La erliquiosis y anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection. The most common causative species include Anaplasma phagocytophilum, which infect and multiply within granulocytes. The clinical presentation can vary widely, but often includes fever, malaise, headache, myalgia, and arthralgias. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis son infecciones bacterianas transmitidas por garrapatas. Las especies causantes más comunes son Ehrlichia chaffeensis Ehrlichia chaffeensis A species of gram-negative bacteria that is the causative agent of human ehrlichiosis. This organism was first discovered at fort chaffee, arkansas, when blood samples from suspected human ehrlichiosis patients were studied. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis y Anaplasma phagocytophilum Anaplasma phagocytophilum A species of gram-negative bacteria in the genus anaplasma, family anaplasmataceae, formerly called ehrlichia phagocytophila or ehrlichia equi. This organism is tick-borne (ixodes) and causes disease in horses and sheep. In humans, it causes human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, que infectan y se multiplican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria monocitos y granulocitos, respectivamente. La presentación clínica puede variar mucho, pero a menudo incluye fiebre, malestar, cefalea, mialgias y artralgias. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos pacientes se produce una erupción maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination o petequial. Síntomas gastrointestinales, neurológicos y respiratorios, también pueden presentarse El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sospecha clínica y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las pruebas de reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) o de anticuerpos confirmadas. El tratamiento es con doxiciclina.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
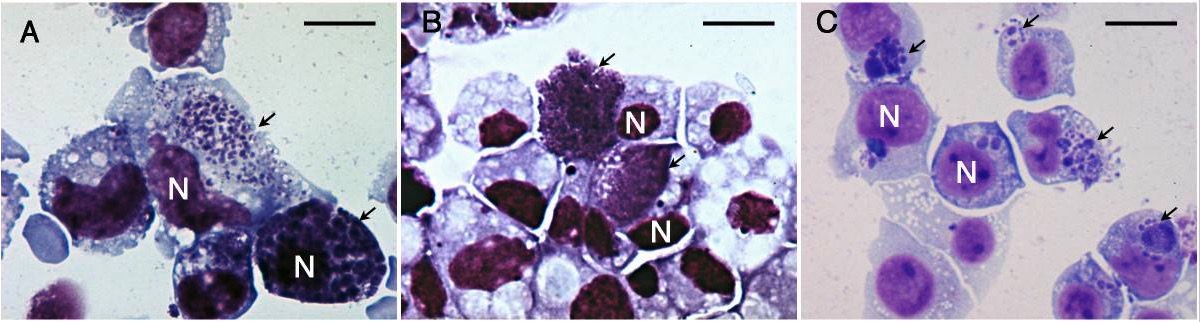
Imágenes microscópicas de células infectadas con anaplasmosis teñidas con Giemsa:
Los núcleos celulares están etiquetados como “N” y las flechas señalan las mórulas de Anaplasma.
Las especies más destacadas son:
Causas raras de erliquiosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos:
Para erliquiosis/ anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection. The most common causative species include Anaplasma phagocytophilum, which infect and multiply within granulocytes. The clinical presentation can vary widely, but often includes fever, malaise, headache, myalgia, and arthralgias. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis:
Para enfermedad grave:
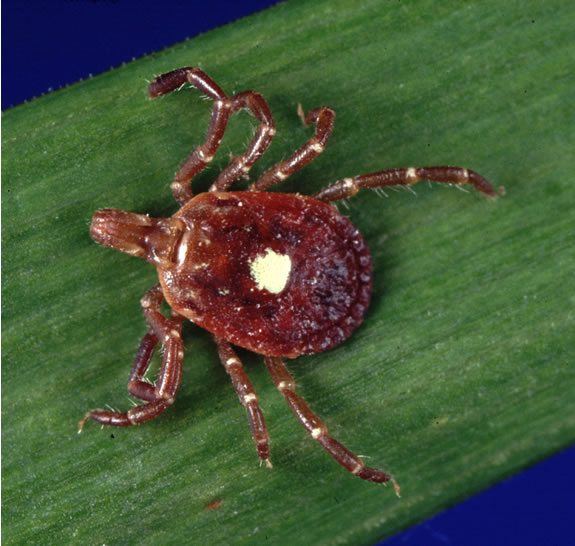

Una garrapata de estrella solitaria, que puede transmitir E. chaffeensis
Imagen: “Amblyomma americanum tick” por James Gathany. Licencia: Dominio Público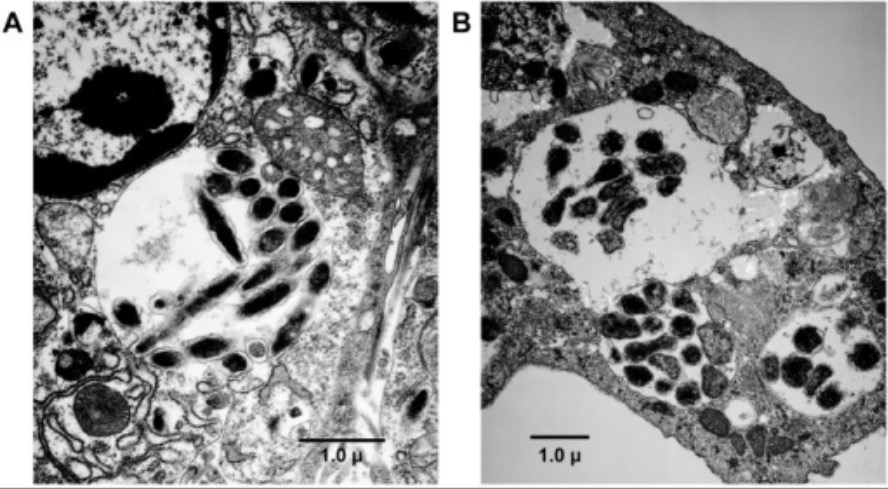
Análisis por microscopía electrónica de transmisión de garrapatas infectadas por E. chaffeensis:
Los organismos de E. chaffeensis aparecen en las vacuolas citoplasmáticas de la célula del intestino medio de la garrapata.
