Una fractura de cadera es una ruptura en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la corteza del fémur en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la articulación de la cadera, ya sea entre los LOS Neisseria trocánteres (intertrocantéreos) o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuello femoral. La fractura de cadera es una lesión grave y puede resultar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum complicaciones potencialmente mortales. Las causas incluyen un impacto de alta energía debido a un traumatismo, como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum accidentes automovilísticos, o un traumatismo de baja energía (caídas) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis. La presentación clínica incluye dolor Dolor Inflammation inguinal, sensibilidad a la palpación, inmovilidad y deformidad de las extremidades inferiores. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente y mediante imagenología. El tratamiento definitivo es generalmente quirúrgico, pero depende del tipo de fractura y del estado del paciente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Una fractura de cadera es una ruptura en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la corteza del fémur en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la articulación femoroacetabular (cadera), ya sea entre los LOS Neisseria trocánteres mayor y menor (intertrocantérea) o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuello femoral.
La cadera es una articulación esférica formada por la cabeza femoral y el acetábulo (cavidad). La irrigación a la cabeza femoral proviene de la arteria circunfleja.
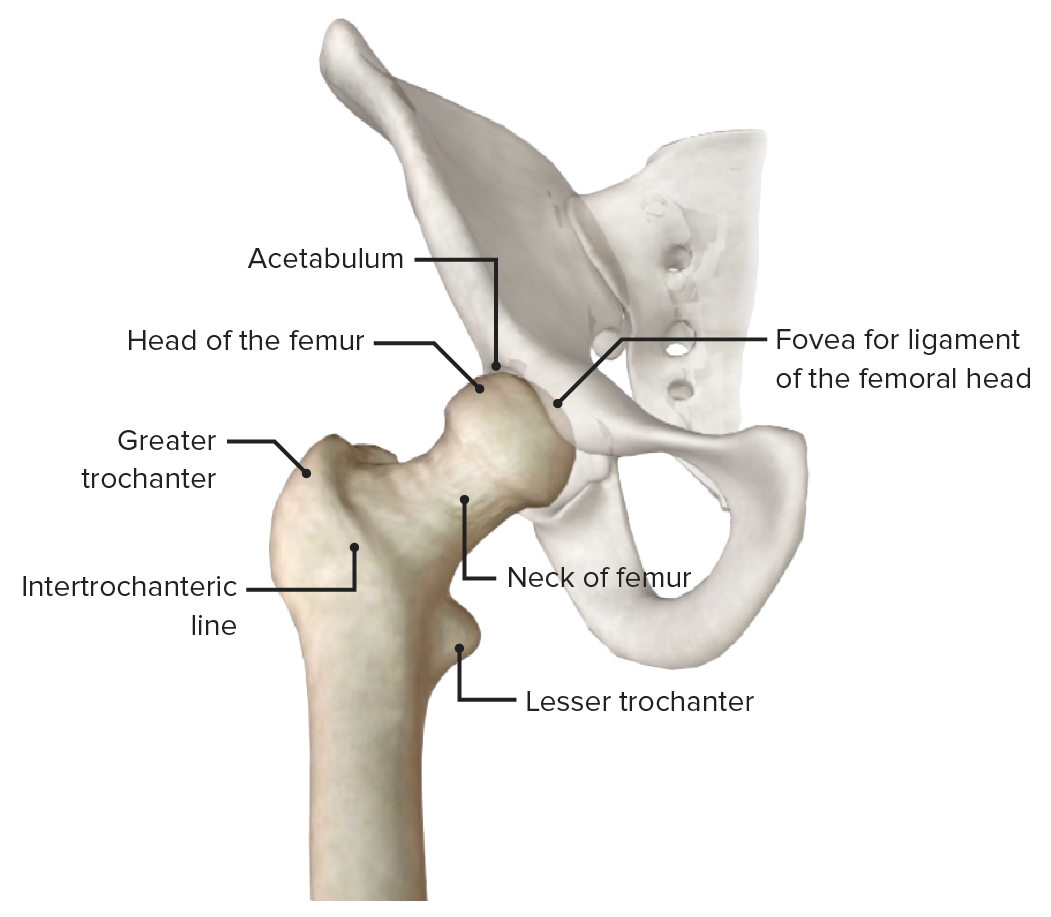
Vista anterior de la articulación de la cadera (pelvis atenuada), con los puntos de referencia óseos del extremo proximal del fémur
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por Lecturio
Vistas anterior y posterior de la articulación de la cadera con los ligamentos extraarticulares
Imagen por Lecturio.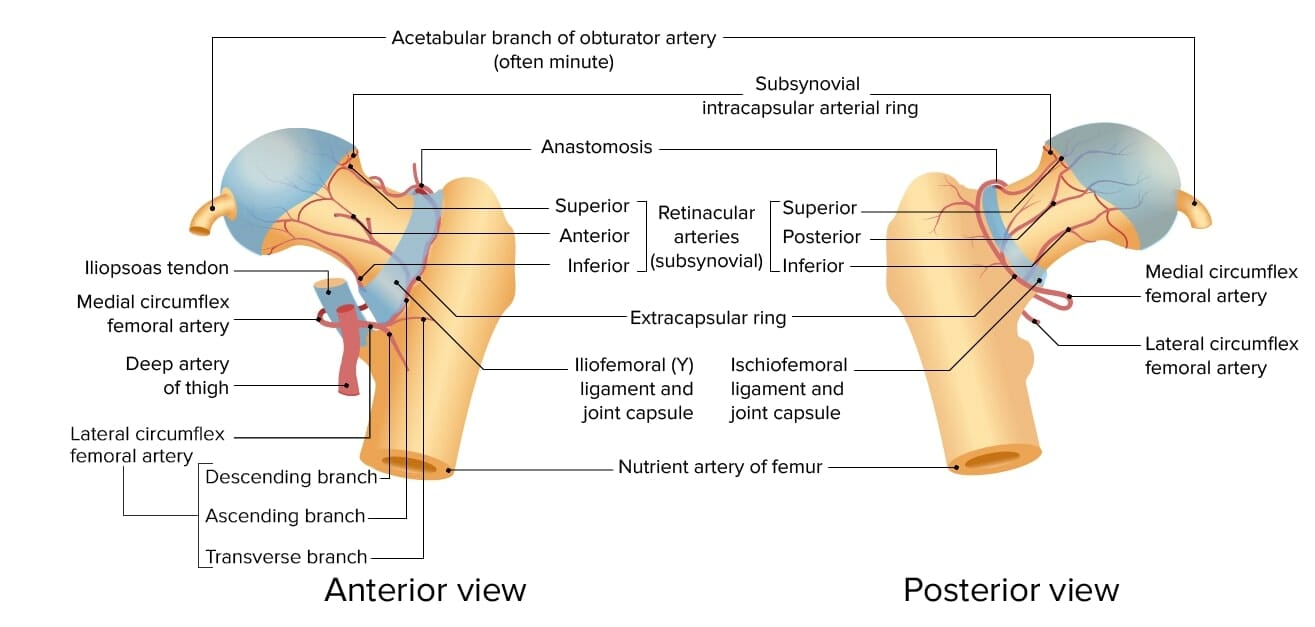
Irrigación de la cabeza y el cuello del fémur
Imagen por Lecturio.Las fracturas de cadera se clasifican por ubicación anatómica y tipo de fractura. Reconocer estas fracturas es importante para el tratamiento quirúrgico.
