Las equinocandinas son un grupo de agentes fungicidas que atacan la pared celular fúngica. Las equinocandinas inhiben la β-glucano sintasa, que a su vez inhibe la producción de β-glucano, un componente estructural clave de las paredes celulares de los LOS Neisseria hongos. Los LOS Neisseria tres medicamentos principales de esta clase incluyen caspofungina, micafungina y anidulafungina. Las equinocandinas se usan principalmente para tratar infecciones por Candida Candida Candida is a genus of dimorphic, opportunistic fungi. Candida albicans is part of the normal human flora and is the most common cause of candidiasis. The clinical presentation varies and can include localized mucocutaneous infections (e.g., oropharyngeal, esophageal, intertriginous, and vulvovaginal candidiasis) and invasive disease (e.g., candidemia, intraabdominal abscess, pericarditis, and meningitis). Candida/Candidiasis y Aspergillus Aspergillus A genus of mitosporic fungi containing about 100 species and eleven different teleomorphs in the family trichocomaceae. Echinocandins en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas que están gravemente enfermas o que tienen neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia. Aunque las equinocandinas tienen un espectro de actividad más estrecho que algunas otras clases de antimicóticos, son clínicamente útiles debido a sus perfiles de toxicidad relativamente bajos y significativamente menos interacciones farmacológicas que los LOS Neisseria azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles y la anfotericina B. La resistencia a las equinocandinas generalmente es poco común, pero está surgiendo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunas cepas de C. glabrata, generalmente a través de mutaciones que reducen la afinidad de este medicamento por la β-glucano sintasa.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las equinocandinas son un grupo de agentes antifúngicos que se dirigen a la pared celular fúngica y se usan típicamente para tratar la candidiasis Candidiasis Candida is a genus of dimorphic, opportunistic fungi. Candida albicans is part of the normal human flora and is the most common cause of candidiasis. The clinical presentation varies and can include localized mucocutaneous infections (e.g., oropharyngeal, esophageal, intertriginous, and vulvovaginal candidiasis) and invasive disease (e.g., candidemia, intraabdominal abscess, pericarditis, and meningitis). Candida/Candidiasis invasiva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia o que están gravemente enfermas.
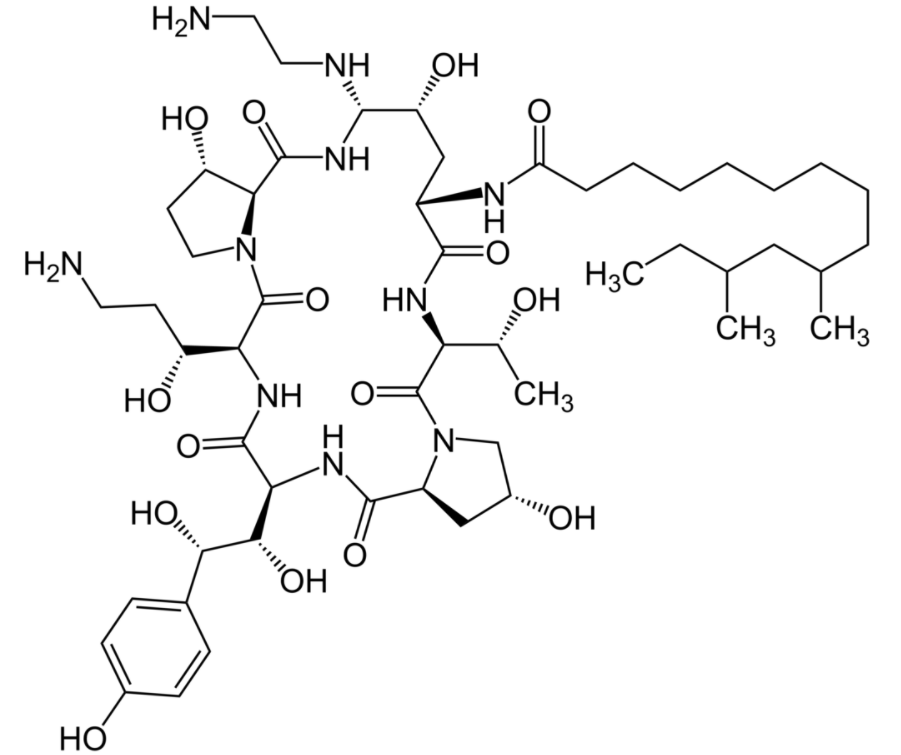
Estructura química de caspofungina
Imagen: “Caspofungin” por FEERERO. Licencia: Dominio Público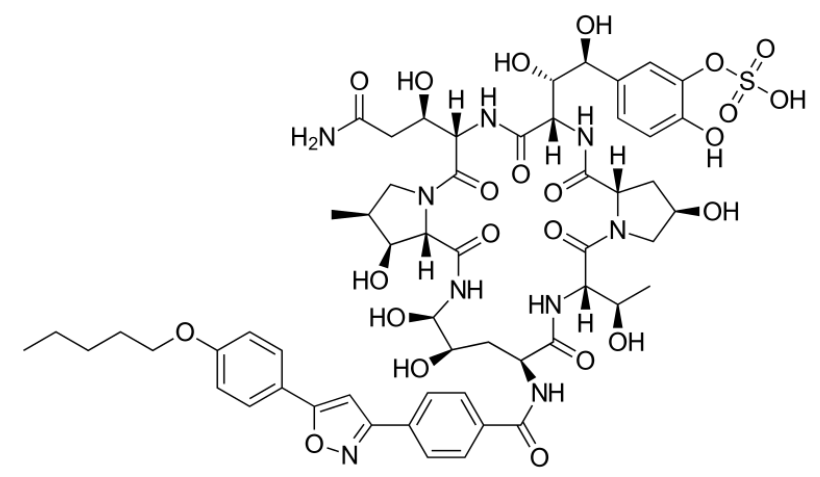
Estructura química de la micafungina.
Imagen: “Micafungin” de Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público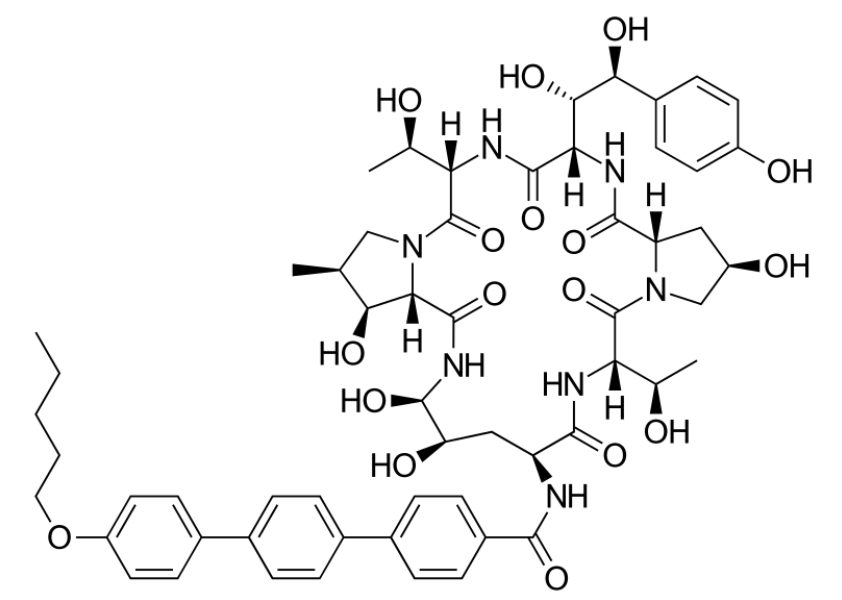
Estructura química de la anidulafungina
Imagen: “Anidulafungin” por Vaccinationist. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLas equinocandinas ejercen sus efectos al AL Amyloidosis inhibir la producción de la pared celular fúngica al AL Amyloidosis interferir con la síntesis de β-glucano, una importante componente estructural.