Una amplia gama de animales salvajes y domésticos pueden servir como reservorios. Los LOS Neisseria más destacados son:
Erliquiosis monocítica humana:
Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection. The most common causative species include Anaplasma phagocytophilum, which infect and multiply within granulocytes. The clinical presentation can vary widely, but often includes fever, malaise, headache, myalgia, and arthralgias. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis granulocítica humana:
El periodo de incubación suele ser 1–2 semanas, y la presentación clínica puede variar mucho.
Características de la erliquiosis monocítica humana y la anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection. The most common causative species include Anaplasma phagocytophilum, which infect and multiply within granulocytes. The clinical presentation can vary widely, but often includes fever, malaise, headache, myalgia, and arthralgias. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis granulocítica humana:
Hallazgos más comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum erliquiosis monocítica humana:
Estudios definitivos:
Estudios de laboratorio de soporte:
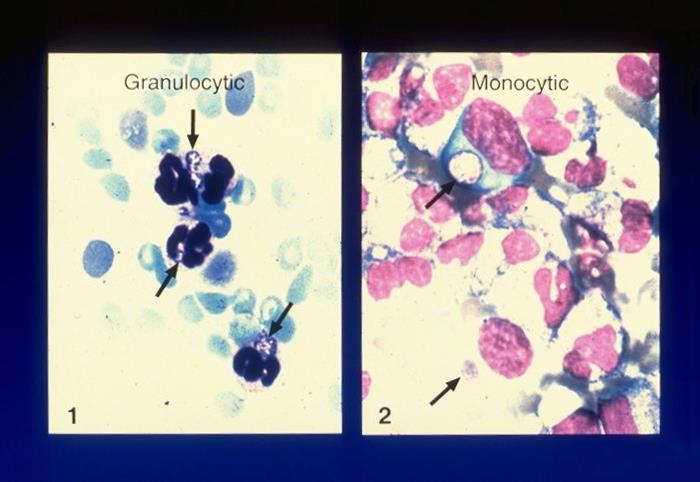
Evaluaciones de frotis de sangre periférica para la erliquiosis y la anaplasmosis:
Estos frotis de sangre muestran mórulas intracelulares de A. phagocytophilum (1) y E. chaffeensis (2).
La doxiciclina es el antibiótico de elección.
Evitar las picaduras de garrapatas es la clave para prevenir estas enfermedades.
| Organismo | Ehrlichia chaffeensis Ehrlichia chaffeensis A species of gram-negative bacteria that is the causative agent of human ehrlichiosis. This organism was first discovered at fort chaffee, arkansas, when blood samples from suspected human ehrlichiosis patients were studied. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis | Anaplasma phagocytophilum Anaplasma phagocytophilum A species of gram-negative bacteria in the genus anaplasma, family anaplasmataceae, formerly called ehrlichia phagocytophila or ehrlichia equi. This organism is tick-borne (ixodes) and causes disease in horses and sheep. In humans, it causes human granulocytic ehrlichiosis. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis | Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia rickettsii A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the etiologic agent of rocky mountain spotted fever. Its cells are slightly smaller and more uniform in size than those of rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia | Borrelia burgdorferi Borrelia burgdorferi A specific species of bacteria, part of the borrelia burgdorferi group, whose common name is lyme disease spirochete. Borrelia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enfermedad | Erliquiosis monocítica humana | Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis Anaplasmosis is a tick-borne bacterial infection. The most common causative species include Anaplasma phagocytophilum, which infect and multiply within granulocytes. The clinical presentation can vary widely, but often includes fever, malaise, headache, myalgia, and arthralgias. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis granulocítica humana | Fiebre de las Montañas Rocosas | Enfermedad de Lyme |
| Micro |
|
|
|
|
| Vector | Garrapata de la estrella solitaria | Garrapata Ixodes | Garrapata Dermacentor Dermacentor A widely distributed genus of ticks, in the family ixodidae, including a number that infest humans and other mammals. Several are vectors of diseases such as tularemia; rocky mountain spotted fever; colorado tick fever; and anaplasmosis. Rickettsia | Garrapata Ixodes |
| Reservorio | Venado de cola blanca | Ratón de patas blancas | Garrapata Dermacentor Dermacentor A widely distributed genus of ticks, in the family ixodidae, including a number that infest humans and other mammals. Several are vectors of diseases such as tularemia; rocky mountain spotted fever; colorado tick fever; and anaplasmosis. Rickettsia |
|
| Distribución geográfica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos | Estados del sureste y centro-sur | Estados del noreste y del alto medio oeste | Estados del sureste y centro-sur | Estados del noreste y del medio oeste |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
| Tratamiento | Doxiciclina |
|
||