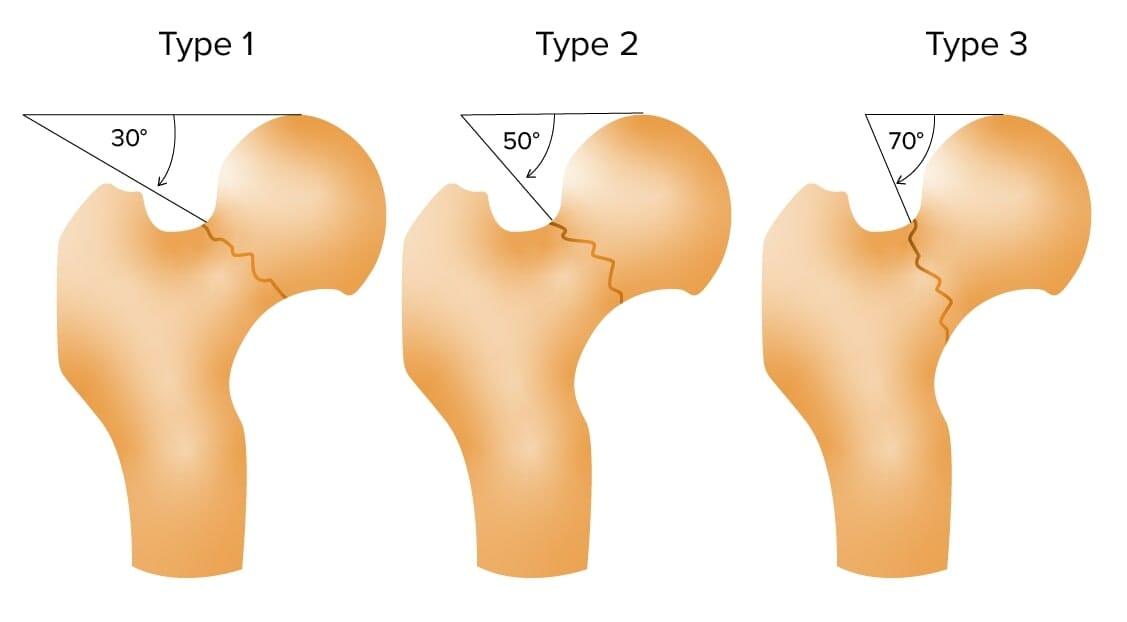
Clasificación de Pauwel de las fracturas de cuello de fémur
Imagen por Lecturio.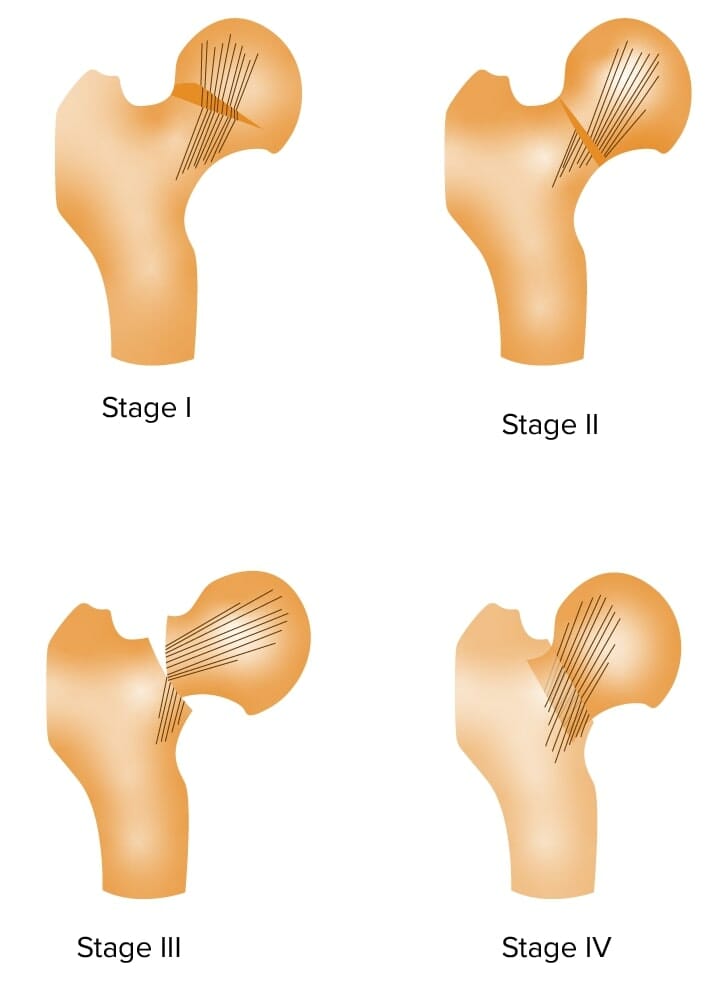
Clasificación de jardín de las fracturas de cuello de fémur
Imagen por Lecturio.El principio general detrás de todas las fracturas es que el hueso está sujeto a una carga que supera su capacidad, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una pérdida de integridad estructural.
La presentación de un paciente con fractura de cadera depende de la situación clínica.
El diagnóstico de una fractura de cadera se realiza clínicamente y con imagenología diagnóstica. Una fractura de cadera puede complicarse con una luxación dependiendo del grado de aducción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el momento del impacto, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum accidentes automovilísticos.
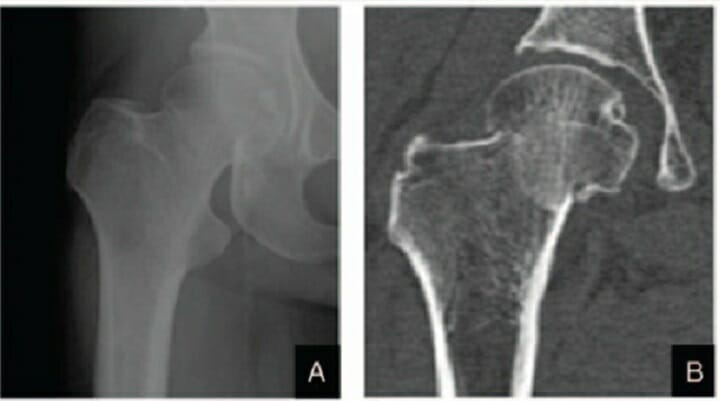
Fractura de cuello femoral derecho en estadio I de Garden:
A: Radiografía anteroposterior
B: TC coronal
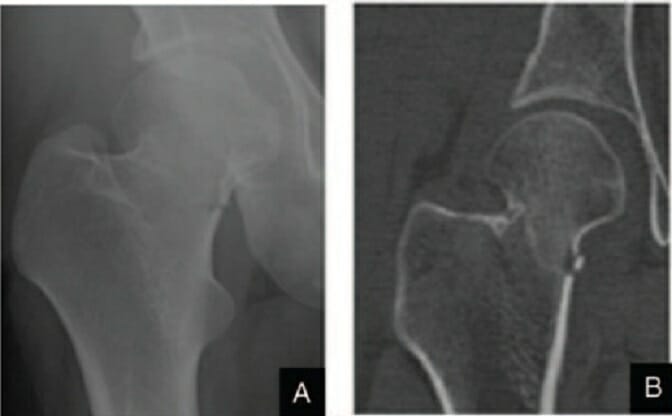
Fractura de cuello de fémur derecho en estadio II de Garden:
A: Radiografía anteroposterior
B: TC coronal
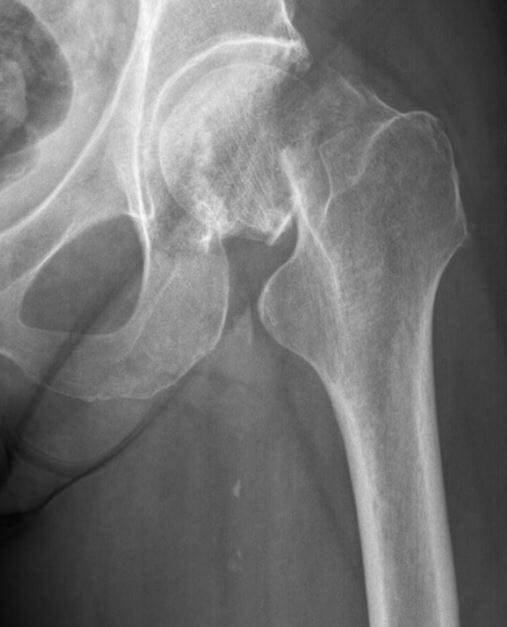
