Aunque la sangre entera fresca era el único producto disponible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria primeros años de la transfusión, la llegada de las técnicas de fraccionamiento de la sangre entera ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia permitido un uso más eficiente de los LOS Neisseria distintos componentes sanguíneos. Los LOS Neisseria hemoderivados fraccionados, preparados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria centros de transfusión de sangre, incluyen eritrocitos, plaquetas, plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products fresco congelado (PFC) y crioprecipitado. Estos productos se transfunden para diferentes indicaciones y cada uno aborda diferentes patologías.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
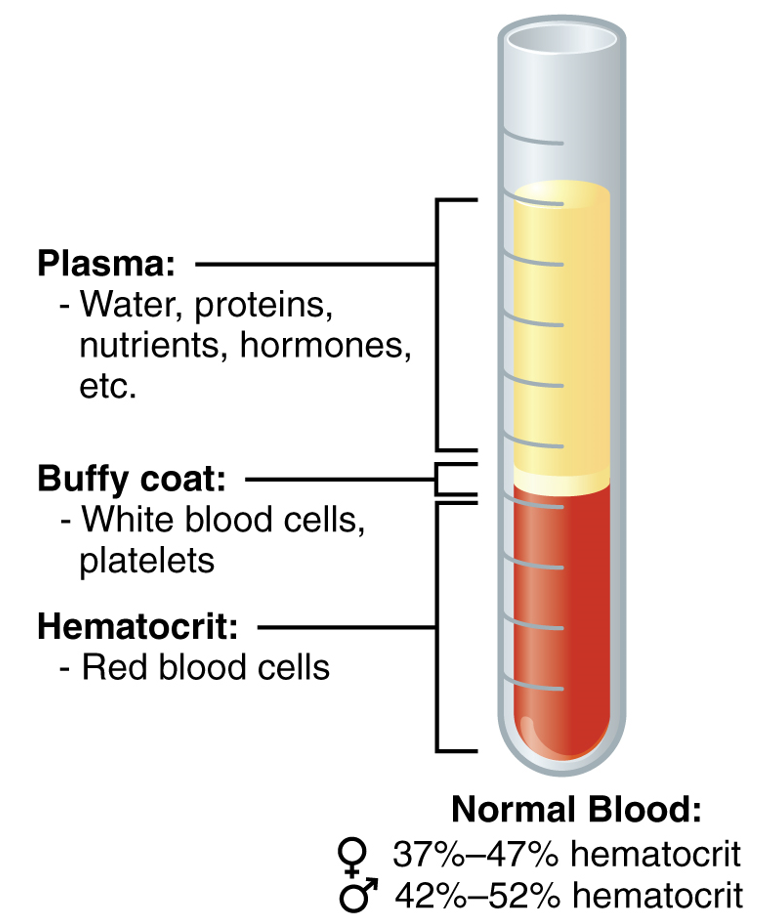
Un tubo centrifugado que muestra los componentes de la sangre entera (plasma, eritrocitos, plaquetas y leucocitos)
Imagen: “The cellular elements of blood include a vast number of erythrocytes and comparatively fewer leukocytes and platelets” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 4.0| Tipo de sangre | Puede donar a individuos con grupo sanguíneo: | Puede recibir de donantes con grupo sanguíneo: |
|---|---|---|
| A+ | A+, AB+ | A+, A–, O+, O |
| A– | A+, A-, AB+, AB– | A-, O– |
| B+ | B+, AB+ | B+, B–, O+, O– |
| B- | B+, B–, AB+, AB– | B–, O– |
| O+ | A+, B+, O+, AB+ | O+, O– |
| O– | A todos | O– |
| AB+ | AB+ | De todos |
| AB– | AB+, AB- | AB–, A–, B–, O– |
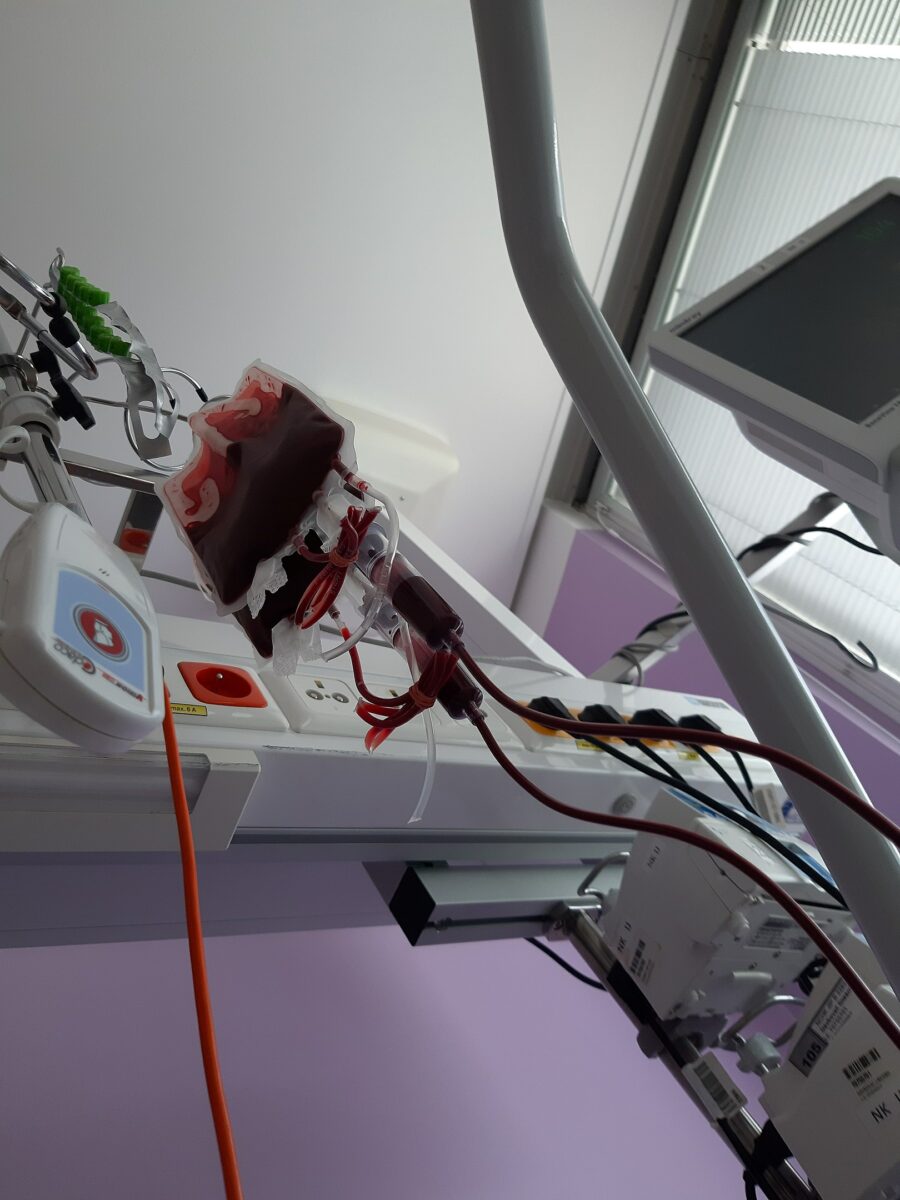
Imagen del proceso de extracción de sangre:
