Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores del sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona constituyen una clase importante de medicamentos para el tratamiento de las enfermedades cardiovasculares. Son agentes antihipertensivos de 1ra línea, que además pueden utilizarse como tratamiento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el IM, la insuficiencia cardíaca, la nefropatía diabética y el ictus. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores del sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona incluyen los LOS Neisseria IECA, los LOS Neisseria ARA, los LOS Neisseria inhibidores directos de la renina, los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de los LOS Neisseria receptores de la angiotensina y de la neprilisina y los LOS Neisseria antagonistas de la aldosterona, que afectan a diferentes componentes de la vía del SRAA. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, el uso de inhibidores del SRAA provoca una disminución de la vasoconstricción y del volumen sanguíneo. Entre los LOS Neisseria efectos adversos más comunes se encuentran la hiperpotasemia, la tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, el angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema y la pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis, que son más frecuentes con el uso de los LOS Neisseria IECA que de los LOS Neisseria ARA.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores del sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona constituyen una clase importante de medicamentos para el tratamiento de las enfermedades cardiovasculares y son agentes de 1ra línea para el tratamiento de la hipertensión.
Descripción general del SRAA
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos de la clase de los LOS Neisseria inhibidores del SRAA incluyen:
| Sitio de acción | Clase | Subclase |
|---|---|---|
| Renales | Medicamentos que afectan al AL Amyloidosis SRAA |
|
| Diuréticos |
|
|
| Extrarrenales | Vasodilatadores directos | |
| Agentes que actúan a través del sistema nervioso simpático |
|
Todos los LOS Neisseria medicamentos de una misma clase tienen la misma estructura básica, pero diferentes grupos funcionales unidos, lo que explica sus diferentes perfiles farmacocinéticos y de seguridad.
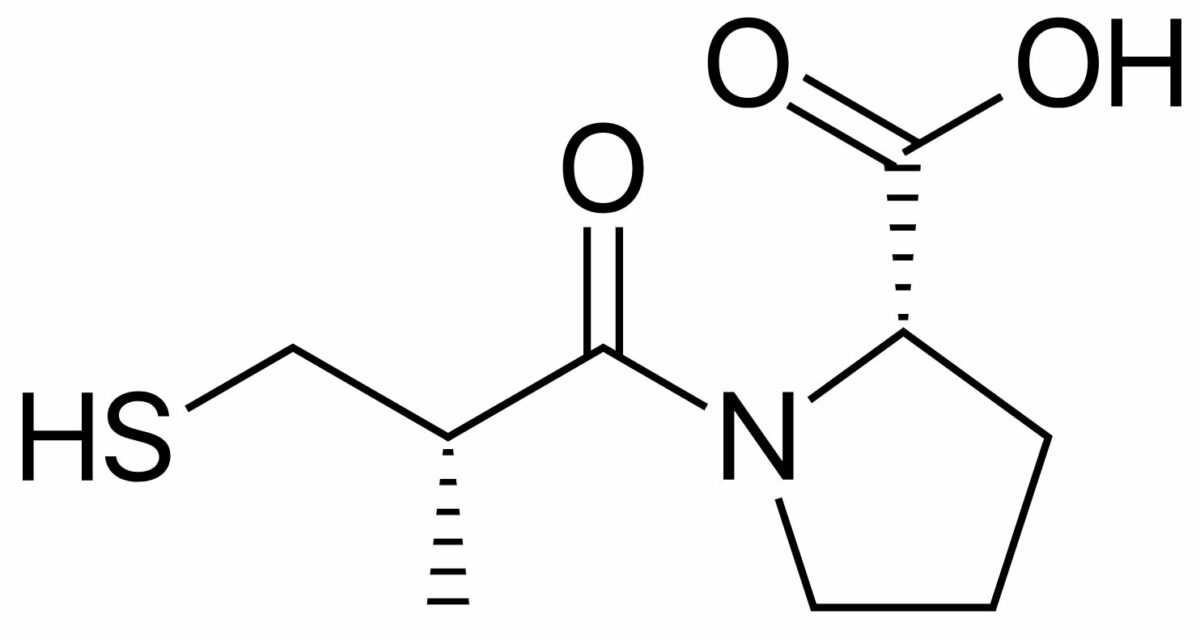
Estructura química del captopril (marca Capoten), un IECA muy utilizado
Imagen: “Captopril structure” por Vaccinationist. Licencia: Dominio Público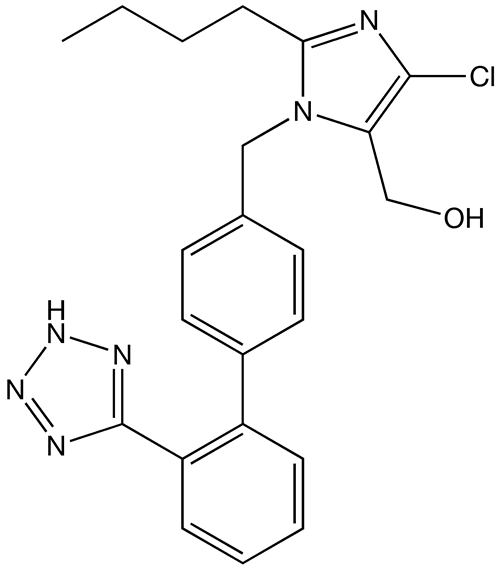
Estructura química del losartán, un ARA ampliamente utilizado
Imagen: “Losartan structure” por Techelf. Licencia: Dominio Público| Clase del medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Efectos fisiológicos |
|---|---|---|
| IECA | Inhibe la ECA, evitando:
|
Disminución de la resistencia vascular periférica vía:
|
| ARA | Inhiben los LOS Neisseria receptores de angiotensina-1, impidiendo que ejerzan sus efectos |
|
| DRi | Inhibe directamente la actividad de la renina, bloqueando la conversión del angiotensinógeno en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum angiotensina I | ↓ Angiotensina I, angiotensina II y aldosterona → ↓ resistencia vascular periférica. |
| ARNI ARNi Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors | Combinación de ARA y un inhibidor de la neprilisina:
|
|
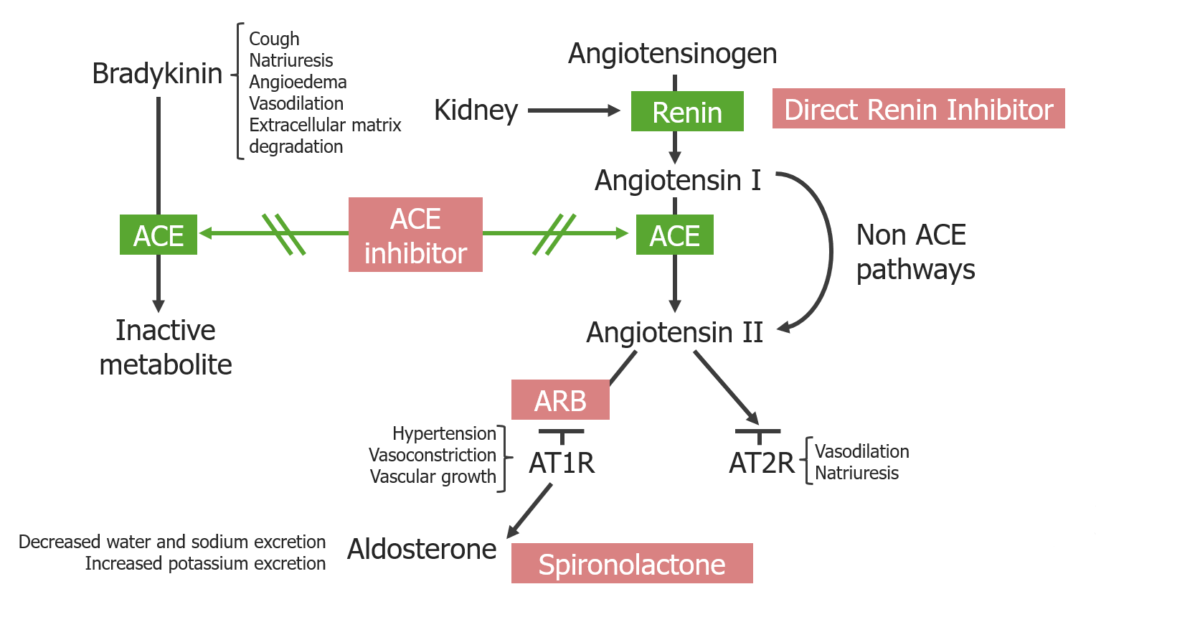
Descripción general de los inhibidores del SRAA y su sitio de acción:
Los inhibidores de la ECA bloquean tanto la degradación de la bradicinina como la generación de angiotensina II.
Los ARA bloquean los receptores de angiotensina II tipo 1. Los inhibidores directos de la renina bloquean la generación de angiotensina I.
La espironolactona bloquea los receptores mineralocorticoides en las células principales de los túbulos renales distales y del conducto colector cortical.
| Medicamento | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IECA |
|
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria medicamentos tienen una unión mínima a las proteínas y volúmenes de distribución relativamente modestos | Los LOS Neisseria profármacos se activan por hidrólisis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado; los LOS Neisseria medicamentos activos no se modifican. |
|
| ARA |
|
|
Metabolismo hepático |
|
| DRI: aliskiren Aliskiren Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors |
|
Unión a proteínas: 50% | Grado de metabolismo hepático desconocido |
|
Los LOS Neisseria efectos adversos más comunes de los LOS Neisseria IECA y los LOS Neisseria ARA se muestran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tabla.
| Síntoma | IECA | ARA (y ARNI ARNi Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors) |
|---|---|---|
| Hiperpotasemia | 1% | 0,3% |
| Tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome | 10%‒20% | 1 por cada 1 000 |
| Pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis | 1 por cada 5 000 |
|
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema | 1 por cada 2 000 | 1 por cada 20 000 |
Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios adicionales pueden incluir:
| Medicamentos | Mecanismos | Efectos fisiológicos | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|---|
| IECA | Inhibe la ECA, que:
|
|
|
| ARA | Inhiben los LOS Neisseria receptores de angiotensina-1, impidiendo que ejerzan sus efectos |
|
|
| Bloqueadores de los LOS Neisseria canales de calcio | Se unen e inhiben los LOS Neisseria canales de calcio de tipo L en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria miocitos cardíacos y el músculo liso vascular |
|
|
| Betabloqueadores | Inhiben los LOS Neisseria receptores β de las catecolaminas con distinta afinidad por los LOS Neisseria receptores β1 frente a los LOS Neisseria β2 |
|
|
| Diuréticos tiazídicos | ↓ Reabsorción de NaCl en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el túbulo contorneado distal mediante la inhibición del cotransportador de Na+/cloro |
|
|
| Diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome | Inhiben el cotransportador luminal de Na+/K+/cloro en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama ascendente gruesa del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle |
|
|
| Diuréticos ahorradores de K+ |
|
|
|