Fractura del cuello del fémur derecho en estadio III de Garden
Imagen: “Femoral Neck fracture” por Jillian Kazley. Licencia: CC BY 4.0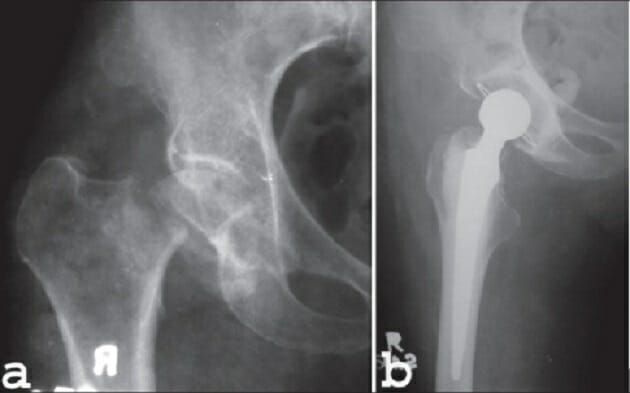
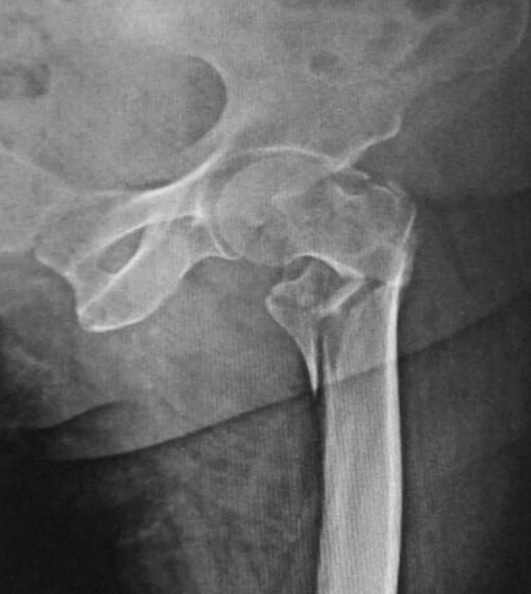
Radiografía de una fractura de cadera trocantérica conminuta
Imagen: “X-ray of a comminuted hip fracture” por Rohan R. Memon, Drashtant Patel and Nishant Juva. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El tratamiento definitivo depende del tipo de fractura y requiere la consulta con un cirujano ortopédico.
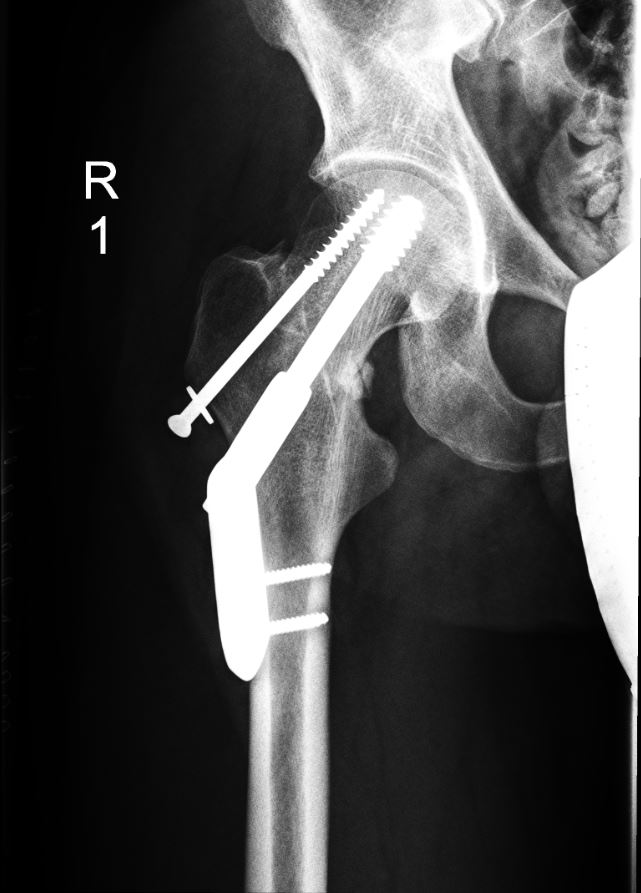
Fractura desplazada no especificada del fémur derecho con reparación quirúrgica
Imagen: “Hip fractures with DHS 1” por Prof. Dr. med. Ralf Puls. Licencia: CC BY 3.0