La infertilidad es la incapacidad de concebir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el contexto de relaciones sexuales regulares. Las causas más comunes de infertilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres están relacionadas con la disfunción ovulatoria o la obstrucción de las trompas, mientras que, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hombres, los LOS Neisseria espermatozoides anormales son una causa común. El diagnóstico de infertilidad implica evaluaciones de laboratorio para la función ovulatoria y una histerosalpingografía para determinar la permeabilidad de las trompas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres y análisis de semen para evaluar la condición en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hombres. El manejo implica el tratamiento de la patología subyacente cuando sea posible y puede incluir la inducción de la ovulación con coito programado o inseminación intrauterina, fertilización in vitro y gametos de donante o por sustitución gestacional o adopción.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La infertilidad se define como la incapacidad de una pareja para concebir después de 12 meses de relaciones sexuales regulares, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que la mujer es < 35 años de edad o después de 6 meses de relaciones regulares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pareja, cuando la mujer es > 35 años de edad.
Para lograr el embarazo, la mujer debe estar ovulando con trompas de Falopio permeables y un útero receptivo, mientras que el hombre debe producir esperma que sea capaz de fertilizar el ovocito.
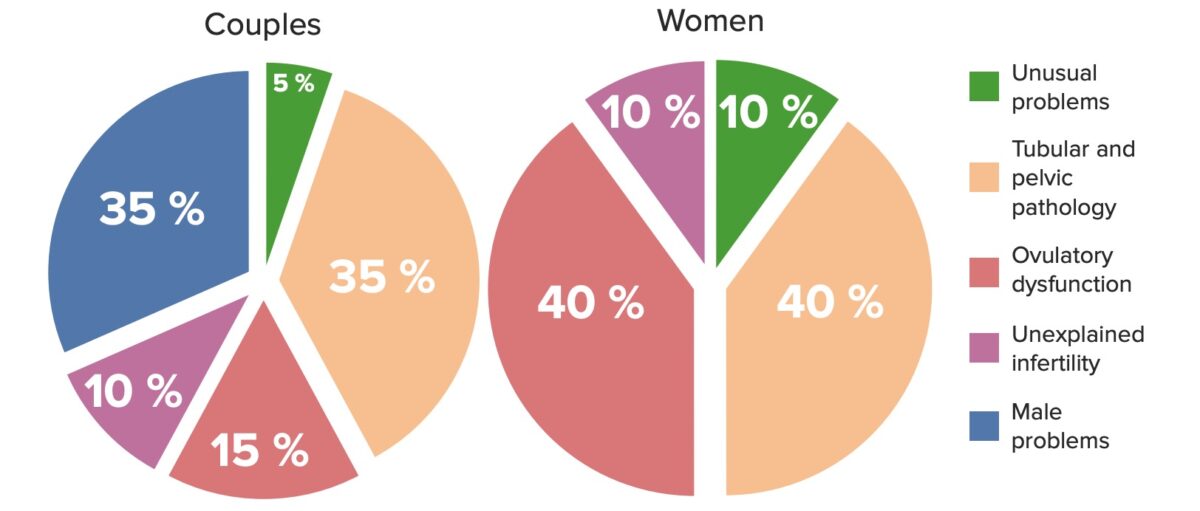
Etiologías de la infertilidad en la pareja (izquierda) y en la mujer (derecha)
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Las causas de la infertilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres se pueden categorizar como disfunción ovulatoria, factores tubáricos y factores uterinos.
