La difilobotriasis es una infección parasitaria intestinal causada por varios cestodos de los LOS Neisseria géneros Dibothriocephalus y Adenocephalus, anteriormente clasificados como Diphyllobothrium Diphyllobothrium Diphyllobothriasis represents an intestinal parasitic infection caused by the cestode Diphyllobothrium. Diphyllobothriasis is acquired by ingestion of late larvae in undercooked or raw fish. The clinical presentation of diphyllobothriasis varies from asymptomatic, nonspecific symptoms to intestinal obstruction, and/or vitamin B12 deficiency. Dibothriocephalus/Diphyllobothriasis, (también conocido como “tenia de los LOS Neisseria peces” o “tenia ancha”). La difilobotriasis se adquiere por la ingesta de larvas infecciosas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pescado poco cocido o crudo (p. ej., salmón, trucha). La presentación clínica de la difilobotriasis varía desde pacientes asintomáticos, síntomas inespecíficos, hasta obstrucción intestinal y/o deficiencia de vitamina B12. El diagnóstico se establece mediante la identificación de huevos o proglótides en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heces. El tratamiento incluye terapia antihelmíntica y si es necesario, suplemento de vitamina B12.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La difilobotriasis es una infección parasitaria causada por cestodos (tenia) de los LOS Neisseria géneros Dibothriocephalus y Adenocephalus.
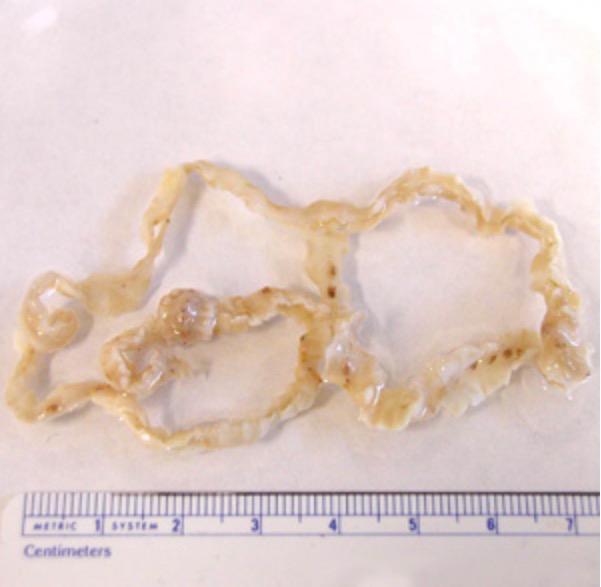
Imagen de un Diphyllobothrium latum adulto
Imagen: “Dibothriocephalus latus with ruler” por CDC. Licencia: CC BY 3.0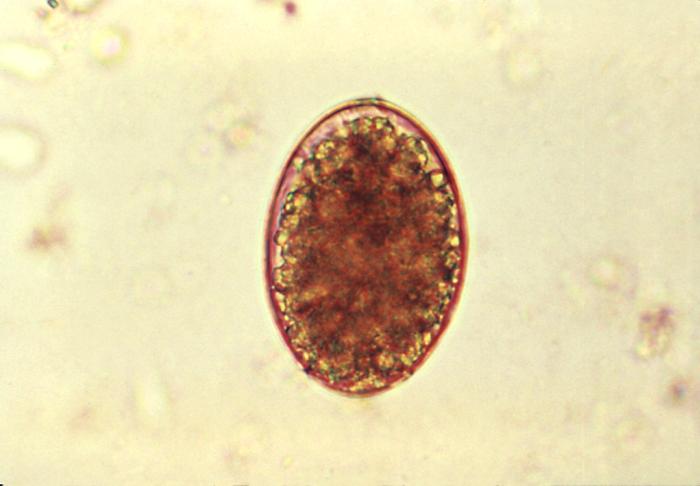
Microfotografía de un huevo de Diphyllobothrium latum:
Los huevos son elipsoidales u ovalados.
Huéspedes definitivos:
Huéspedes intermediarios:
La difilobotriasis se transmite por el consumo de pescado crudo o poco cocido.
