La carcinogénesis es el desarrollo del cáncer mediante la transformación de células sanas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum células cancerosas. Este complejo proceso ocurre debido a mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) que impiden el proceso normal de división celular. Las células normales tienen muerte celular programada, pero las células cancerosas proliferan sin regulación. Los LOS Neisseria cambios genéticos que causan el cáncer pueden ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células reproductoras de los LOS Neisseria óvulos y los LOS Neisseria espermatozoides y propagarse a la descendencia. Los LOS Neisseria cambios somáticos se adquieren durante la vida de un individuo debido a la exposición a sustancias químicas cancerígenas, tabaco, radiación y otros factores. Las mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria oncogenes Oncogenes Genes whose gain-of-function alterations lead to neoplastic cell transformation. They include, for example, genes for activators or stimulators of cell proliferation such as growth factors, growth factor receptors, protein kinases, signal transducers, nuclear phosphoproteins, and transcription factors. A prefix of 'v-' before oncogene symbols indicates oncogenes captured and transmitted by retroviruses; the prefix 'c-' before the gene symbol of an oncogene indicates it is the cellular homolog (proto-oncogenes) of a v-oncogene. Carcinogenesis que promueven el crecimiento celular y los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure supresores de tumores que reducen el crecimiento celular son mecanismos importantes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la desregulación de la división celular y conducen al AL Amyloidosis cáncer. Los LOS Neisseria cánceres se clasifican por su tipo de célula y su ubicación.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
