Las hormonas son moléculas mensajeras que se sintetizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una parte del cuerpo y se mueven a través del torrente sanguíneo para ejercer efectos reguladores específicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum otra parte del cuerpo. Las hormonas juegan un papel fundamental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la coordinación de las actividades celulares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el cuerpo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta a los LOS Neisseria cambios constantes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria entornos interno y externo. El trabajo de las hormonas permite que el cuerpo mantenga la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death y regule el crecimiento y el desarrollo. Las hormonas generalmente se fabrican a partir de aminoácidos o se derivan del colesterol (este último grupo se conoce como hormonas esteroideas). Las hormonas ejercen sus efectos uniéndose a receptores en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la superficie celular (la mayoría de las hormonas basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aminoácidos) o dentro del citosol (hormonas esteroideas). En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum última instancia, la unión a los LOS Neisseria receptores desencadena cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la expresión génica o la actividad enzimática dentro de la célula.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las hormonas son moléculas mensajeras que se sintetizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una parte del cuerpo y se mueven a través del torrente sanguíneo para ejercer efectos reguladores específicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum otra parte del cuerpo.
Las principales funciones de las hormonas incluyen:
Las principales glándulas endocrinas del cuerpo incluyen:
| Glándula/órgano | Hormona secretada por la glándula/órgano | Efecto primario de la hormona |
|---|---|---|
| Hipotálamo | Hormona liberadora de tirotropina | Estimula los LOS Neisseria tirotropos hipofisarios para secretar hormona estimulante de la tiroides |
| Hormona liberadora de corticotropina | Estimula a los LOS Neisseria corticotropos hipofisarios para que secreten la hormona adrenocorticotropa (ACTH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) | |
| Hormona liberadora de gonadotropina | Estimula a los LOS Neisseria gonadotropos hipofisarios para que secreten hormona foliculoestimulante y hormona luteinizante | |
| Hormona liberadora de la hormona del crecimiento | Estimula los LOS Neisseria somatotropos hipofisarios para secretar hormona del crecimiento | |
| Somatostatina | Inhibe la liberación de hormona del crecimiento y hormona estimulante de la tiroides de la hipófisis | |
| Dopamina | Inhibe la liberación de prolactina de los LOS Neisseria lactotropos hipofisarios | |
| Hipófisis anterior | Hormona estimulante de la tiroides | Estimula la secreción de las hormonas tiroideas |
| ACTH | Estimula la secreción de hormonas por la corteza suprarrenal | |
| Hormona foliculoestimulante | Estimula la producción de gametos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las gónadas | |
| Hormona luteinizante | Estimula la producción de andrógenos gonadales | |
| Hormona de crecimiento | Promueve el crecimiento de los LOS Neisseria tejidos del cuerpo | |
| Prolactina | Favorece la producción de leche materna | |
| Hipófisis posterior | Hormona antidiurética | Estimula la absorción de agua por los LOS Neisseria riñones |
| Oxitocina | Estimula:
|
|
| Glándula pineal | Melatonina | Regula los LOS Neisseria ciclos de sueño |
| Glándula tiroidea | Hormonas tiroideas:
|
Estimula el metabolismo celular |
| Calcitonina | ↓ Ca2+ sérico | |
| Glándula paratiroidea | Hormona paratiroidea (PTH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) | ↑ Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ sérico |
| Corteza suprarrenal | Mineralocorticoides: aldosterona |
|
Glucocorticoides:
|
|
|
| Andrógenos | Estimula las características sexuales secundarias | |
| Médula suprarrenal | Catecolaminas:
|
Estimula la reacción de lucha o huida |
