El examen de la piel es una parte fundamental del examen físico estándar. Este examen consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una inspección minuciosa de la piel de todo el cuerpo. La evaluación se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum identificar signos anormales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel, como el cuero cabelludo, los LOS Neisseria orificios, las uñas y las superficies mucosas. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos dermatológicos pueden representar procesos localizados o pueden ser un signo de enfermedad sistémica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las lesiones cutáneas primarias ocurren como resultado directo de un proceso patológico, mientras que las lesiones cutáneas secundarias son aquellas que resultan de la manipulación de la piel.
| Lesión cutánea primaria | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Mácula |
|
| Pápula | Lesión cutánea pequeña palpable ≤ 1 cm de diámetro |
| Placa | Lesión palpable, elevada > 1 cm |
| Nódulo |
|
| Vesícula | Ampolla pequeña que contiene líquido ≤ 1 cm de diámetro |
| Bulla Bulla Blister filled with fluid, > 1 cm diameter Generalized and Localized Rashes | Ampolla grande que contiene líquido > 1 cm de diámetro |
| Pústula | Vesícula llena de pus |
| Lesiones cutáneas secundarias | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Escama |
|
| Costra | Exudados secos, como pus o sangre |
| Fisura |
|
| Úlcera |
|
| Erosión |
|
| Necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage | Tejido de piel muerta |
| Atrofia |
|
| Cicatriz | Reemplazo de la piel con tejido fibroso y conectivo como resultado de la destrucción |