La bolsa de colección cuelga mientras se extrae sangre de un donante
| Componentes sanguíneos | Subcomponentes sanguíneos | Tipo | Lugar de producción | Tareas principales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products 43%–63% | Agua 92% | Líquido | Se absorbe en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal o se obtiene durante el metabolismo | Medio de transporte |
| Proteínas plasmáticas 7% | Albúmina 54%–60% | Hígado |
|
|
| Globulinas 35%–38% | Alfa globulinas: hígado | Transportar y mantener la concentración osmótica | ||
| Beta globulinas: hígado | Transportar y mantener la concentración osmótica | |||
| Gammaglobulinas (inmunoglobulinas): células plasmáticas | Respuesta inmune | |||
| Fibrinógeno 4%–7% | Hígado | Coagulación de la sangre durante la hemostasia | ||
| Proteínas reguladoras < 1% |
|
Varias localizaciones | Regular Regular Insulin diversas funciones corporales | |
| Otras sustancias disueltas 1%. |
|
|
Muchas funciones diferentes | |
| Elementos formes 37%–54% | Eritrocitos 99% | Eritrocitos | Médula roja | Transporta gases, O2 y algo de CO2 |
|
|
Médula roja | Respuesta inmune inespecífica | |
|
Linfocitos: médula ósea y tejido linfoide | Linfocitos: respuesta inmune específica | ||
| Monocitos: médula roja | Monocitos: respuesta inmune inespecífica | |||
| Plaquetas < 1% | — | Megacariocitos: médula roja | Hemostasia |
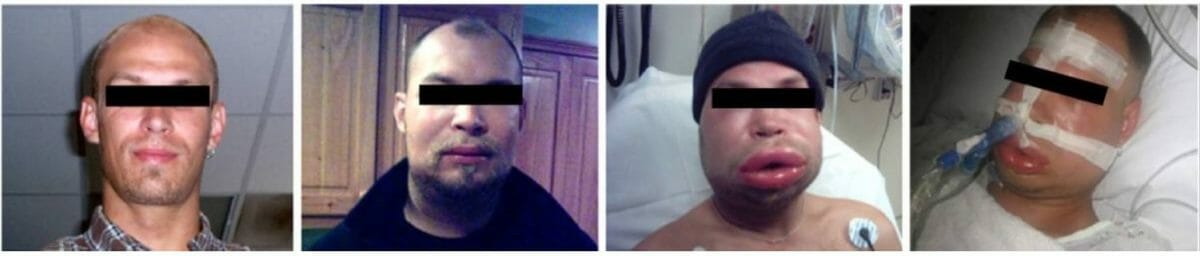
Individuos experimentando episodios agudos de angioedema hereditario
Imagen: “F1: HAE patient experiencing HAE attacks” por Bygum A. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0