| Gónadas | Testosterona | Estimula:
|
| Estrógeno y progesterona |
|
|
| Inhibina | Inhibe selectivamente la liberación de hormona foliculoestimulante | |
| Placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity | Estrógeno | Apoya la fisiología materna durante el embarazo |
| Progesterona |
|
|
| Gonadotropina coriónica humana (hCG, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) | Mantiene la actividad endocrina del cuerpo lúteo | |
| Lactógeno placentario humano | Altera la secreción de insulina materna para ↑ glucosa para el feto | |
| Factor de crecimiento similar a la insulina | Regula el crecimiento fetal | |
| Hormona liberadora de ACTH placentaria y glucocorticoides | Regular Regular Insulin el desarrollo y la maduración de los LOS Neisseria órganos |
| Glándula/órgano | Hormona secretada por la glándula/órgano | Efecto primario de la hormona |
|---|---|---|
| Estómago | Gastrina, histamina | Estimula la secreción de ácido clorhídrico ( HCl HCL Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare, chronic, B-cell leukemia characterized by the accumulation of small mature B lymphocytes that have “hair-like projections” visible on microscopy. The abnormal cells accumulate in the peripheral blood, bone marrow (causing fibrosis), and red pulp of the spleen, leading to cytopenias. Hairy Cell Leukemia) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el estómago |
| Serotonina | Estimula la motilidad gástrica | |
| Páncreas | Insulina | ↓ Niveles de azúcar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre al AL Amyloidosis mover la glucosa a través de las membranas celulares hacia el espacio intracelular |
| Glucagón | ↑ Niveles de azúcar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sangre al AL Amyloidosis estimular la gluconeogénesis y la glucogenólisis | |
| Intestinos | Secretina |
|
| Colecistoquinina |
|
|
| Polipéptido insulinotrópico dependiente de la glucosa |
|
|
| Péptido similar al AL Amyloidosis glucagón-1 ( GLP-1 GLP-1 A peptide of 36 or 37 amino acids that is derived from proglucagon and mainly produced by the intestinal l cells. Glp-1(1-37 or 1-36) is further n-terminally truncated resulting in glp-1(7-37) or glp-1-(7-36) which can be amidated. These glp-1 peptides are known to enhance glucose-dependent insulin release, suppress glucagon release and gastric emptying, lower blood glucose, and reduce food intake. Insulinomas) |
|
|
| Timo | Timopoyetina | Regula la función inmunológica |
| Tejido adiposo | Leptina | Suprime la ingesta de alimentos |
| Corazón | Péptido natriurético auricular (ANP, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) | Reduce el volumen plasmático al AL Amyloidosis estimular la diuresis |
| Hígado | Angiotensinógeno | Un precursor de la angiotensina II, un potente vasoconstrictor que estimula la aldosterona |
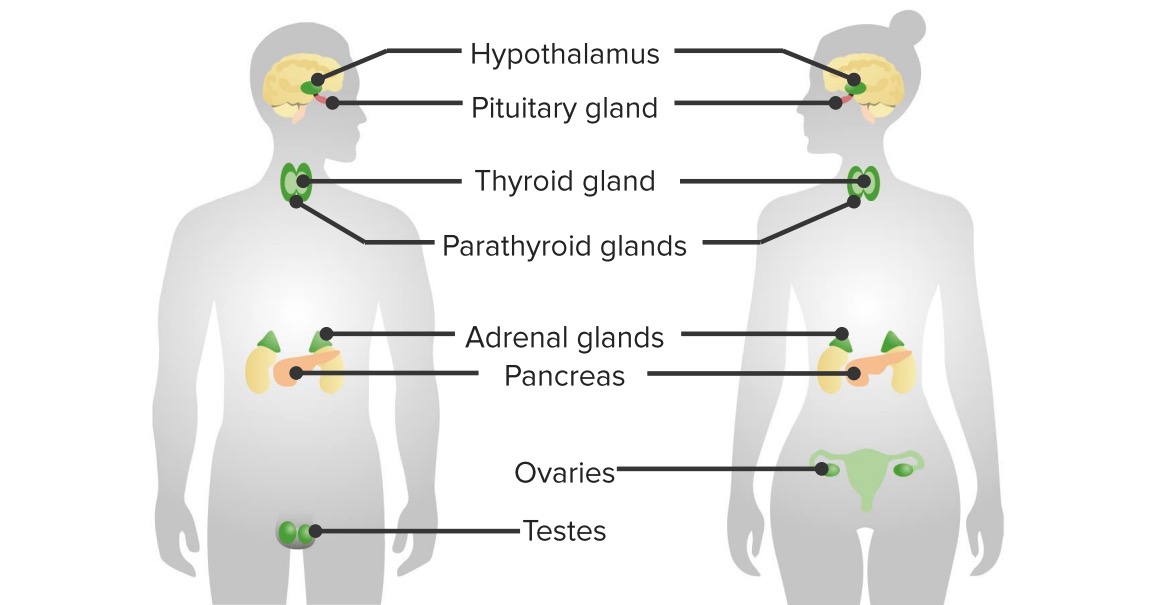
Órganos principales del sistema endocrino
Imagen por Lecturio.La mayoría de las hormonas están basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aminoácidos.
La mayoría de las hormonas se unen a los LOS Neisseria receptores, que luego transmiten su mensaje a través de mensajeros secundarios y/o cascadas de señales. Las hormonas esteroideas, cuando se unen a sus receptores, pueden unirse directamente al AL Amyloidosis ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) y afectar la expresión génica.
Hay varias formas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum que las hormonas envían mensajes por todo el cuerpo:
Los LOS Neisseria receptores de membrana plasmática suelen ser necesarios para las hormonas basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aminoácidos y utilizan sistemas de 2do mensajero y cascadas de señales:
Los LOS Neisseria receptores intracelulares generalmente provocan la activación directa de genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure:
Señalización de hormonas esteroideas
Imagen por Kevin Ahern, MD.Prácticamente, todas las hormonas enumeradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las tablas pueden secretarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niveles anormales, lo que da como resultado una amplia gama de afecciones clínicas. Algunas de estas afecciones incluyen: