El cáncer de tiroides es un trastorno neoplásico que surge de las células de la glándula tiroidea: las células foliculares tiroideas (carcinomas papilares, foliculares y anaplásicos) y las células C productoras de calcitonina (carcinomas medulares). Los LOS Neisseria cánceres más raros derivan de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos (linfoma) y/o de elementos estromales y vasculares (sarcoma). Las mutaciones conductoras que afectan a la vía de los LOS Neisseria receptores tirosina quinasa (como RET y BRAF) y antecedentes familiares de cáncer o síndromes relacionados aumentan el riesgo. La exposición a la radiación ionizante y la deficiencia de yodo también se consideran factores de riesgo. Los LOS Neisseria principales tipos pueden presentarse como nódulos tiroideos o ganglios linfáticos cervicales agrandados. El enfoque diagnóstico incluye la hormona estimulante de la tiroides, el ultrasonido y la biopsia. Las opciones de tratamiento son la extirpación quirúrgica de la glándula tiroidea, con la adición de terapia con yodo radiactivo y terapia sistémica, dependiendo del tipo y la extensión de la neoplasia tiroidea.
Last updated: Mar 14, 2022
El cáncer de tiroides un trastorno neoplásico que surge de las células de la glándula tiroidea, incluidas las células foliculares tiroideas (tirocitos), las células C productoras de calcitonina, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos y/o los LOS Neisseria elementos estromales y vasculares.
Cáncer de tiroides:
La malignidad se presenta como un nódulo tiroideo solitario.
| Tipo | Incidencia | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Diferenciado (originado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria tirocitos) | ||
| Carcinoma papilar |
|
|
| Carcinoma folicular |
|
|
| No diferenciado (originado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria tirocitos) | ||
| Carcinoma anaplásico |
|
|
| Con origen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células C parafoliculares | ||
| Carcinoma medular |
|
|
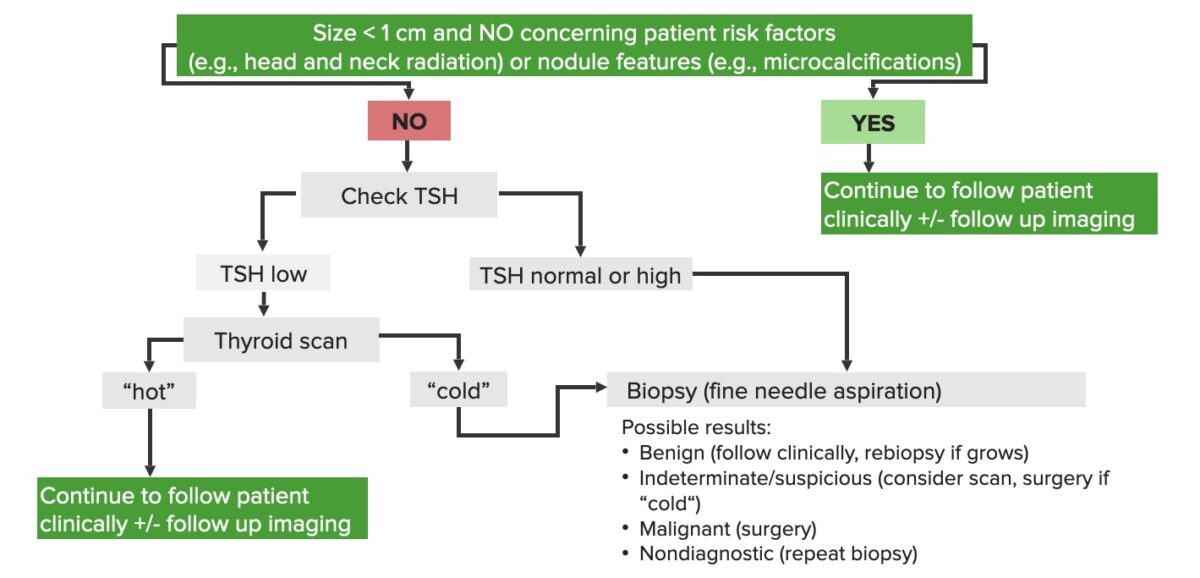
Diagrama esquemático del enfoque diagnóstico de los nódulos tiroideos
Imagen por Lecturio.| Tipo | Características histopatológicas |
|---|---|
| Carcinoma papilar |
|
| Carcinoma folicular |
|
| Carcinoma medular |
|
| Carcinoma anaplásico |
|
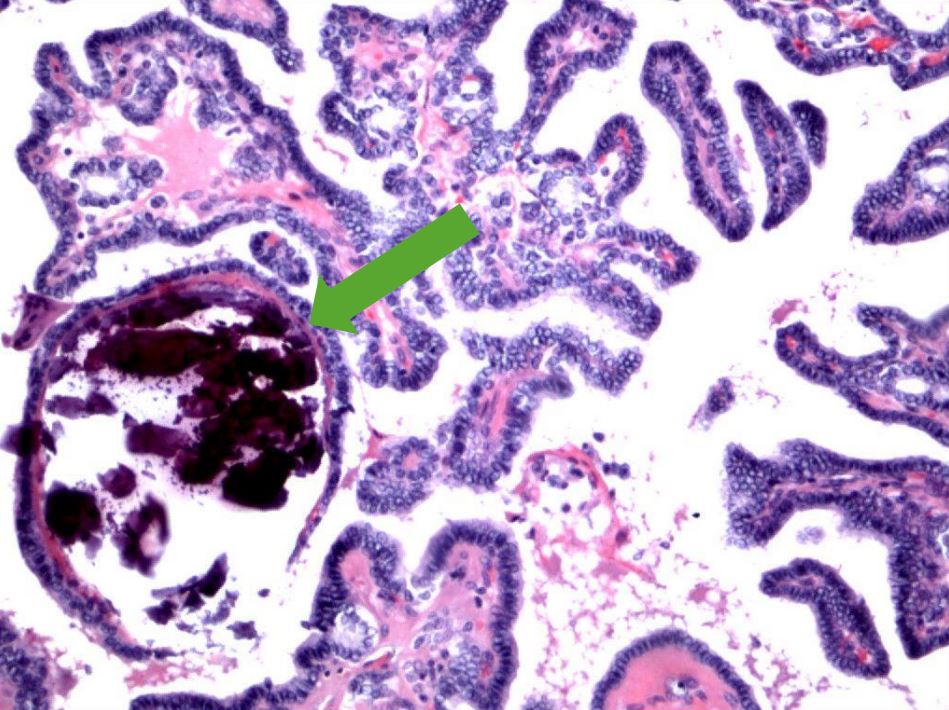
Carcinoma papilar de tiroides:
Obsérvense las papilas ramificadas y las concreciones azules que representan cuerpos de psamoma (flecha).
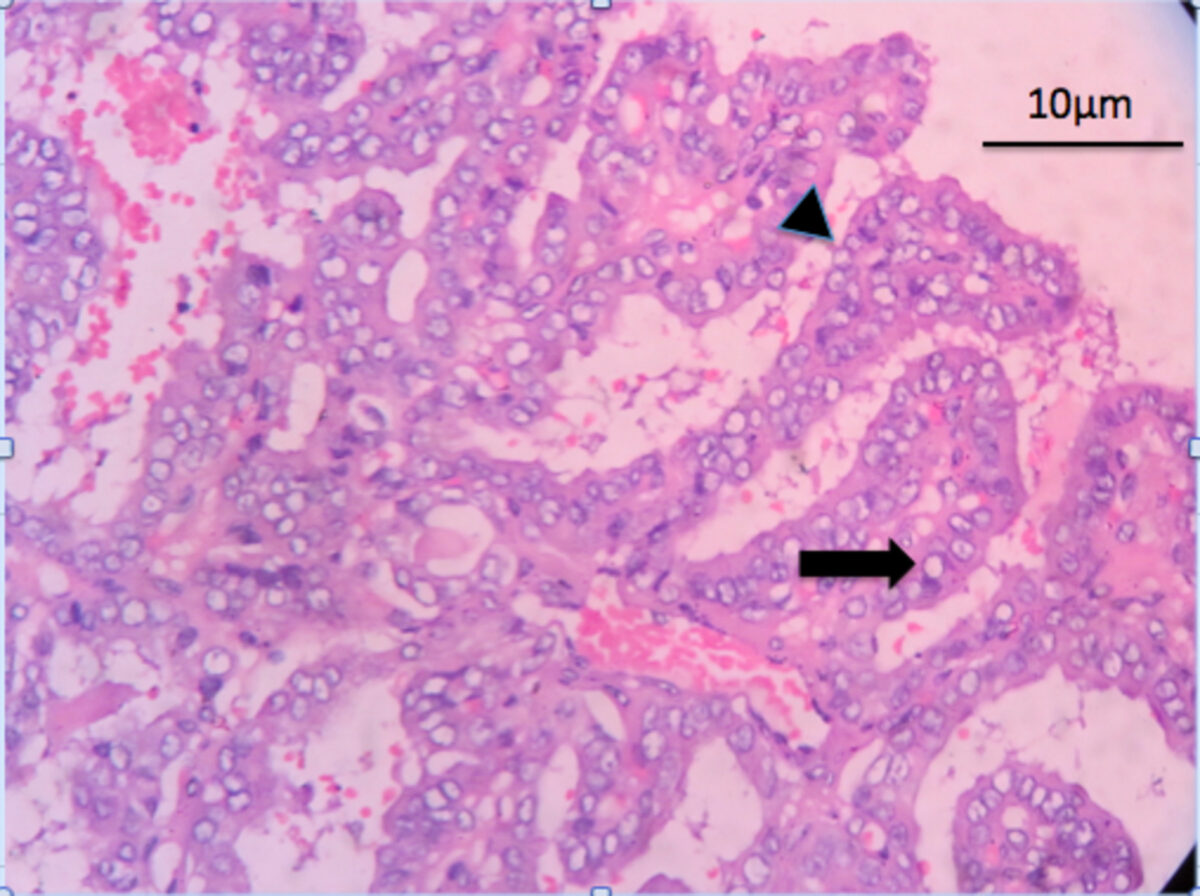
