La ginecomastia es una proliferación benigna de tejido ductal glandular mamario masculino, generalmente bilateral, causada por el aumento de la actividad de los LOS Neisseria estrógenos, la disminución de la actividad de la testosterona o algunos medicamentos. La condición es común y fisiológica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum neonatos, adolescentes y adultos mayores hombres. Algunos casos son patológicos o secundarios a enfermedad hepática crónica, enfermedad renal o hipertiroidismo. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos son asintomáticos y no necesitan tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La ginecomastia asintomática es tan común que puede ser casi considerada como una condición normal, con una distribución trimodal según la edad.
La ginecomastia se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 grandes grupos: fisiológica, patológica e idiopática.
Para recordar las causas de la ginecomastia, recuerda el acrónimo “CODES” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
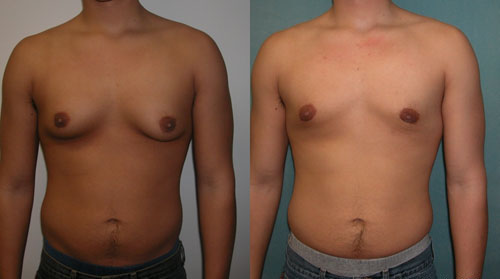
Ginecomastia fisiológica en un varón adolescente
Imagen: “Adolescent Gynecomastia corrected by surgery protocol” por David Andrew Copeland, Dr. Mordcai Blau. Licencia: Licencia de Documentación Libre de GNULas siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la ginecomastia: