Los LOS Neisseria agentes antiadrenérgicos son medicamentos que bloquean la actividad de las catecolaminas, principalmente la norepinefrina. Hay 2 tipos principales de receptores adrenérgicos (receptores alfa y beta) y hay varios subtipos de cada uno. Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antiadrenérgicos se pueden clasificar según su especificidad para los LOS Neisseria diferentes receptores, y las clases principales incluyen bloqueadores selectivos de los LOS Neisseria receptores beta-1, bloqueadores beta no selectivos, bloqueadores alfa y beta mixtos, bloqueadores selectivos de los LOS Neisseria receptores alfa-1 y bloqueadores alfa-1 no selectivos. Hay muchos receptores beta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el corazón, por lo que estos medicamentos se usan principalmente para indicaciones cardíacas, que incluyen IM, angina de pecho, insuficiencia cardíaca (estable) e hipertensión (como agente alternativo). Los LOS Neisseria receptores alfa son prominentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el músculo liso, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vasculatura. Los LOS Neisseria alfabloqueadores causan una vasodilatación significativa y están indicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la hipertensión y la hiperplasia prostática benigna (HPB). Es posible la presentación de efectos secundarios significativos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El sistema nervioso autónomo se subdivide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las vías simpática y parasimpática. Ambas vías contienen 2 neuronas eferentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum serie conocidas como neuronas preganglionares y postganglionares.
Neurona preganglionar:
Neurona postganglionar:
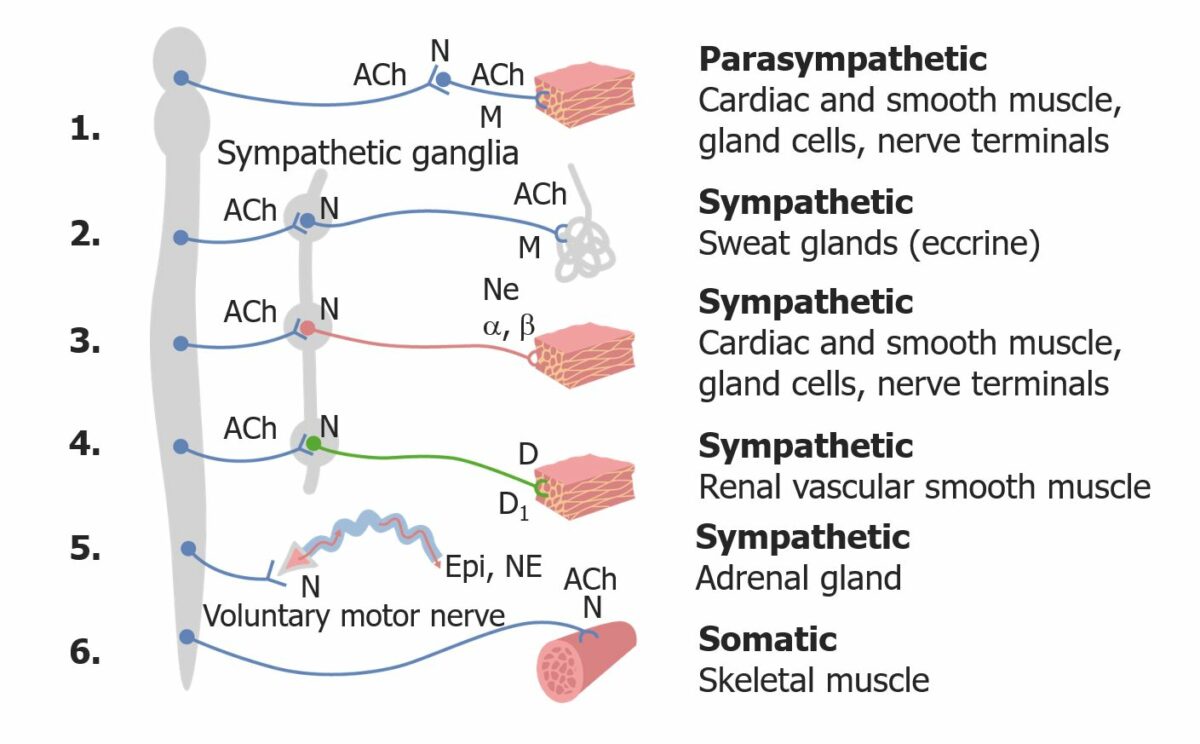
Descripción general del sistema nervioso autónomo
ACh: acetilcolina
N: receptor nicotínico
M: receptor muscarínico
α y β: receptores adrenérgicos α y β
NE: norepinefrina
D: dopamina
D1: receptor de dopamina
Epi: epinefrina
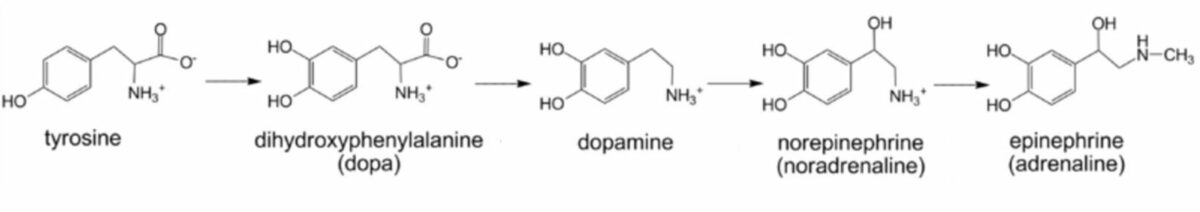
Estructura química de las catecolaminas
Imagen: Catecholamine biosynthesis” por Michael Skovbo Windahl. Licencia: CC0 1.0, recortada por Lecturio.
Estructura química del propranolol
Imagen: “B1-selective beta blockers” por Yikrazuul. Licencia: Dominio Público, recortada por Lecturio.
Estructura química del carvedilol
Imagen: “B1-selective beta blockers” por Yikrazuul. Licencia: Dominio Público, recortada por Lecturio.
Estructura química del metoprolol
Imagen: “B1-selective beta blockers” por Yikrazuul. Licencia: Dominio Público, recortada por Lecturio.
Estructura química de la prazosina
Imagen: “Prazosin” de Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria medicamentos antiadrenérgicos actúan inhibiendo los LOS Neisseria receptores adrenérgicos postganglionares. Estos son receptores acoplados a proteína G.
Receptores alfa:
Receptores beta: beta-1, beta-2 y beta-3
Los LOS Neisseria receptores adrenérgicos se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el cuerpo y desencadenan una amplia variedad de efectos. Los LOS Neisseria efectos fisiológicos de los LOS Neisseria agentes antiadrenérgicos son bloquear cualquiera que sea la respuesta típica de ese receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum particular.
| Sistema | Órgano | Receptores | Acciones fisiológicas de la estimulación del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (agonismo) | Efectos fisiológicos del bloqueo del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (antagonismo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ojo | Músculo radial del iris | α1 | Contracción → dilatación pupilar | Relajación → contracción de la pupila |
| Músculo ciliar | β | Se relaja → aplana el cristalino → mejor para enfoque de largo alcance | ↓ Relajación → cristalino más redondo → enfoque de corto alcance | |
| Epitelio ciliar | β | ↑ Producción de humor Humor Defense Mechanisms acuoso | ↓ Secreción de humor Humor Defense Mechanisms acuoso → ↓ PIO | |
| Sistema cardiovascular | SA | β1, β2 | Aceleración (↑ FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions) | ↓ FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions |
| Marcapasos ectópicos | β1, β2 | Aceleración (↑ FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions) | ↓ FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | |
| Contractilidad de aurículas y ventrículos | β1, β2 | ↑ Contractilidad | ↓ Contractilidad | |
| Músculo liso de la pared vascular | α1 | Vasoconstricción | Vasodilatación → puede causar hipotensión ortostática y taquicardia refleja | |
| β2 | Vasodilatación | Vasoconstricción → ↑ resistencia periférica | ||
| Músculo liso pulmonar | Músculo liso bronquiolar | β2 | Broncodilatación | Broncoconstricción (especialmente con asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis) |
| Músculo liso del tracto gastrointestinal | Paredes intestinales | α2, β2 | Relajación (↓ motilidad) | ↑ Motilidad → puede provocar diarrea |
| Músculos del esfínter | α1 | Se contrae (evita que el quimo avance) | Relajación de esfínteres → ↑ riesgo de acidez estomacal | |
| Músculo liso genitourinario | Pared vesical | β2, β3 | Se relaja | ↓ Resistencia al AL Amyloidosis flujo de orina |
| Esfínteres uretrales | α1 | Se contrae | ↓ Resistencia al AL Amyloidosis flujo de orina → ↑ riesgo de incontinencia | |
| Útero embarazado | α | Contraccion uterina | Relajación uterina | |
| β2 | Relajación uterina | Contracciones uterinas → trabajo de parto/trabajo de parto pretérmino | ||
| Pene y vesículas seminales | α | Eyaculación | Dificultad con la eyaculación | |
| Funciones metabólicas | Hígado | α, β2 | Gluconeogénesis, glucogenólisis | ↓ Glucogenólisis → puede perjudicar la recuperación de la hipoglucemia |
| Tejido adiposo | β3 | Lipólisis | Inhibición de la lipólisis | |
| Riñón | β1 | Liberación de renina | Supresión de la liberación de renina |
Estos medicamentos tienen efectos inhibidores tanto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria receptores beta como alfa-1
Las diferencias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la farmacocinética pueden ayudar a determinar qué medicamento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una clase particular es óptimo para un escenario clínico determinado.
| Medicamento | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prazosina (bloqueador α1 selectivo) | Comienzo: 2‒4 horas |
|
Hepático extenso a través de desmetilación y conjugación |
|
| Fentolamina (bloqueador alfa no selectivo |
|
Ampliamente distribuida | Hepático |
|
| Propranolol Propranolol A widely used non-cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Propranolol has been used for myocardial infarction; arrhythmia; angina pectoris; hypertension; hyperthyroidism; migraine; pheochromocytoma; and anxiety but adverse effects instigate replacement by newer drugs. Antiadrenergic Drugs (bloqueador β no selectivo) |
|
|
Extenso metabolismo hepático de 1er paso |
|
| Atenolol Atenolol A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic blocker possessing properties and potency similar to propranolol, but without a negative inotropic effect. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) (betabloqueador selectivo β1) |
|
|
Mínimo metabolismo hepático |
|
| Metoprolol Metoprolol A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias. Antiadrenergic Drugs (betabloqueador selectivo β1) |
|
|
Amplio metabolismo hepático de 1er paso |
|
| Carvedilol Carvedilol A carbazole and propanol derivative that acts as a non-cardioselective beta blocker and vasodilator. It has blocking activity for alpha 1 adrenergic receptors and, at higher doses, may function as a blocker of calcium channels; it also has antioxidant properties. Carvedilol is used in the treatment of hypertension; angina pectoris; and heart failure. It can also reduce the risk of death following myocardial infarction. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) (bloqueo mixto α y β) |
|
|
Amplio metabolismo hepático de 1er paso |
|
Las interacciones medicamentosas también son importantes para varios medicamentos dentro de esta clase.
Si bien los LOS Neisseria antagonistas alfa-2 tienen pocos usos clínicos, los LOS Neisseria antagonistas alfa-1 y alfa no selectivos se usan por su capacidad para causar vasodilatación y relajación del músculo liso. Se utilizan con frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de:
Los LOS Neisseria betabloqueadores tienen una variedad de indicaciones. Se utilizan con frecuencia por sus efectos inotrópicos y cronotrópicos negativos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el corazón.
Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antiadrenérgicos deben usarse con precaución y titularse lentamente para evitar efectos secundarios.
| Medicamento | Efectos secundarios | Contraindicaciones |
|---|---|---|
| Betabloqueadores |
|
|
| Bloqueadores alfa-1 (prazosina) |
|
Hipersensibilidad conocida al AL Amyloidosis medicamento |
| Antagonistas alfa no selectivos (fenoxibenzamina, fentolamina) |
|
|
Aunque los LOS Neisseria betabloqueadores son generalmente seguros, la sobredosis puede producir síntomas de toxicidad, generalmente dentro de las 2 horas (casi siempre dentro de las 6). Los LOS Neisseria síntomas incluyen:
| Medicamento | Mecanismo | Efectos fisiológicos | Indicación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metoprolol Metoprolol A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias. Antiadrenergic Drugs | Bloqueador selectivo β1 |
|
|
| Propranolol Propranolol A widely used non-cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Propranolol has been used for myocardial infarction; arrhythmia; angina pectoris; hypertension; hyperthyroidism; migraine; pheochromocytoma; and anxiety but adverse effects instigate replacement by newer drugs. Antiadrenergic Drugs | Betabloqueador no selectivo |
|
|
| Carvedilol Carvedilol A carbazole and propanol derivative that acts as a non-cardioselective beta blocker and vasodilator. It has blocking activity for alpha 1 adrenergic receptors and, at higher doses, may function as a blocker of calcium channels; it also has antioxidant properties. Carvedilol is used in the treatment of hypertension; angina pectoris; and heart failure. It can also reduce the risk of death following myocardial infarction. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | Bloqueadores α y β no selectivos |
|
|
| Prazosina | Bloqueador selectivo α1 |
|
|
| Fentolamina | Antagonista α-adrenérgico no selectivo |
|
|