Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica bloquean las enzimas de la anhidrasa carbónica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el túbulo contorneado proximal, inhibiendo la reabsorción de bicarbonato de sodio (NaHCO3), lo que provoca diuresis y acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis metabólica. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica también bloquean la anhidrasa carbónica presente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ojos y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células gliales, lo que provoca una disminución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la producción de humor Humor Defense Mechanisms acuoso y de líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR) respectivamente. La acetazolamida es el prototipo de los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica se utilizan principalmente para el tratamiento de la enfermedad de las alturas, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con alcalosis metabólica, glaucoma Glaucoma Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by typical visual field defects and optic nerve atrophy seen as optic disc cupping on examination. The acute form of glaucoma is a medical emergency. Glaucoma is often, but not always, caused by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). Glaucoma y, a veces, como tratamiento adyuvante para ciertos tipos de epilepsias y pacientes con aumento de la presión intracraneal. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica no se utilizan para el tratamiento de la hipertensión.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica son diuréticos que bloquean las enzimas de la anhidrasa carbónica.
La acetazolamida es una sulfonamida.
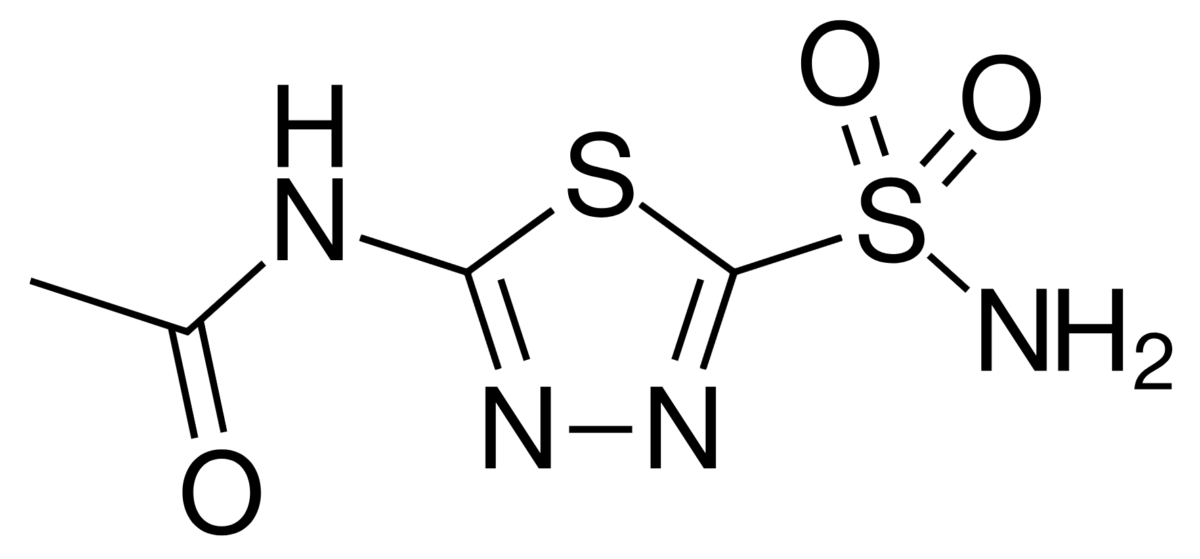
Estructura química de la acetazolamida
Imagen: “Acetazolamida” por Ayacop. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl bicarbonato no puede ser reabsorbido directamente por los LOS Neisseria riñones; primero debe ser convertido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum CO2 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lumen y luego reconvertido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum HCO3– una vez dentro de la célula. Esta reacción se produce a través de los LOS Neisseria siguientes procesos:
