La corioamnionitis, comúnmente conocida como infección intraamniótica, es una complicación obstétrica común que involucra infección e inflamación de las membranas fetales, el líquido amniótico, la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity o el feto. La corioamnionitis generalmente es causada por una infección polimicrobiana que asciende desde el tracto genitourinario inferior. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo primarios incluyen ruptura prolongada de membranas y trabajo de parto prolongado. La corioamnionitis se diagnostica por los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos, incluida la fiebre materna. La corioamnionitis se trata con antibióticos y asegurando el progreso continuo del trabajo de parto (o iniciando el progreso) hacia el parto. La corioamnionitis generalmente se resuelve poco después del parto. Es posible que se produzcan importantes complicaciones maternas y fetales que justifiquen un diagnóstico y tratamiento oportunos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
También conocida como infección intraamniótica, la corioamnionitis es una infección, y la inflamación resultante, de cualquier combinación de las membranas fetales (corion y amnios), líquido amniótico, placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity, cordón umbilical (funisitis) y/o del feto.
La corioamnionitis es la causa más común de infección periparto, con las siguientes tasas de incidencia:
La infección e inflamación intraamnióticas pueden deberse a los LOS Neisseria siguientes mecanismos:
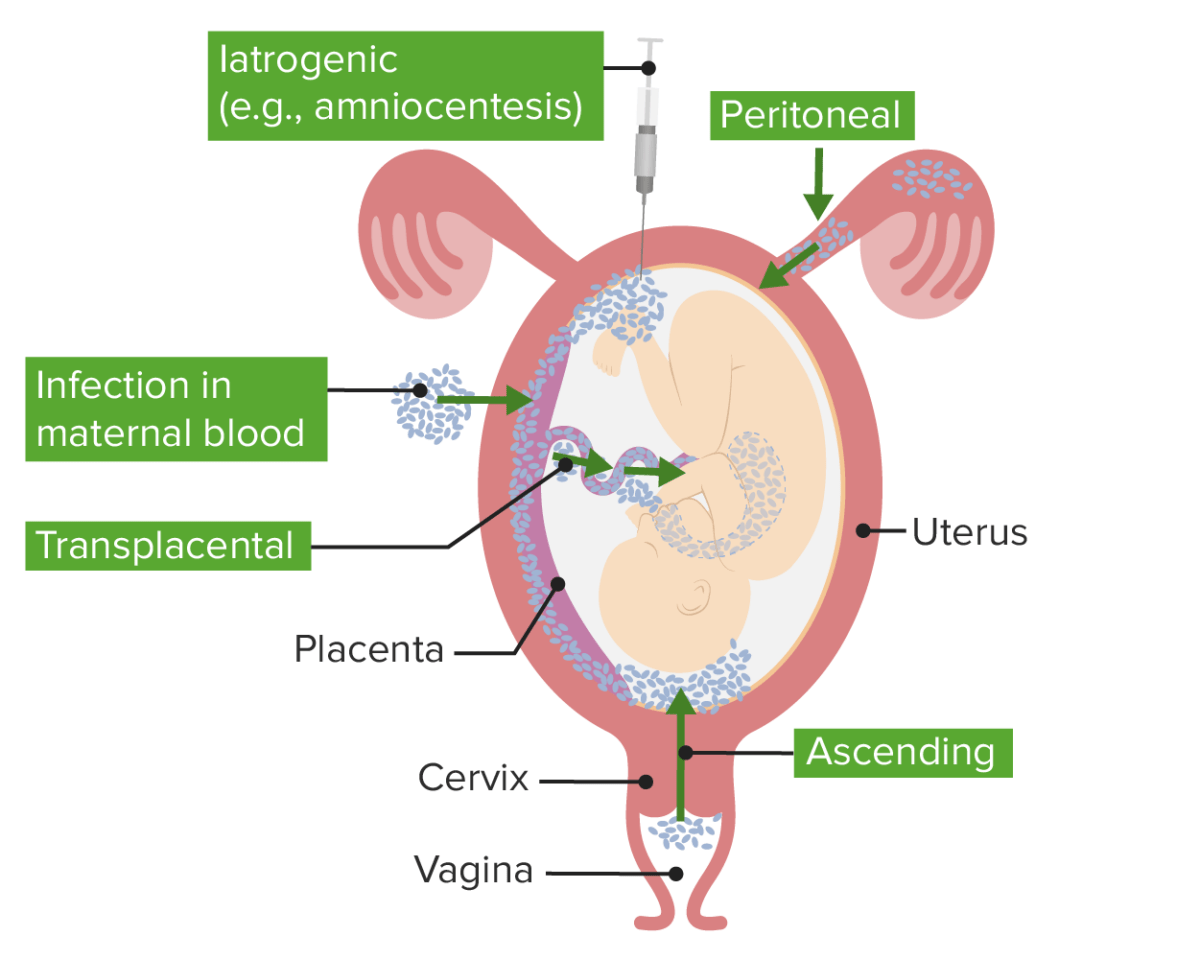
Vías de corioamnionitis/funisitis:
Existen múltiples vías de infección que dan lugar a la corioamnionitis. La infección ascendente con flora cervicovaginal es la etiología más común.
Factores de riesgo:
Por mucho, la causa más común de corioamnionitis es la migración ascendente de la flora cervicovaginal.
La gran mayoría de las mujeres estarán en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum trabajo de parto, tendrán ruptura de membranas o ambas.
Manifestaciones primarias:
Hay 3 categorías de infecciones intraamnióticas:
Fiebre y 1 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
Debe cumplir con los criterios de “sospecha de infección intraamniótica” y al AL Amyloidosis menos 1 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
El objetivo del tratamiento es minimizar los LOS Neisseria riesgos de complicaciones maternas y fetales.
Cuanto más precoz sea la edad gestacional al AL Amyloidosis momento del parto, mayor será el riesgo de complicaciones neonatales.