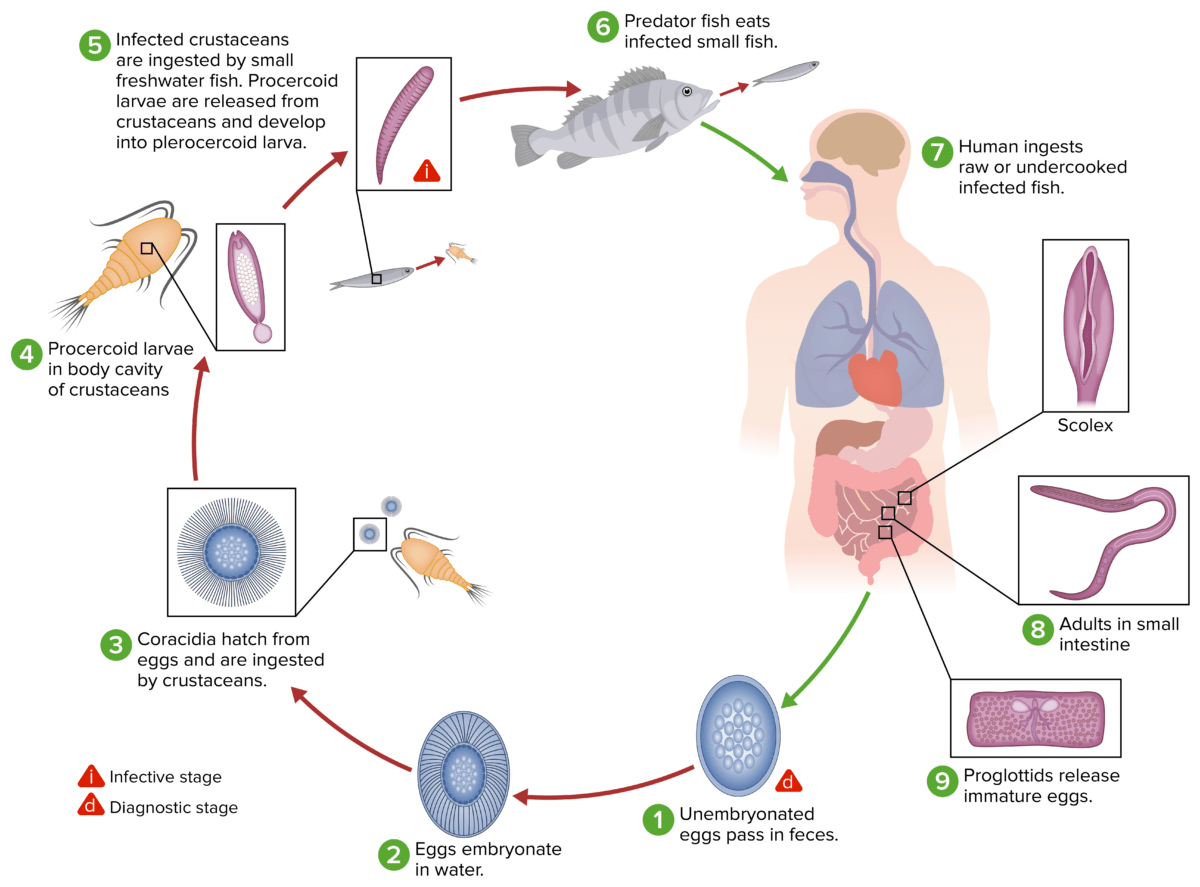
El ciclo vital de las especies de Dibothriocephalus, los agentes causantes de la difilobotriasis
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria siguientes síntomas pueden ser causados por infecciones más graves o por una migración aberrante de las tenias:
| Organismo | Dibothriocephalus latus | Taenia Taenia Taenia belong to the Cestoda class of helminths. Humans are infected with these tapeworms by eating undercooked beef (T. saginata) or pork (T. solium and T. asiatica). Taeniasis is often asymptomatic, but the ingestion of larvae can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea, and constipation or diarrhea. Taenia/Taeniasis saginata | Echinococcus Echinococcus Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus tapeworms. Infection most often occurs from the ingestion of Echinococcus eggs in food or water contaminated with dog feces. Signs and symptoms are caused by hydatid cyst development in visceral organs and depend on the species. Echinococcus/Echinococcosis granulosus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Características |
|
|
|
| Transmisión | Consumo de pescado crudo infectado | Consumo de carne cruda infectada | Fecal-oral (ingestión de agua o alimentos contaminados) |
| Enfermedad | Difilobotriasis | Teniasis | Equinococosis quística |
| Cuadro Clínico |
|
|
Depende de la ubicación y el tamaño de los LOS Neisseria quistes hidatídicos |
| Diagnóstico | Huevos o proglótides en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heces | Huevos o proglótides en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heces |
|
| Tratamiento |
|
|
|
| Prevención |
|
Cocinar bien la carne. |
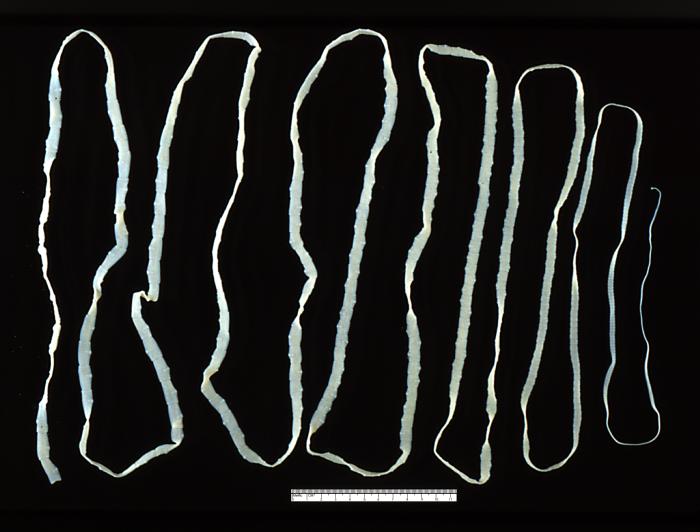
Taenia saginata adulta que mide aproximadamente 4 metros de longitud
Imagen: “5260” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público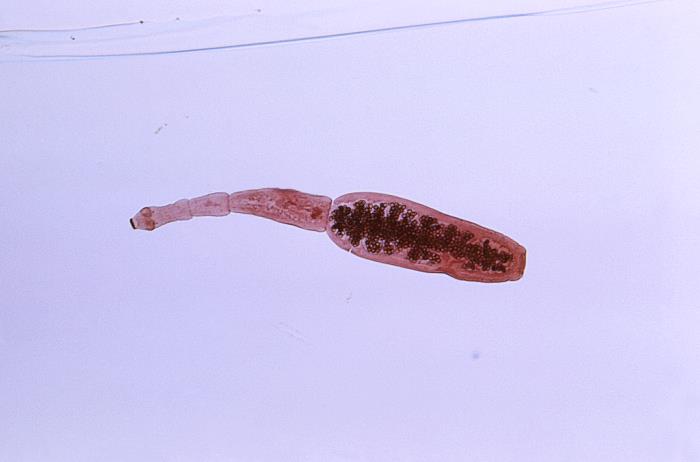
Microfotografía que muestra la morfología de la tenia Echinococcus granulosus:
Obsérvese la cabeza a la izquierda y el escólex con el rostelo en forma de gancho.