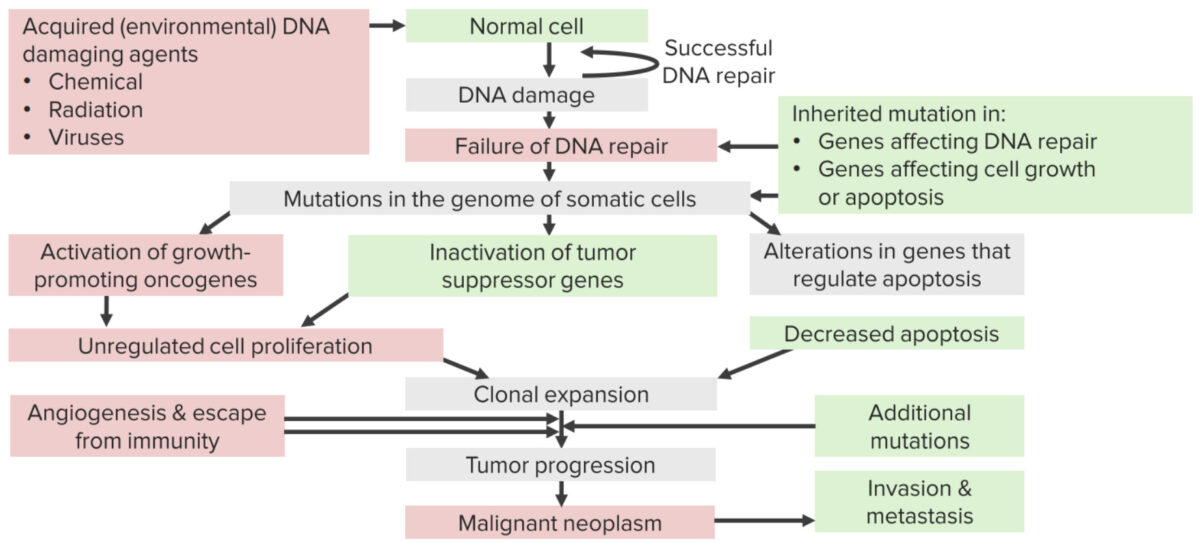
Mecanismos de carcinogénesis debido a carcinógenos que causan daño en el ADN
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0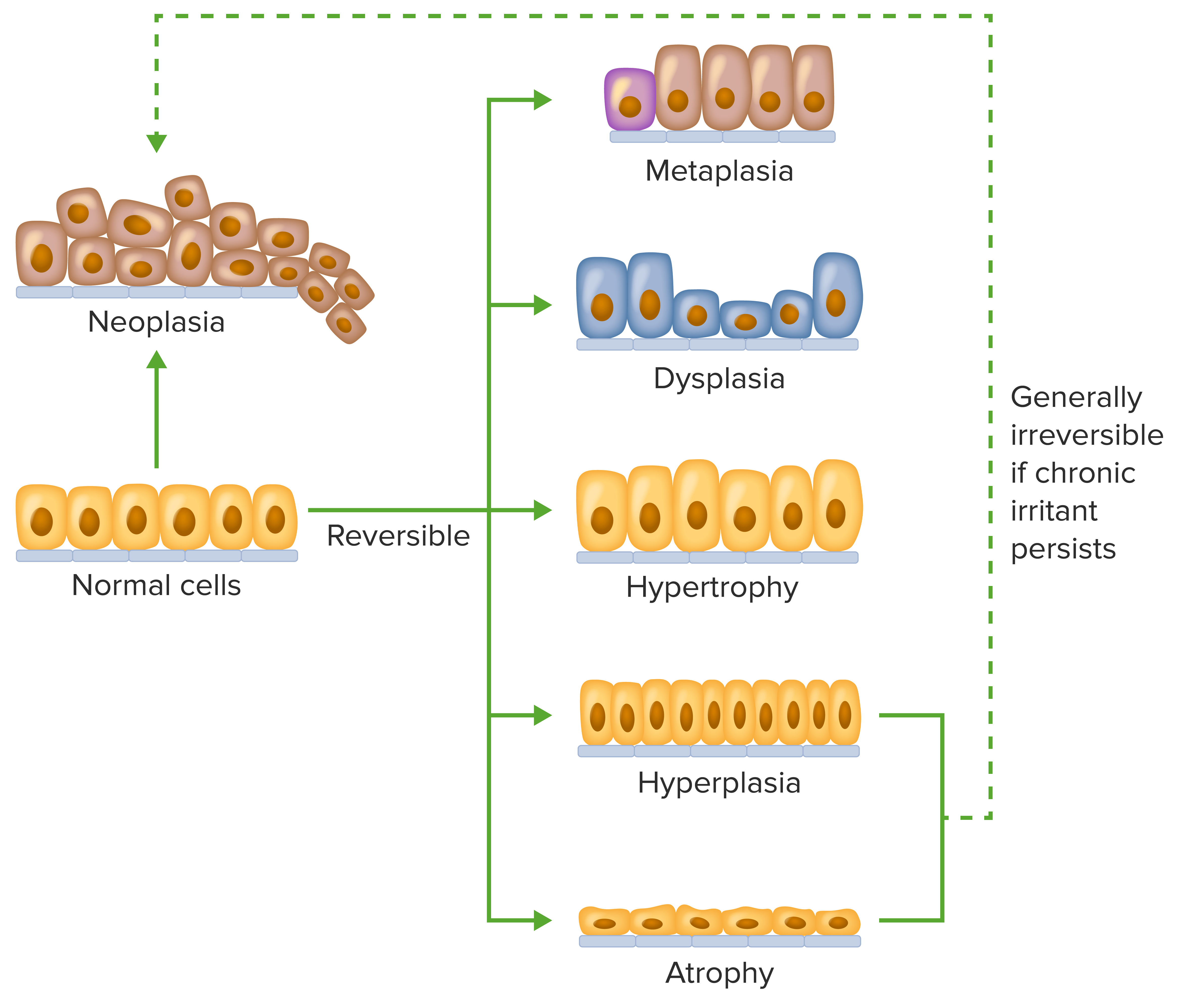
Cambios celulares:
Atrofia: disminución de la masa tisular por disminución del tamaño y/o número de células (reversible) Hiperplasia: aumento del número de células (reversible)
Hipertrofia: aumento del tamaño celular (reversible)
Displasia: cambio en la estructura celular (reversible)
Metaplasia: cambio en el tipo de célula (reversible)
Neoplasia: cambio de tipo y estructura celular (generalmente irreversible)
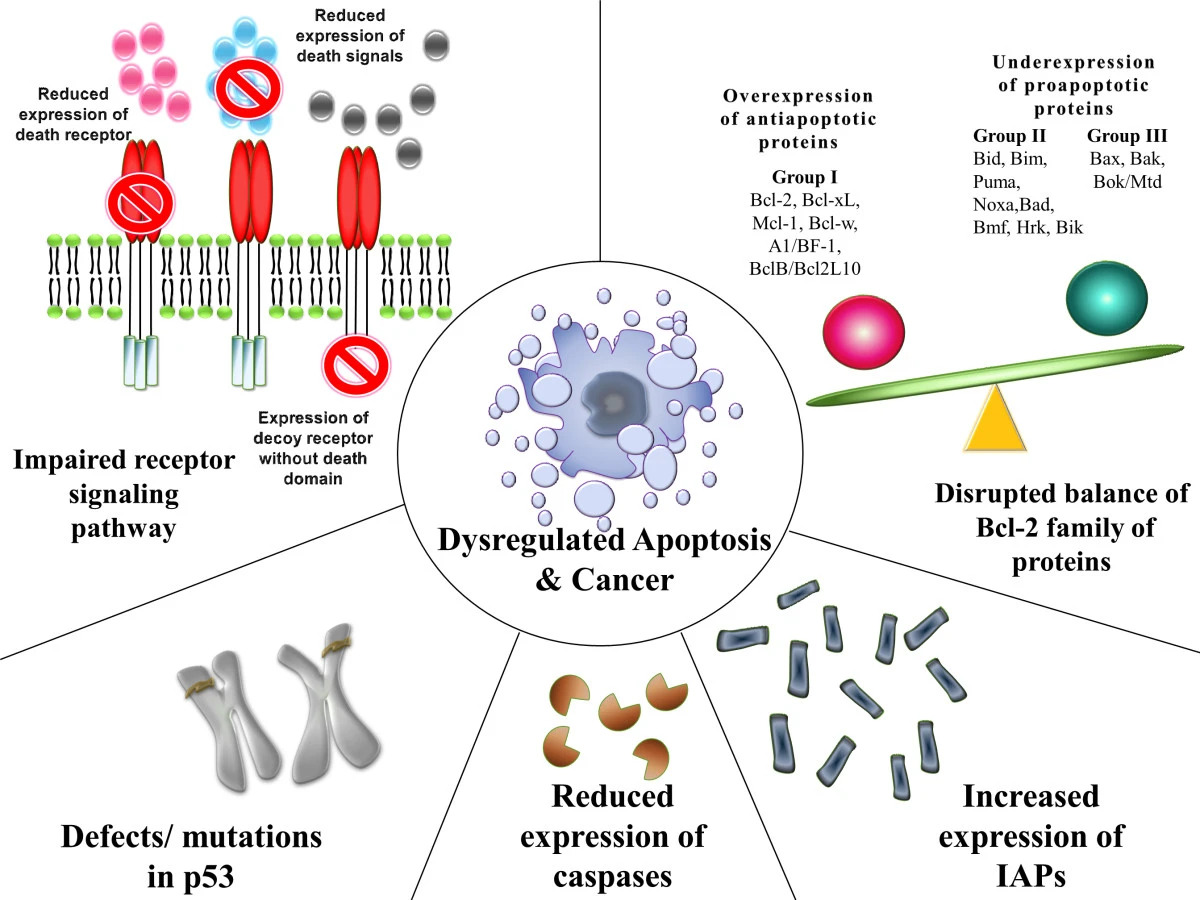
Fisiopatología del cáncer
Imagen: “Mechanisms contributing to evasion of apoptosis and carcinogenesis” por Wong, R.S. Licensia: CC BY 2.0Hay 4 clases de genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure reguladores normales que a menudo son afectados.