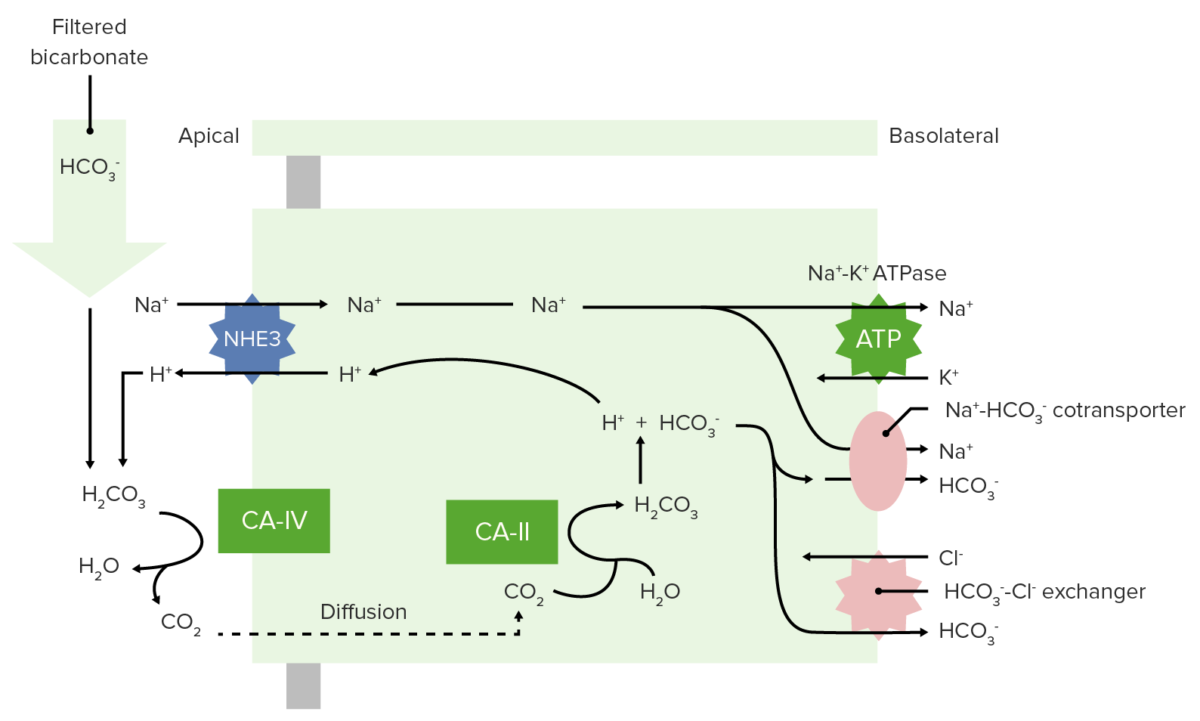
Reabsorción de bicarbonato en el túbulo proximal
NHE3: Intercambiador de Na+-H+ 3
CA-IV: anhidrasa carbónica IV
CA-II: anhidrasa carbónica II
El uso de los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica causa:
| Medicamento | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetazolamida |
|
|
No se metaboliza |
|
| Metazolamida |
|
|
Lento, dentro del tracto gastrointestinal |
|
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la anhidrasa carbónica deben utilizarse con precaución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las siguientes poblaciones:
Algunos de los LOS Neisseria otros diuréticos más comunes son los LOS Neisseria diuréticos tiazídicos (e.g., hidroclorotiazida), diuréticos de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome (e.g., furosemida), diuréticos ahorradores de K+ (e.g., espironolactona) y diuréticos osmóticos (e.g., manitol).
| Medicamento | Mecanismo | Efecto fisiológico | Indicación |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diurético tiazídico: Hidroclorotiazida | ↓ Reabsorción de NaCl en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el TCD a través de la inhibición del cotransportador de Na+/Cl– |
|
|
| Diurético de asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome: Furosemida | Inhibe el cotransportador luminal de Na+/K+/Cl– en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la rama ascendente gruesa del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome de Henle |
|
|
| Diurético ahorrador de potasio: Espironolactona |
|
|
|
| Inhibidor de la anhidrasa carbónica: Acetazolamida | Inhibe tanto la hidratación del CO2 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células epiteliales del TCP como la deshidratación del H2CO3 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lumen del TCP; provocando una excreción ↑ de HCO3– y Na+ |
|
|
| Diuréticos osmóticos: Manitol | ↑ Presión osmótica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el filtrado glomerular → ↑ líquido tubular e impide la reabsorción de agua |
|
|
Los sitios de acción, dentro de la nefrona, para las clases de medicamentos diuréticos
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0