La hemocromatosis hereditaria es un trastorno autosómico recesivo asociado con mayor frecuencia a mutaciones del gen HFE. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes tienen aumentada la absorción intestinal de hierro y el depósito de hierro en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varios órganos, como el hígado, el corazón, la piel y el páncreas. La presentación clínica incluye la tríada de cirrosis, diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus y bronceado de la piel. Otros hallazgos dependen del órgano u órganos involucrados. El diagnóstico consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estudios de hierro, que muestran elevación de transferrina y ferritina. Se recomienda el tamizaje genético entre los LOS Neisseria miembros de la familia. Se realiza imagenología y estudios invasivos dependiendo de las complicaciones asociadas. El tratamiento requiere flebotomía (o terapia de quelación de hierro en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos casos) para prevenir la progresión de la enfermedad. El pronóstico es bueno para los LOS Neisseria pacientes que se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las etapas tempranas de la enfermedad y que están bajo tratamiento. La presencia de fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans hepática es un factor de mal pronóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La hemocromatosis hereditaria es:
Es importante tener en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuenta que las causas de la sobrecarga de hierro pueden superponerse u ocurrir al AL Amyloidosis mismo tiempo.
Trastornos de sobrecarga de hierro secundarios (adquiridos):
Ciertas condiciones requieren una disminución o aumento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la absorción de hierro y el hierro circulante, una vía regulada por la hepcidina:
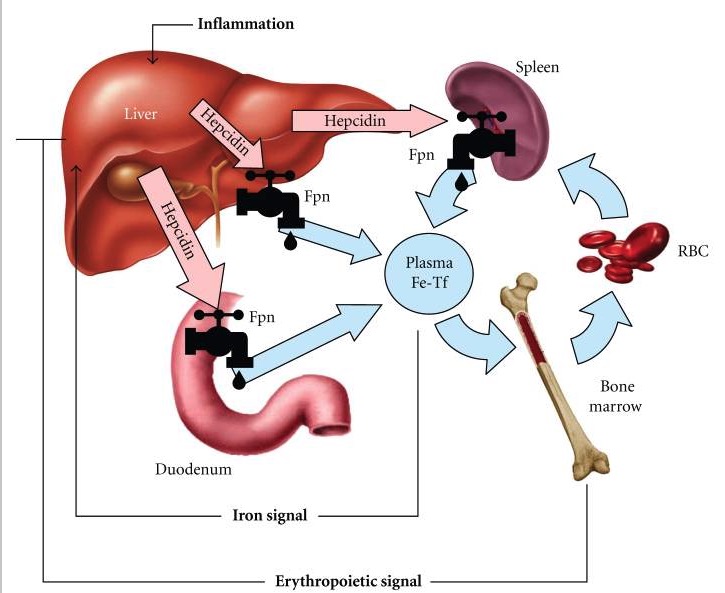
La interacción hepcidina-ferroportina determina el flujo de hierro al plasma.
1. El hierro de la dieta se capta intestinalmente en el duodeno.
2. El hierro se mueve desde el duodeno a través del transportador de hierro, ferroportina, y entra a la circulación a través de transferrina.
3. La transferrina lleva al hierro a la médula ósea para la síntesis de hemoglobina.
4. A medida que los eritrocitos envejecen, son fagocitados por macrófagos (principalmente en el bazo), liberando hierro nuevamente a la circulación a través de ferroportina.
5. Cuando hay un aumento de hierro o inflamación, aumenta la hepcidina, lo que reduce la absorción duodenal de hierro y la liberaciónb de hierro por la degradación de eritrocitos viejos.
6. Cuando se necesita una mayor formación de eritrocitos, la eritropoyetina inhibe la hepcidina para permitir una mayor absorción de hierro (desde el intestino) y liberar hierro desde los macrófagos con eritrocitos envejecidos.
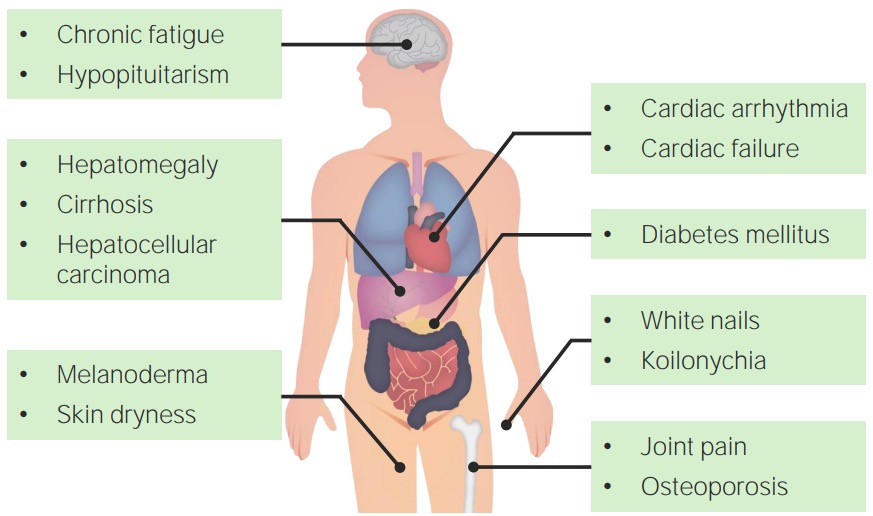
Características clínicas de la hemocromatosis.
Imagen por Lecturio.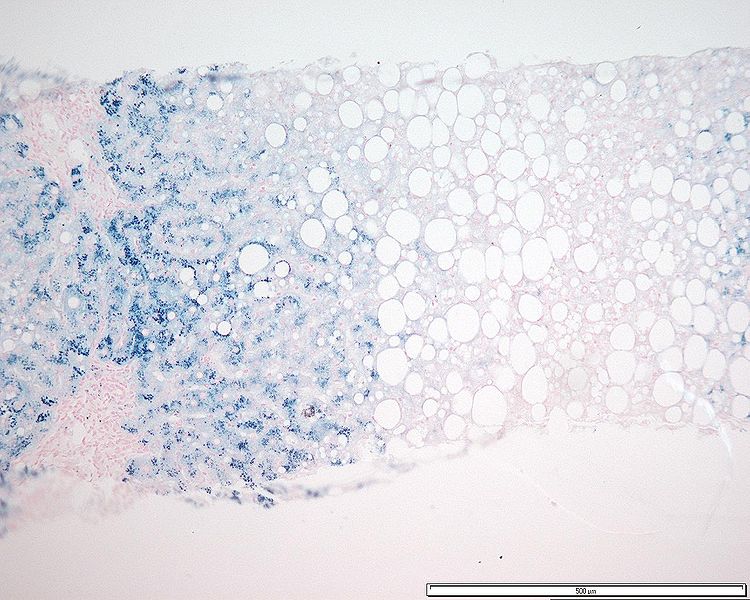
Acumulación de hierro en hepatocitos en un paciente con hemocromatosis (teñido con azul de Prusia de Perls)
Imagen: “Grade 3 hepatocyte iron accumulation” por Mathew, J. et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.