Revisión del eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-ovario:
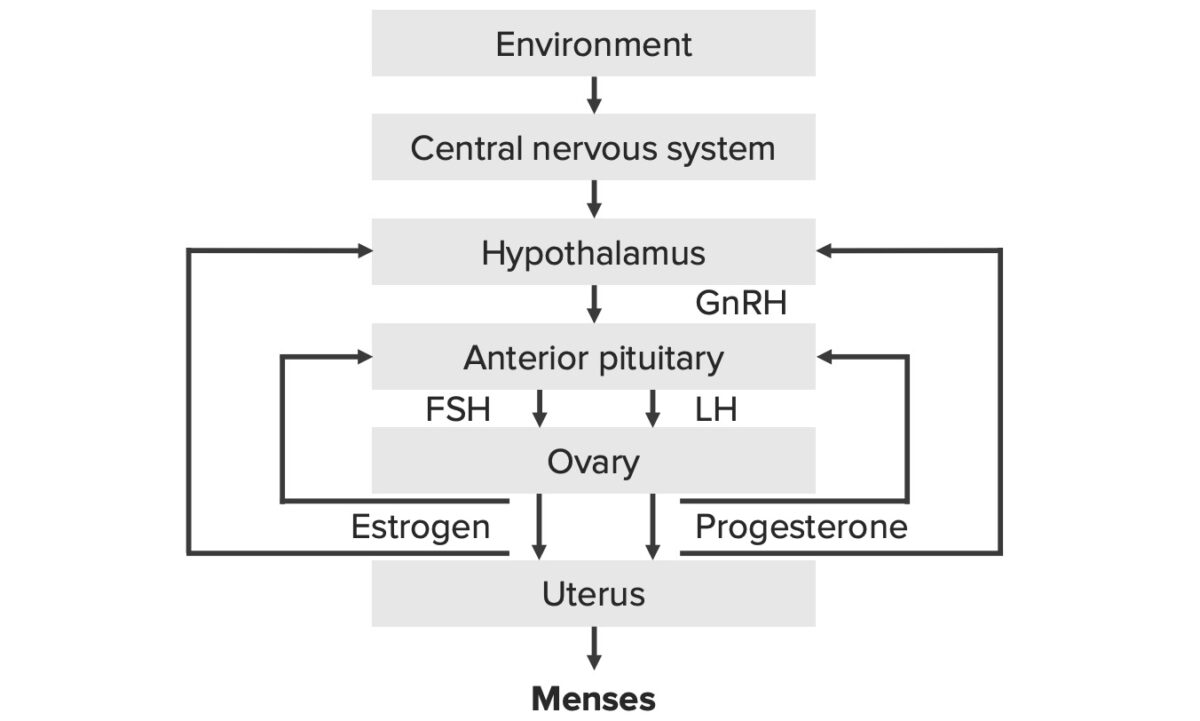
Eje hipotálamo-hipófisis-ovario
GnRH: hormona liberadora de gonadotropina
FSH: hormona foliculoestimulante
LH: hormona luteinizante
Disfunción ovulatoria:
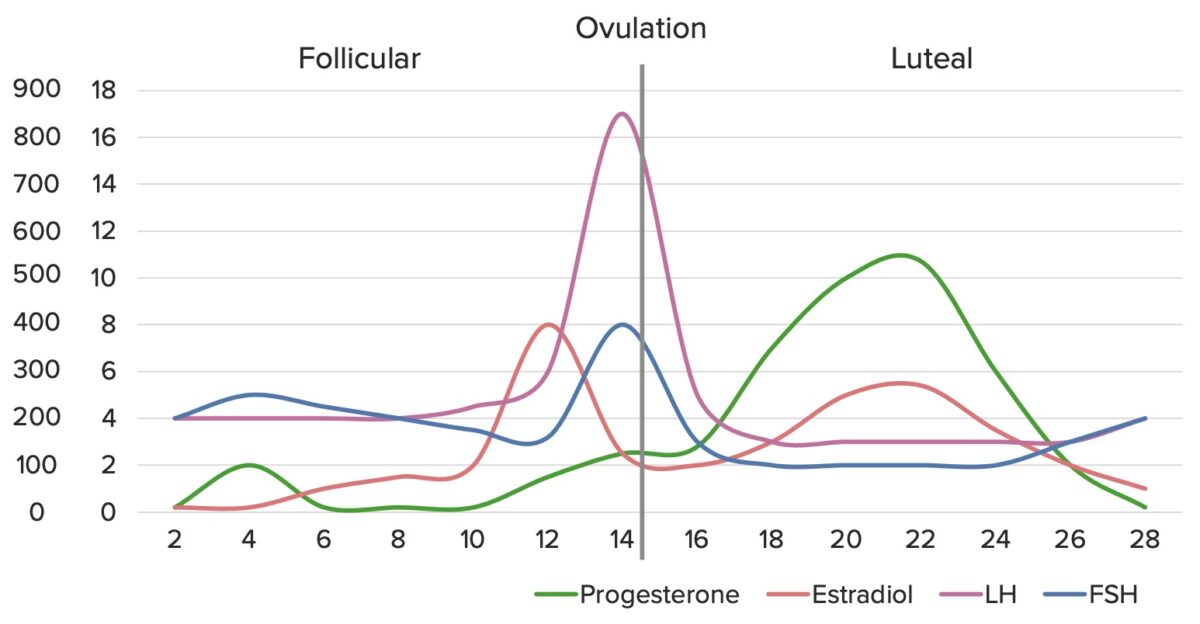
Fluctuaciones hormonales normales a lo largo del ciclo menstrual.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Factores tubáricos:
Factores uterinos:
Trastornos endocrinos y sistémicos:
Defectos testiculares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la espermatogénesis:
Trastornos del transporte espermático y disfunción sexual:
Clínica:
Antecedente menstrual cuidadoso: los LOS Neisseria ciclos regulares con molimina (sensibilidad mamaria cíclica y dolor Dolor Inflammation ovulatorio) sugieren fuertemente la ovulación.
Pruebas de laboratorio:
Imagenología:
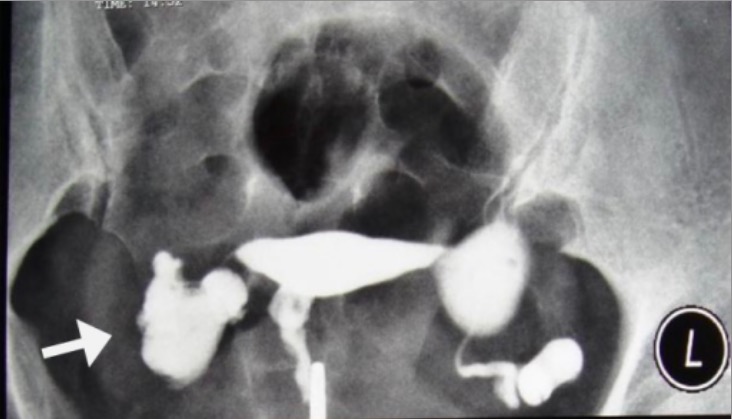
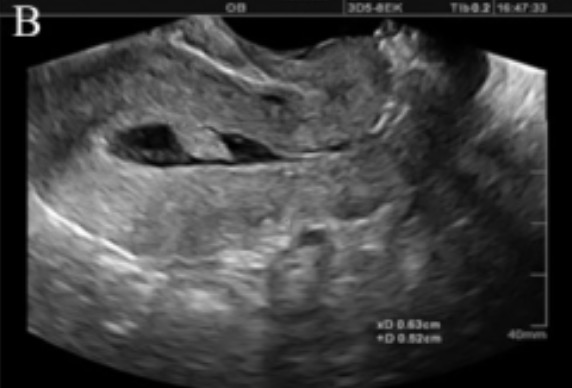
Ultrasonido con infusión de solución salina que muestra una lesión pedunculada (probablemente un pólipo) en la cavidad uterina:
En un ultrasonido transvaginal normal sin la infusión de solución salina, este hallazgo simplemente aparecería como un área de revestimiento endometrial engrosado.
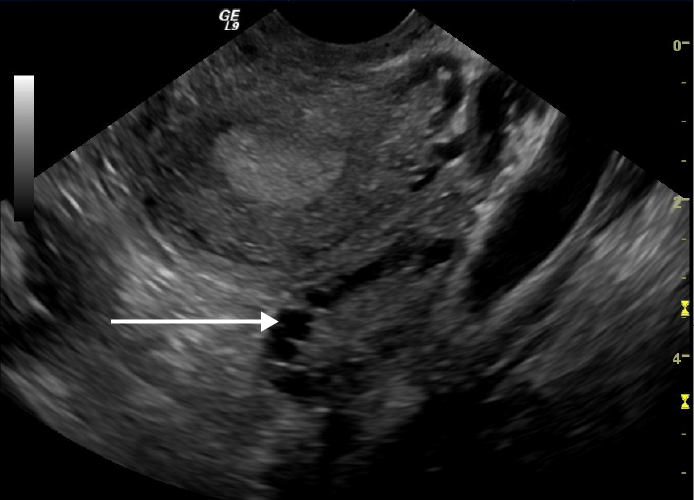
Ultrasonido transvaginal que muestra un ovario poliquístico:
Nótese los múltiples quistes en la periferia del ovario (flecha blanca).
Cirugía:
Análisis de semen:
| Volumen | 1,5–5,0 mL |
|---|---|
| pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance | > 7,2 |
| Viscosidad | < 3 |
| Concentración espermática | 15 millones/mL |
| Recuento total de espermatozoides | > 40 millones/mL |
| Porcentaje de motilidad | > 40% |
| Progresión hacia adelante | > 2 (basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una escala del 0 al AL Amyloidosis 4) |
| Morfología normal | > 4% normales |
| Células redondas | < 1 millón/mL |
| Aglutinación de espermatozoides | < 2 |
Laboratorio e imágenes si el análisis de semen es anormal:

Inseminación intrauterina
Imagen: “Assisted reproductive technology process” por BruceBlaus. Licencia: CC BY 3.0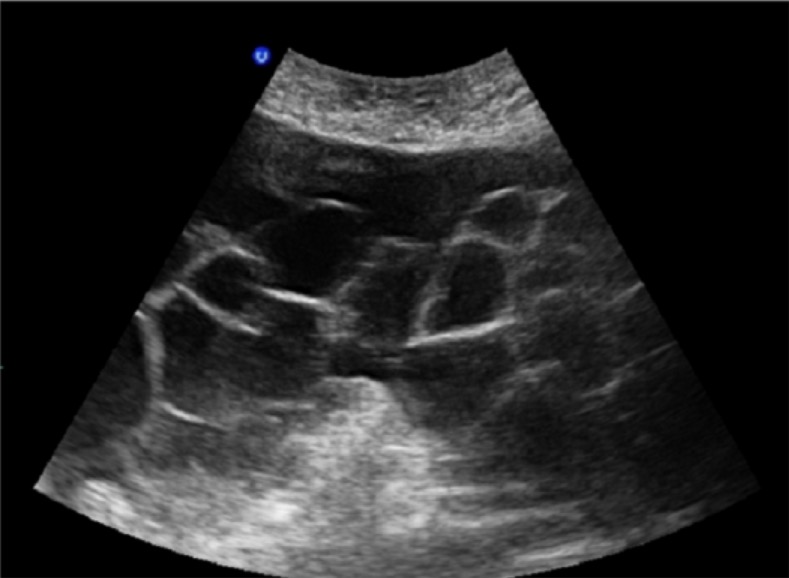
Masas quísticas multiloculares bilaterales en una paciente con síndrome de hiperestimulación ovárica en un embarazo espontáneo con mola invasora
Imagen: “Bilateral multilocular cystic masses” por Myriam Rachad et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0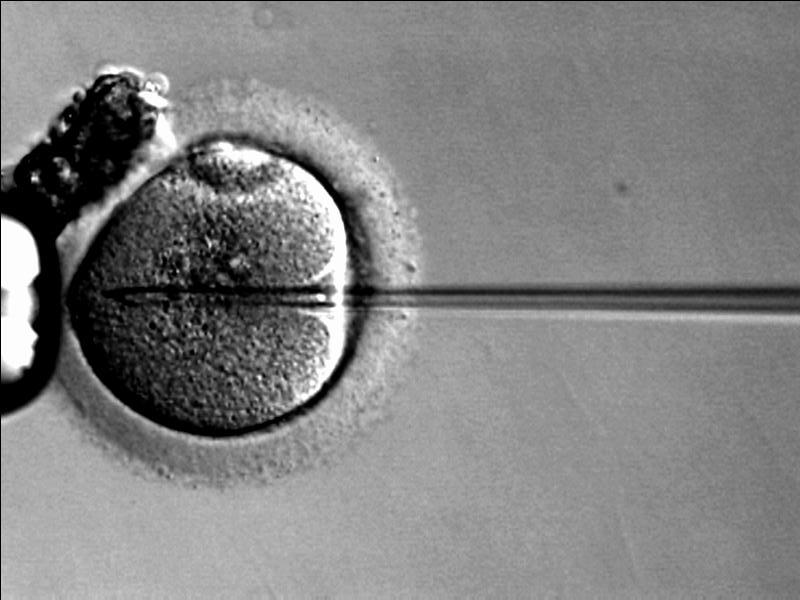
Inyección intracitoplasmática de espermatozoide:
Una técnica utilizada en parejas que tienen baja motilidad en el análisis de semen o múltiples intentos fallidos de fertilización in vitro