| Liquenificación |
|
Todas las superficies cutáneas y mucosas deben examinarse con buena luz. Use guantes, especialmente si la piel está lesionada.
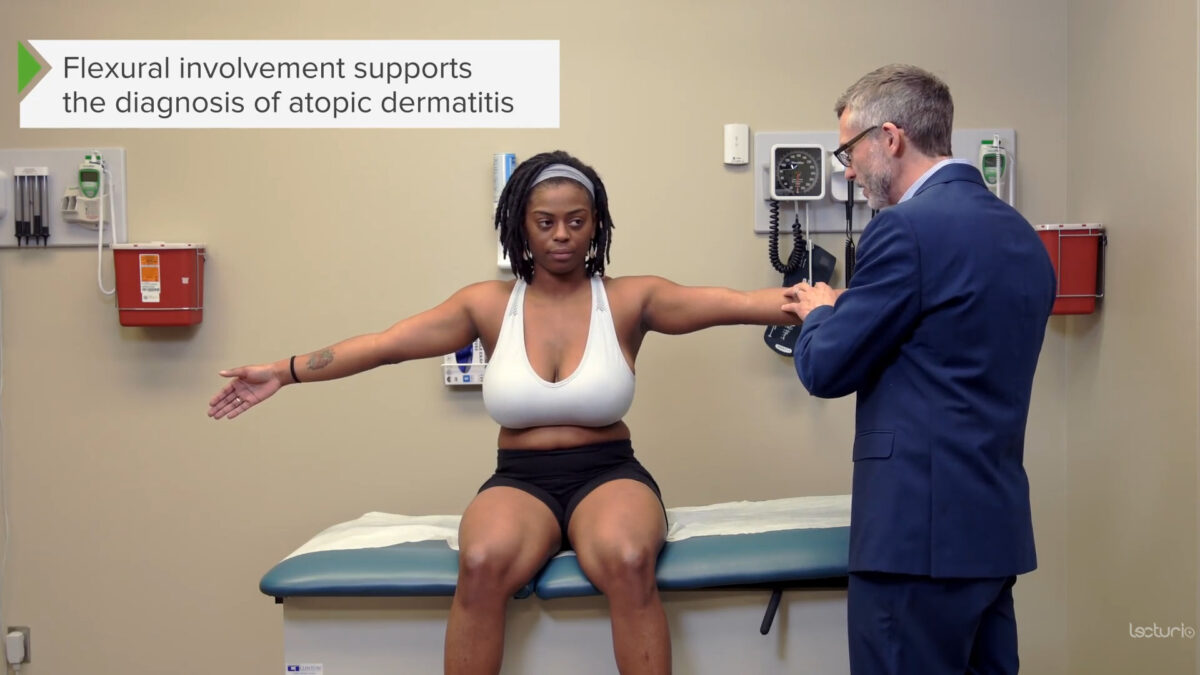
Examen de los aspectos flexores de los brazos (la afectación de las superficies de flexión sugiere con mayor frecuencia dermatitis atópica)
Imagen por Lecturio.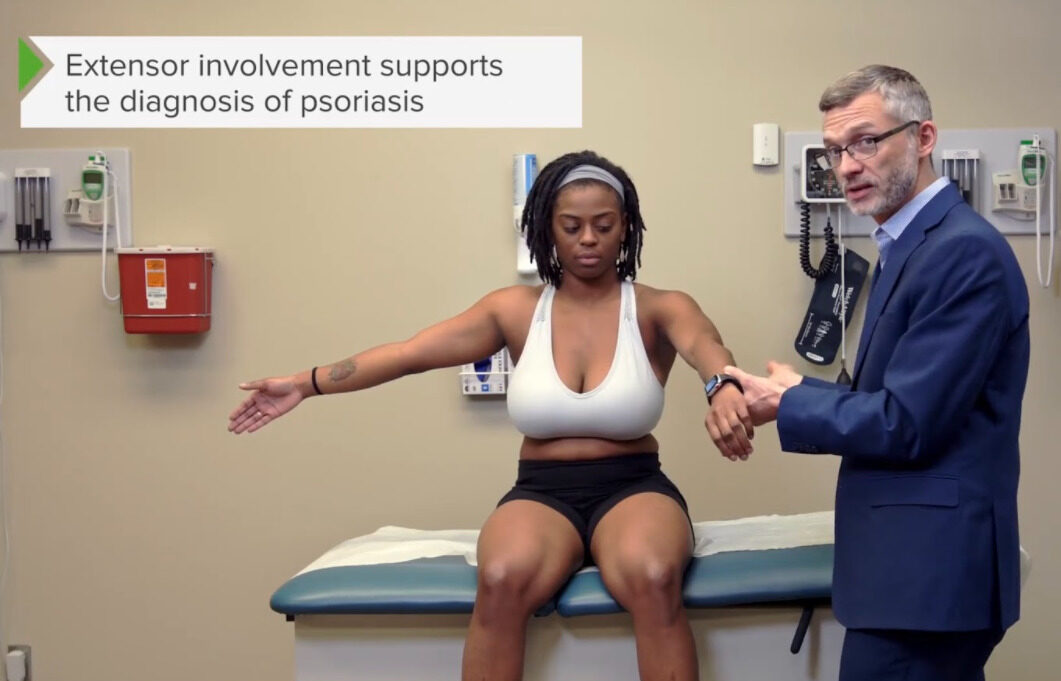
Examen de las superficies extensoras de los brazos (la psoriasis generalmente afecta las superficies extensoras)
Imagen por Lecturio.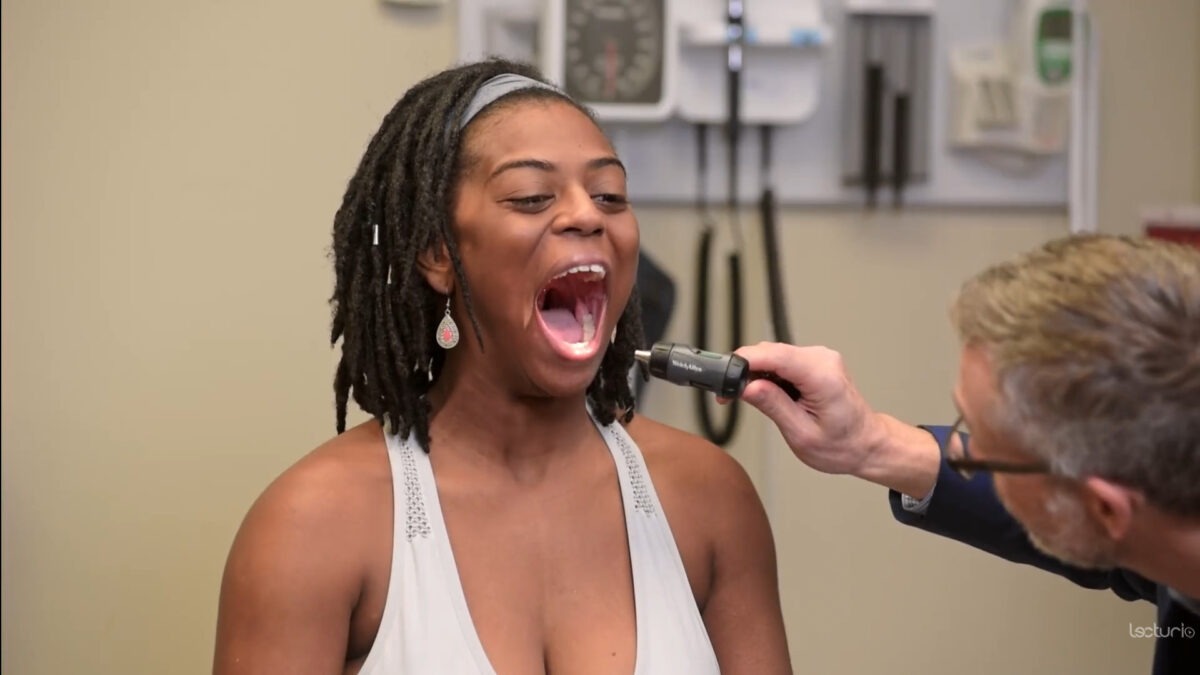
Examen de la boca: superficie bucal y paladar
Imagen por Lecturio.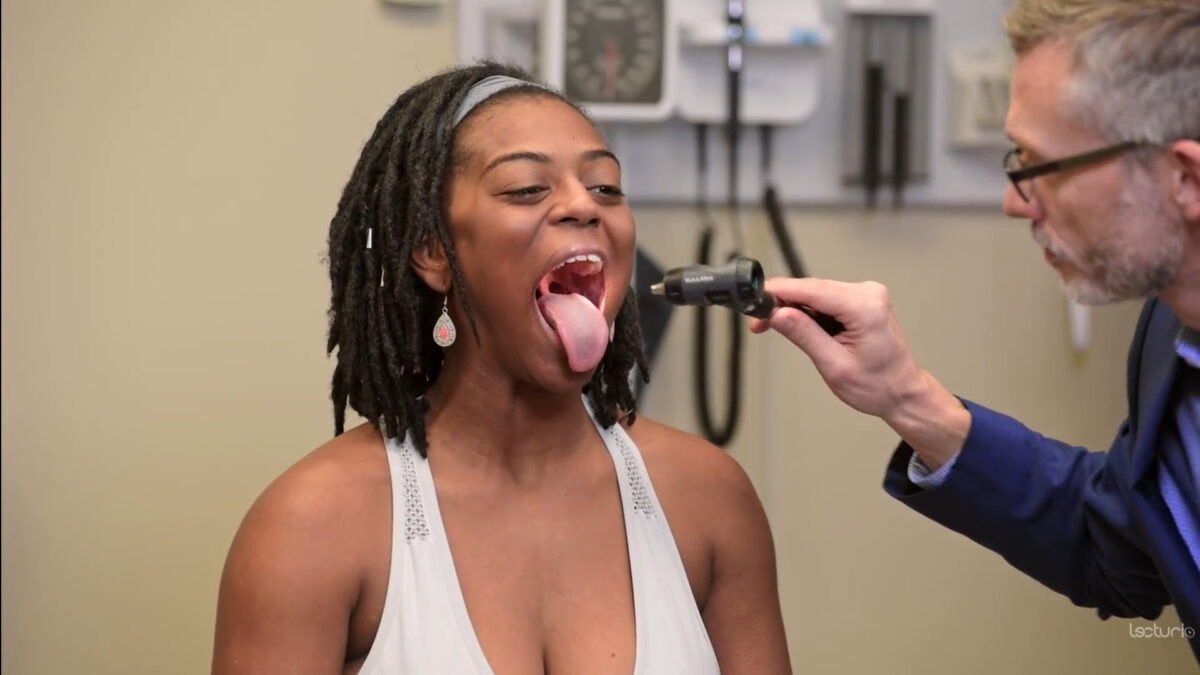
Examen de la lengua
Imagen por Lecturio.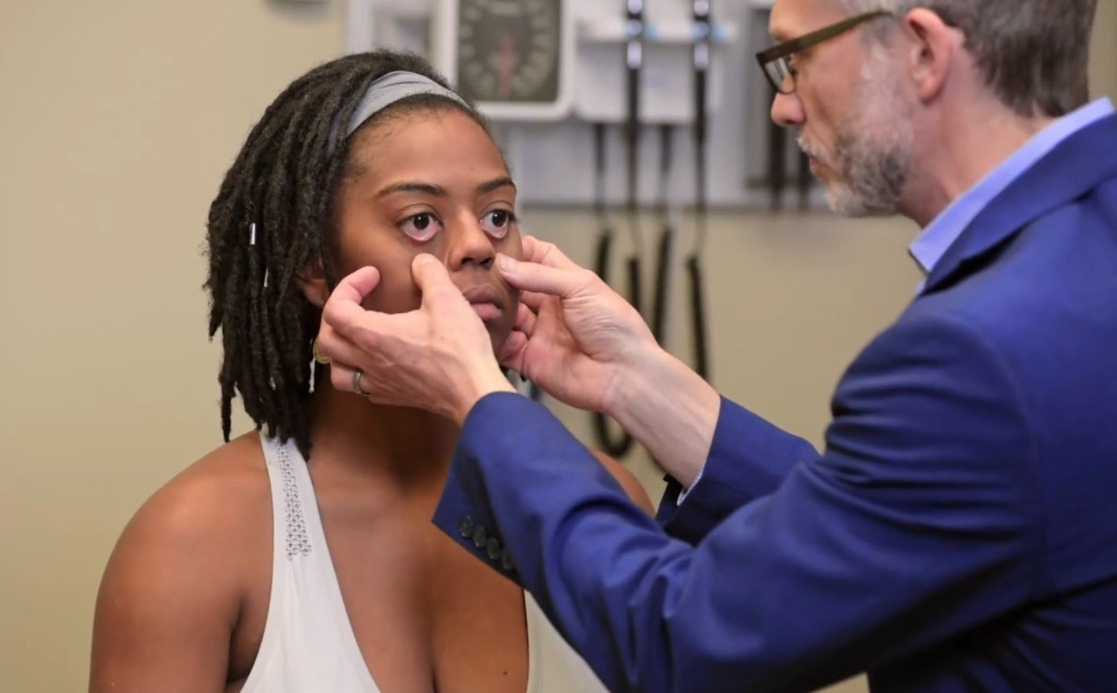
Examen de la conjuntiva
Imagen por Lecturio.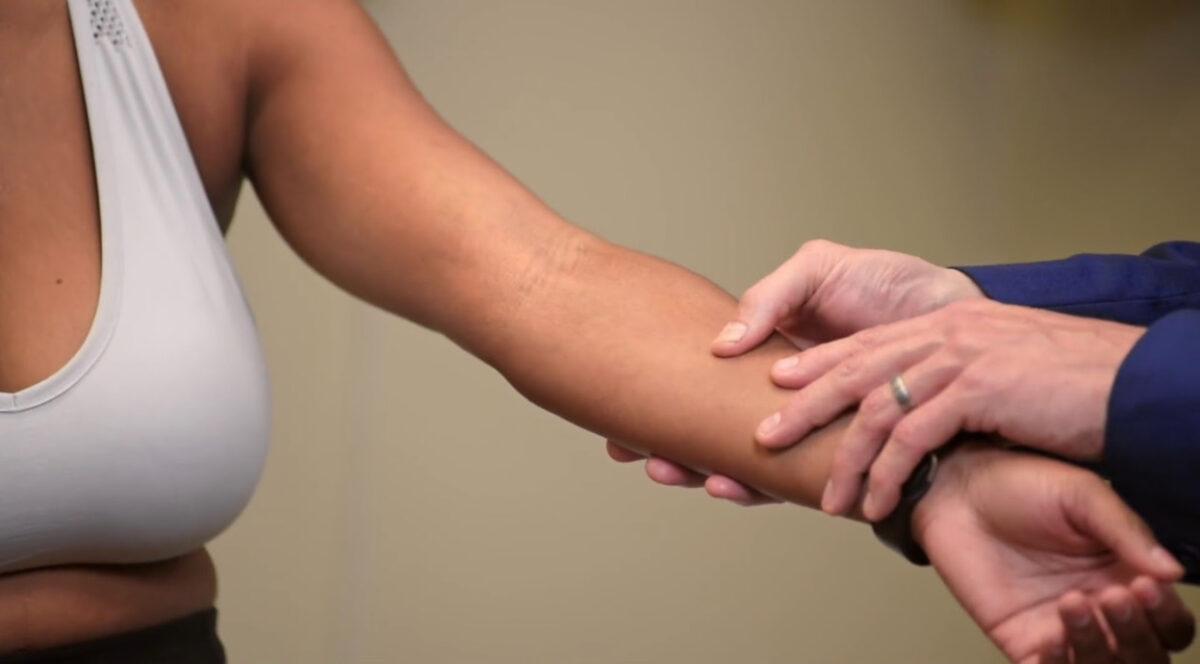
Demostración del signo de Nikolsky
Imagen por Lecturio.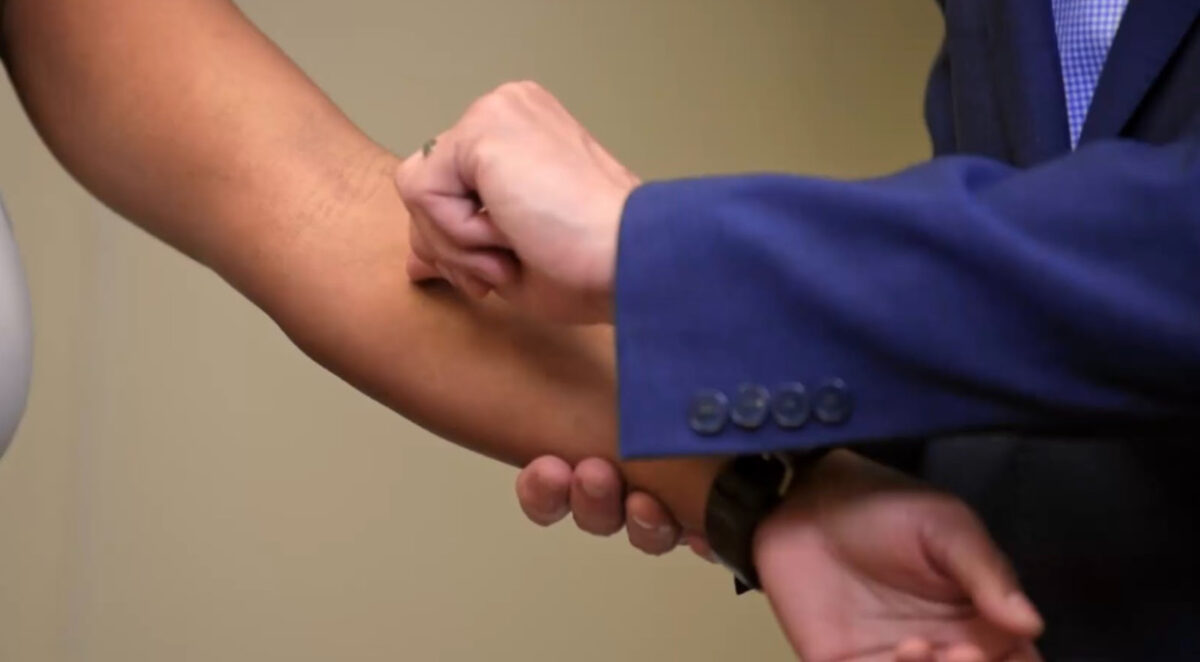
Demostración de dermografismo
Imagen por Lecturio.Evalúe el cabello cuidadosamente, buscando cualquier cambio con respecto a la línea de base del individuo.

Imagen que muestra el patrón de alopecia androgénica en hombres
Imagen por Lecturio.
Imagen que muestra el patrón de alopecia androgénica en mujeres.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Imágenes que muestran la configuración circular de la alopecia areata.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Efluvio telógeno:
Adelgazamiento difuso del cabello que a menudo ocurre por un agente estresante fisiológico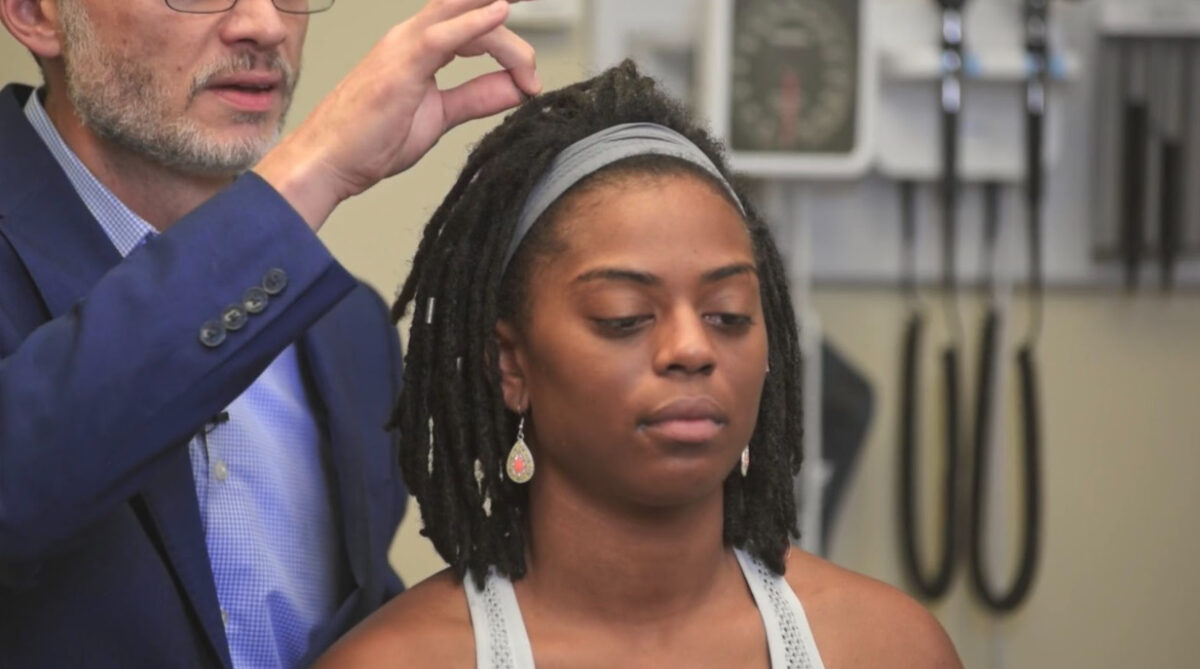
Demostración de la prueba del tirón del cabello
Imagen por Lecturio.| Enfermedad | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Alopecia areata Alopecia Areata Loss of scalp and body hair involving microscopically inflammatory patchy areas. Alopecia |
|
| Alopecia Alopecia Alopecia is the loss of hair in areas anywhere on the body where hair normally grows. Alopecia may be defined as scarring or non-scarring, localized or diffuse, congenital or acquired, reversible or permanent, or confined to the scalp or universal; however, alopecia is usually classified using the 1st 3 factors. Alopecia androgénica |
|
| Efluvio telógeno |
|
Inspeccione y palpe las uñas con cuidado, buscando cualquier cambio.