Características del carcinoma papilar de tiroides:
Tinción de H&E que muestra una arquitectura papilar compleja (punta de flecha) con un núcleo fibrovascular. Las células tumorales presentan un aclaramiento nuclear: Núcleos huérfanos en “ojo de la Huérfana Annie” (flecha)
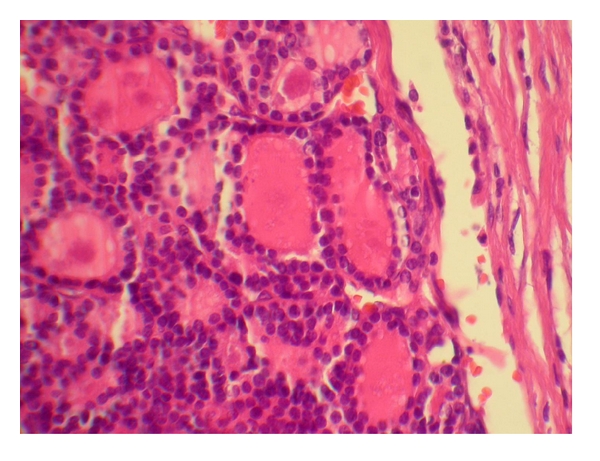
Carcinoma folicular de tiroides: carcinoma que forma folículos con núcleos pequeños y uniformes
Imagen: “Occult follicular thyroid carcinoma presenting as a frontal bone metastasis: a case report” por Tahamtan M, Mokhtari M, Pakbaz S, Tahamtan M. Licencia: CC BY 3.0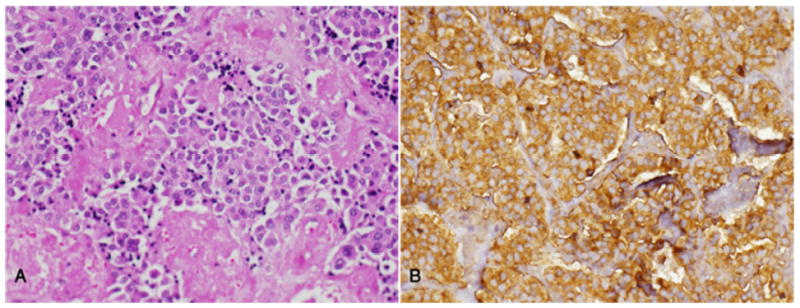
Carcinoma medular de tiroides:
A. Obsérvense las láminas y nidos de células tumorales en un estroma amiloide.
B. Fuerte inmunopositividad para la calcitonina en todas las células tumorales
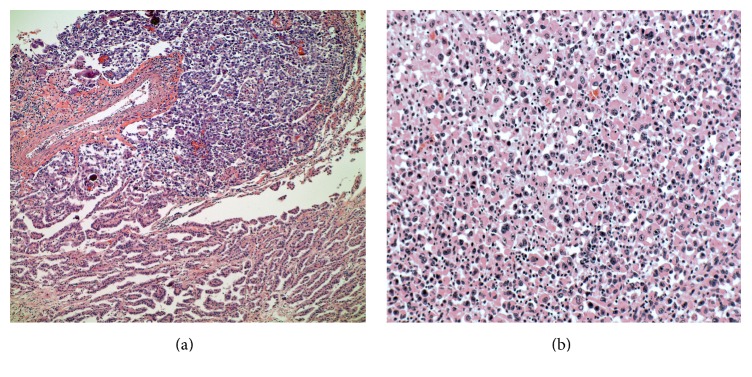
Carcinoma anaplásico de tiroides (carcinoma papilar que se transforma en anaplásico):
(a) 10×: Carcinoma papilar de tiroides (inferior) con transformación a carcinoma anaplásico (superior)
(b) 20×: Vista a mayor potencia del componente de carcinoma anaplásico con núcleos agrandados, nucleolos prominentes y cantidades moderadas de citoplasma eosinófilo
Tras el diagnóstico, deben realizarse más pruebas: