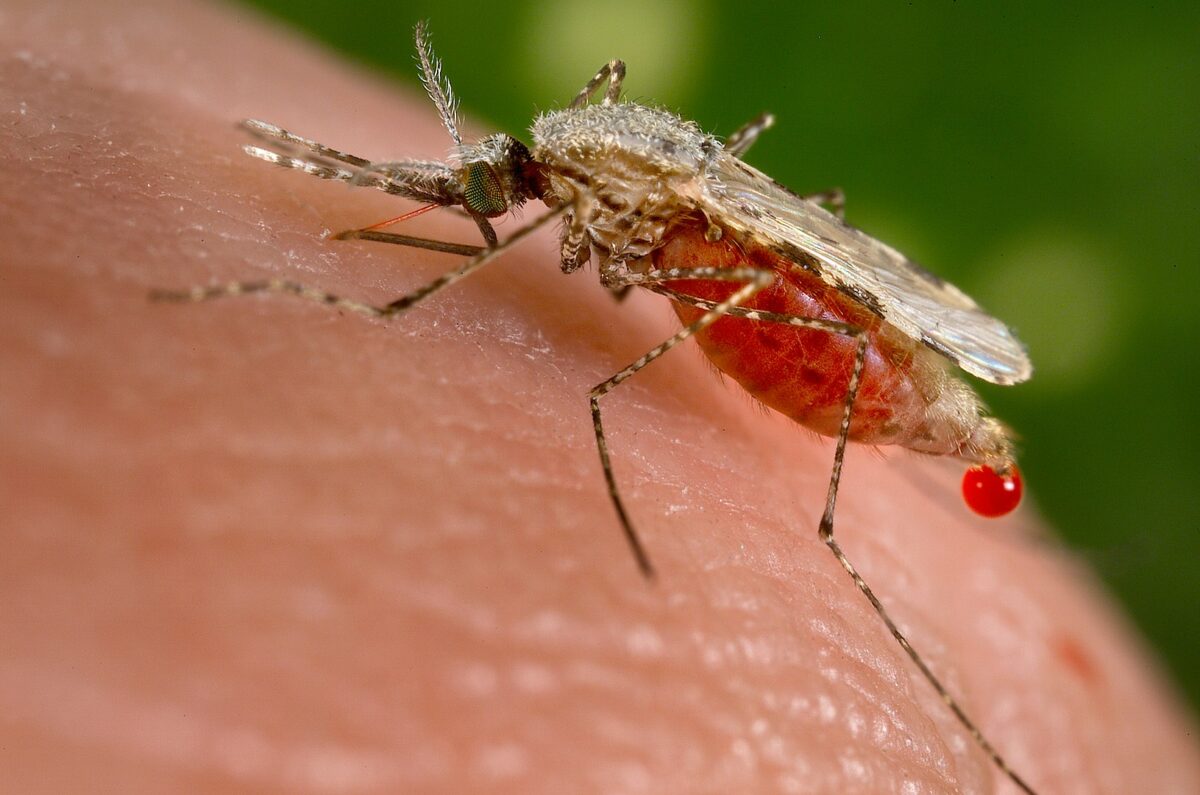
Mosquito Anopheles stephensi alimentándose de sangre humana.
Imagen: “Anopheles stephensi” por Jim Gathany. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoPlasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs es un género de eucariotas unicelulares, que son parásitos obligados de vertebrados e insectos.
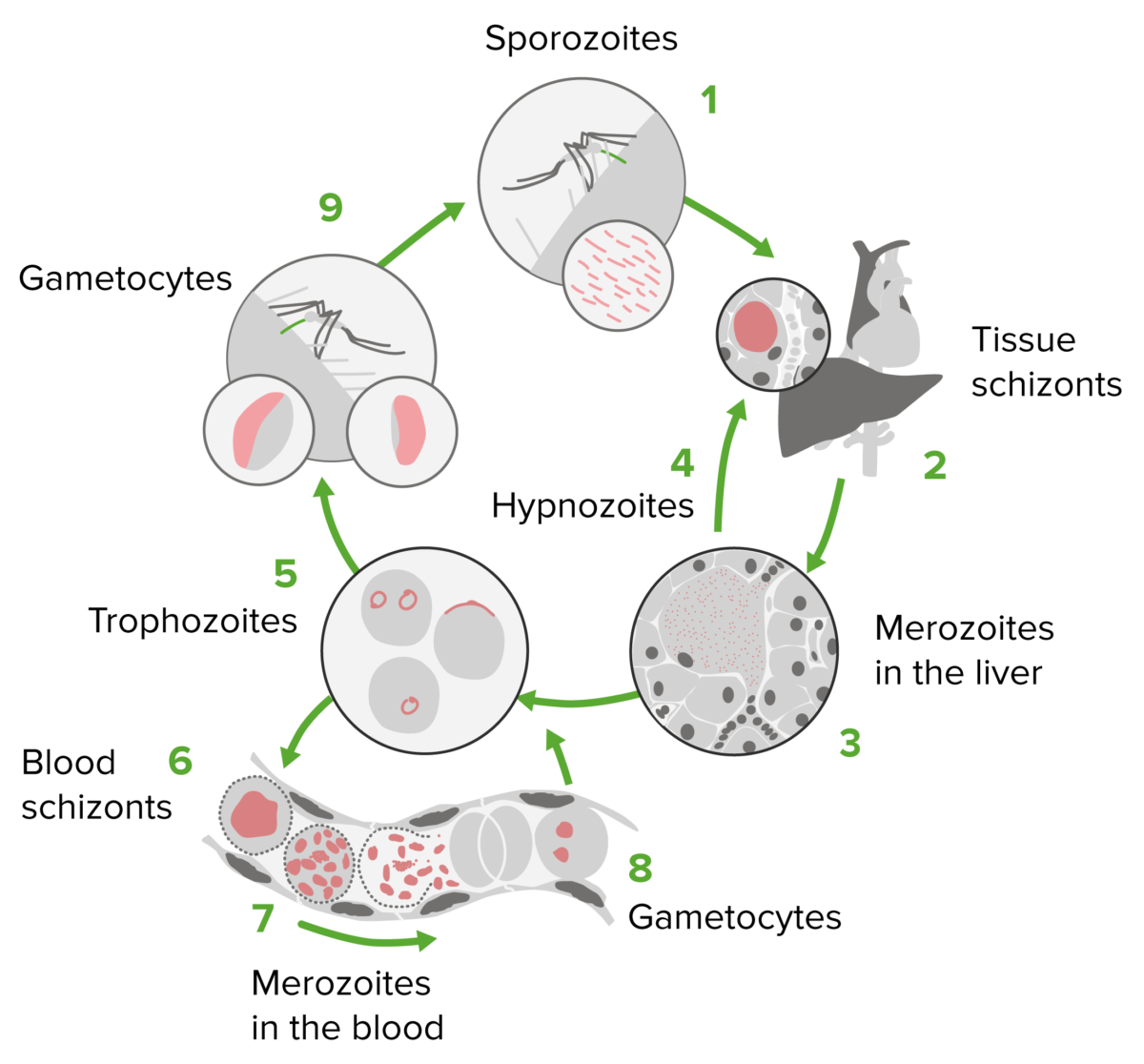
Ciclo de vida del Plasmodium
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0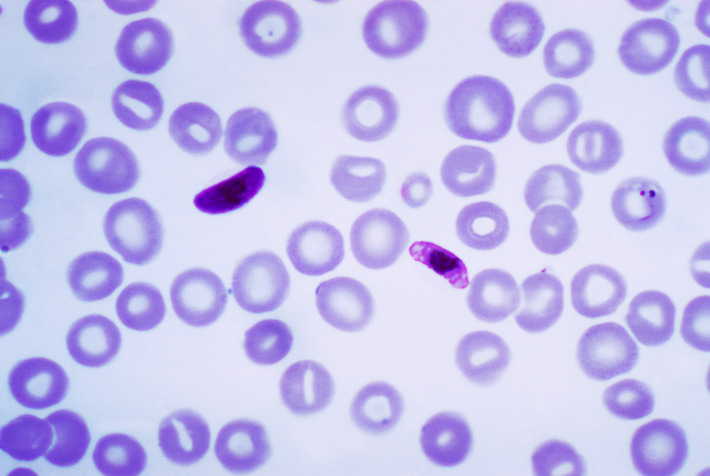
P. falciparum:
Una micrografía de una capa fina teñida con Giemsa que muestra un macrogametocito y un microgametocito del parásito.
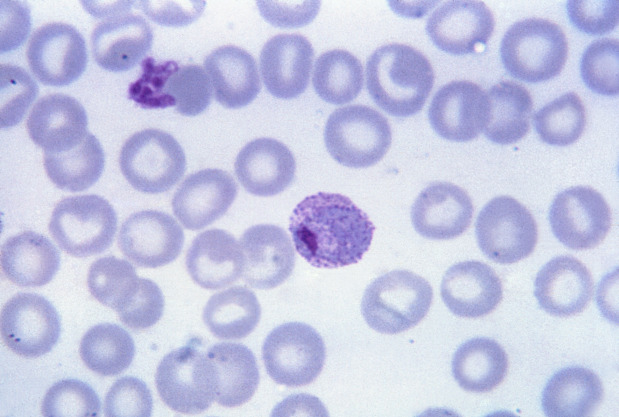
P. vivax:
Una micrografía de una capa fina teñida con Giemsa que muestra un trofozoíto maduro con citoplasma ameboide, grandes puntos de cromatina (gránulos de Schüffner) y un fino pigmento marrón amarillento.
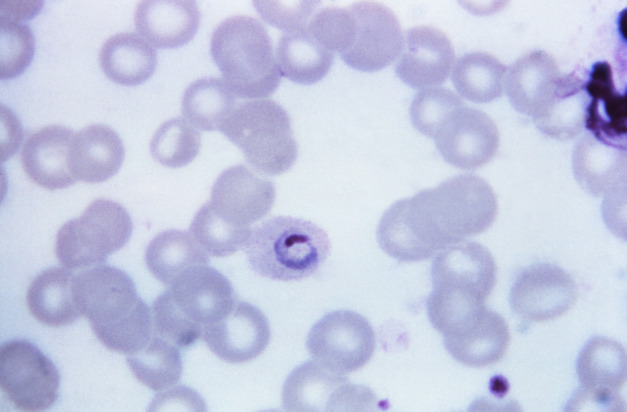
P. ovale:
Una micrografía de una capa fina teñida con Giemsa que muestra un trofozoíto en forma de anillo.
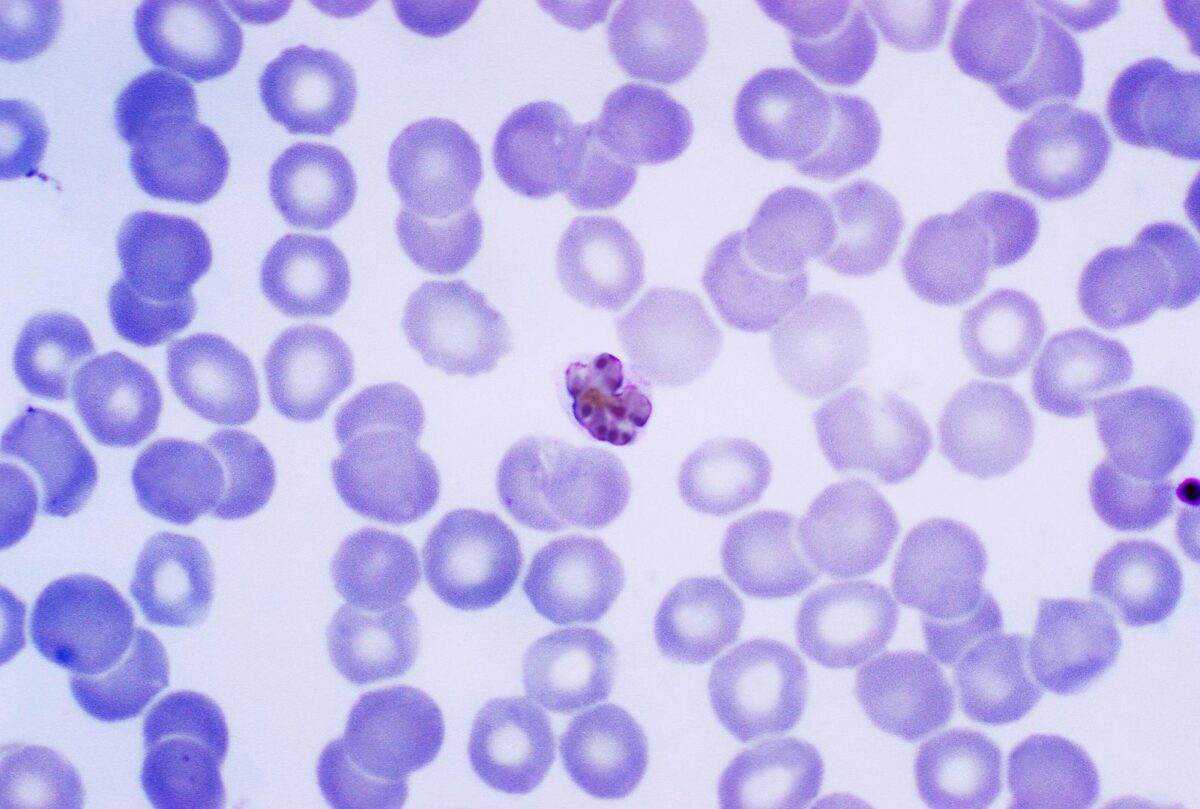
P. malariae:
Una micrografía de una capa fina teñida con Giemsa que muestra un esquizonte maduro dentro de un eritrocito infectado. El parásito contiene 6–12 merozoítos con núcleos grandes y tiene un pigmento grueso de color marrón oscuro.