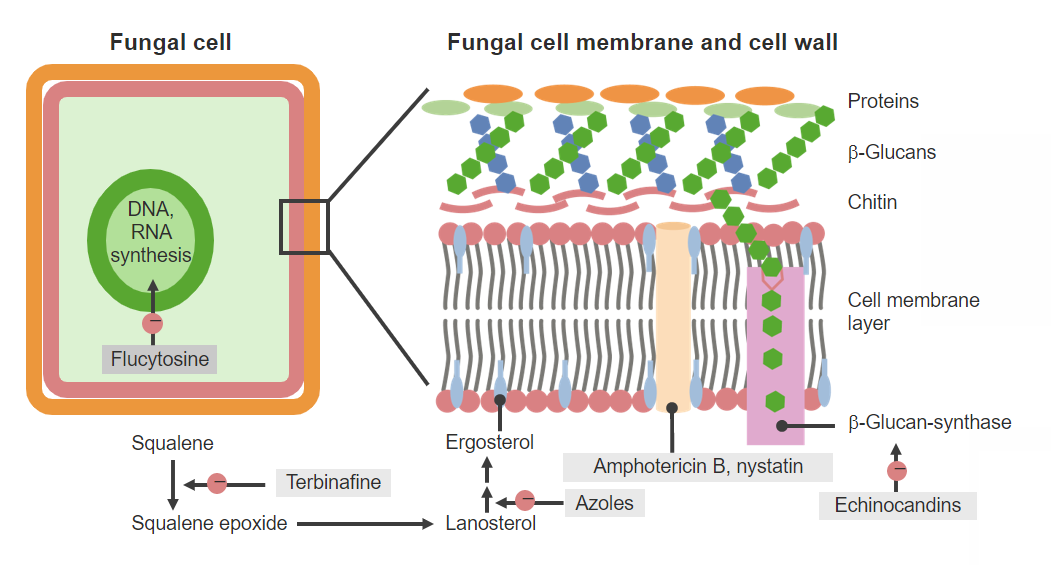
Agentes antifúngicos y mecanismos de acción.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Características comunes a los LOS Neisseria cuatro medicamentos de esta clase:
La caspofungina exhibe una farmacocinética no lineal, trifásica y complicada.
La micafungina exhibe una farmacocinética lineal más predecible.
La anidulafungina exhibe una farmacocinética lineal más predecible.
La rezafungina presenta una farmacocinética lineal y predecible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el rango de dosis terapéuticas.
Las equinocandinas son generalmente intercambiables con respecto a su actividad e indicaciones.
Las equinocandinas se usan más comúnmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia o infecciones por Candida Candida Candida is a genus of dimorphic, opportunistic fungi. Candida albicans is part of the normal human flora and is the most common cause of candidiasis. The clinical presentation varies and can include localized mucocutaneous infections (e.g., oropharyngeal, esophageal, intertriginous, and vulvovaginal candidiasis) and invasive disease (e.g., candidemia, intraabdominal abscess, pericarditis, and meningitis). Candida/Candidiasis.
Las equinocandinas son generalmente muy bien toleradas y tienen baja toxicidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum comparación con otros agentes antifúngicos. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios, si se observan, pueden incluir:
| Clase del medicamento (ejemplos) | Mecanismo de acción | Relevancia clínica |
|---|---|---|
| Azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles (fluconazol, voriconazol) | Inhibe la producción de ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles (un componente crítico de la membrana celular fúngica) al AL Amyloidosis bloquear la enzima lanosterol Lanosterol A triterpene that derives from the chair-boat-chair-boat folding of 2, 3-oxidosqualene. It is metabolized to cholesterol and cucurbitacins. Cholesterol Metabolism 14-α-desmetilasa |
|
| Polienos (anfotericina B, nistatina) | Se une al AL Amyloidosis ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana celular fúngica creando poros artificiales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana → da como resultado la fuga de componentes celulares y conduce a la lisis celular (muerte) | Anfotericina B:
Nistatina:
|
| Equinocandinas (caspofungina, micafungina, anidulafungina) | Inhibe la β-glucano sintasa (la enzima que sintetiza el β-glucano y un componente estructural importante de la pared celular fúngica) → pared celular debilitada → lisis celular |
|
| Griseofulvina |
|
|
| Terbinafina | Inhibe la enzima escualeno epoxidasa → bloquea la producción de epóxido de escualeno, que es un precursor del ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles y un componente crítico de la membrana celular |
|
| Flucitosina | Un análogo de pirimidina con metabolitos:
|
|