| Hallazgos clínicos | Descripción | Posible etiología subyacente |
|---|---|---|
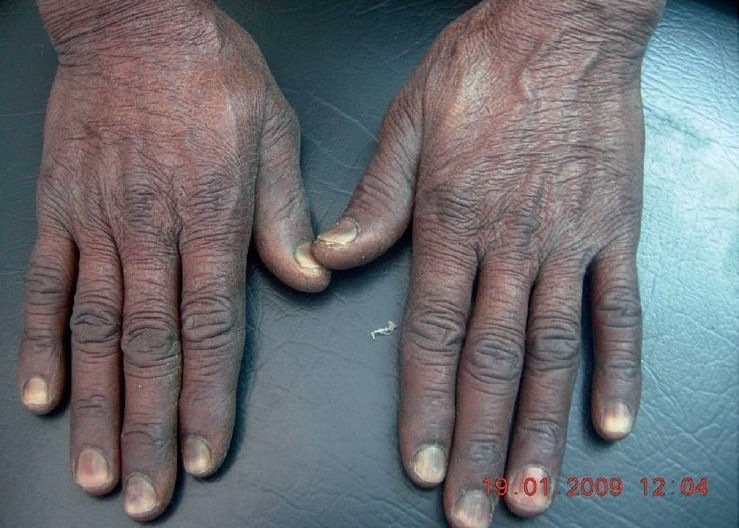
| Dedos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum palillo de tambor | Pérdida de ángulo entre el pliegue ungueal y la placa ungueal |
|
| Onicolisis | Separación distal de la uña |
|
| Depresiones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las uñas |
|
|
| Coiloniquia | Depresión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de cuchara | Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types por deficiencia de hierro |
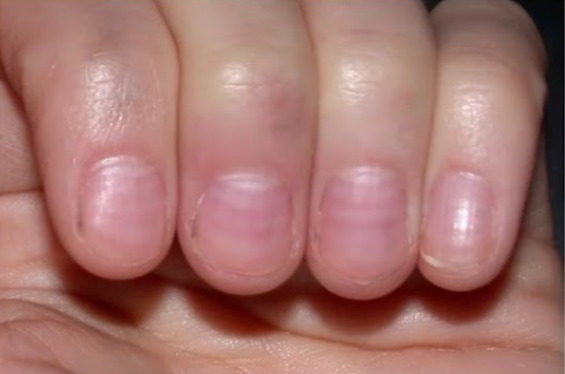
| Líneas de Mees | Rayas blancas |
|
| Uñas quebradizas | Hipotiroidismo | |
| Síndrome de la uña amarilla |
|
|
| Uñas de felpa | Banda proximal roja/marrón en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la placa de la uña |
|
| Uñas mitad y mitad | Nefropatía | |
| Líneas de Muehrcke | Líneas blancas dobles | Hipoalbuminemia |
| Psoriasis Psoriasis Psoriasis is a common T-cell-mediated inflammatory skin condition. The etiology is unknown, but is thought to be due to genetic inheritance and environmental triggers. There are 4 major subtypes, with the most common form being chronic plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis | Dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) atópica | Acné común | Infecciones por hongos | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apariencia |
|
|
|
|
| Distribución | Simétrica, superficies extensoras | Superficies flexoras | Cara, cuello, tórax y espalda |
|
| Hallazgos asociados | Signo de Auspitz: hemorragia puntiforme con eliminación de escamas | Antecedentes de atopia ( asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis y alergias estacionales) | Cicatrización/hiperpigmentación | Confirmado por preparación de KOH |