Los LOS Neisseria azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles son una clase de medicamentos antimicóticos ampliamente utilizados que inhiben la producción de ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles, un componente crítico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana celular fúngica. Las dos subclases principales de azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles son los LOS Neisseria imidazoles Imidazoles Compounds containing 1, 3-diazole, a five membered aromatic ring containing two nitrogen atoms separated by one of the carbons. Chemically reduced ones include imidazolines and imidazolidines. Distinguish from 1, 2-diazole (pyrazoles). Azoles, agentes más antiguos que generalmente solo se usan para aplicaciones tópicas, y los LOS Neisseria triazoles, agentes más nuevos con un amplio espectro de usos. Varios miembros de la clase están indicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento y profilaxis de candidiasis Candidiasis Candida is a genus of dimorphic, opportunistic fungi. Candida albicans is part of the normal human flora and is the most common cause of candidiasis. The clinical presentation varies and can include localized mucocutaneous infections (e.g., oropharyngeal, esophageal, intertriginous, and vulvovaginal candidiasis) and invasive disease (e.g., candidemia, intraabdominal abscess, pericarditis, and meningitis). Candida/Candidiasis, aspergilosis, meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis criptocócica, infecciones fúngicas dimórficas (p.ej.: blastomicosis) y mucormicosis. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios significativos son posibles e incluyen hepatotoxicidad, malestar gastrointestinal, problemas cardíacos y neurotoxicidad. Los LOS Neisseria azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles interactúan con el sistema CYP450 y causan interacciones significativas de medicamento a medicamento con muchos otros medicamentos, lo que podría limitar la utilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas médicamente complejas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles son un grupo de medicamentos antimicóticos ampliamente utilizados, que se pueden clasificar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum dos subgrupos:

Fluconazol
Imagen: “Fluconazole skeletal formula” por Vaccinationist. Licencia: Dominio Público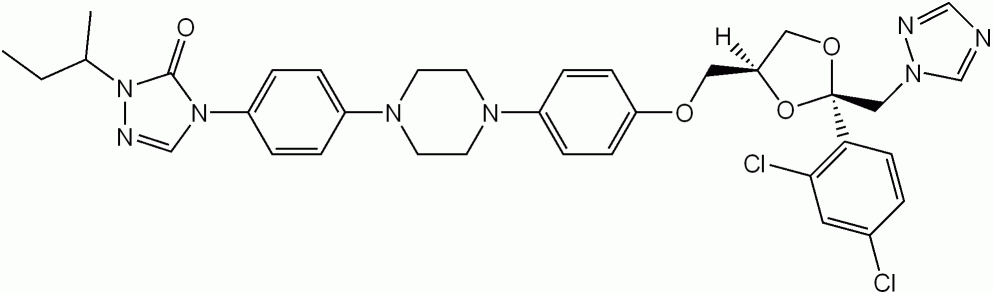
Itraconazol
Imagen: “Itraconazole” por Shaddack. Licencia: Dominio Público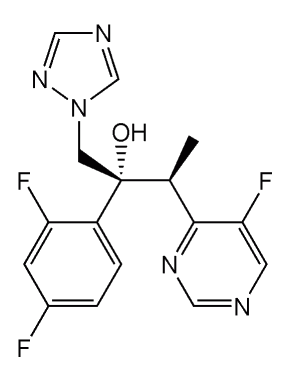
Voriconazol
Imagen: “Voriconazole” por Shaddack. Licencia: Dominio Público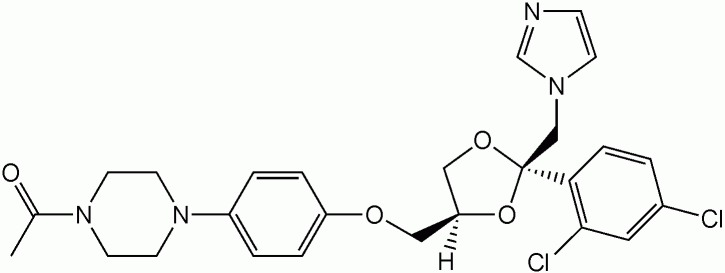
Ketoconazol
Imagen: “Ketoconazole” por Shaddack. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles causan el deterioro de la membrana celular fúngica al AL Amyloidosis inhibir la producción de ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles.
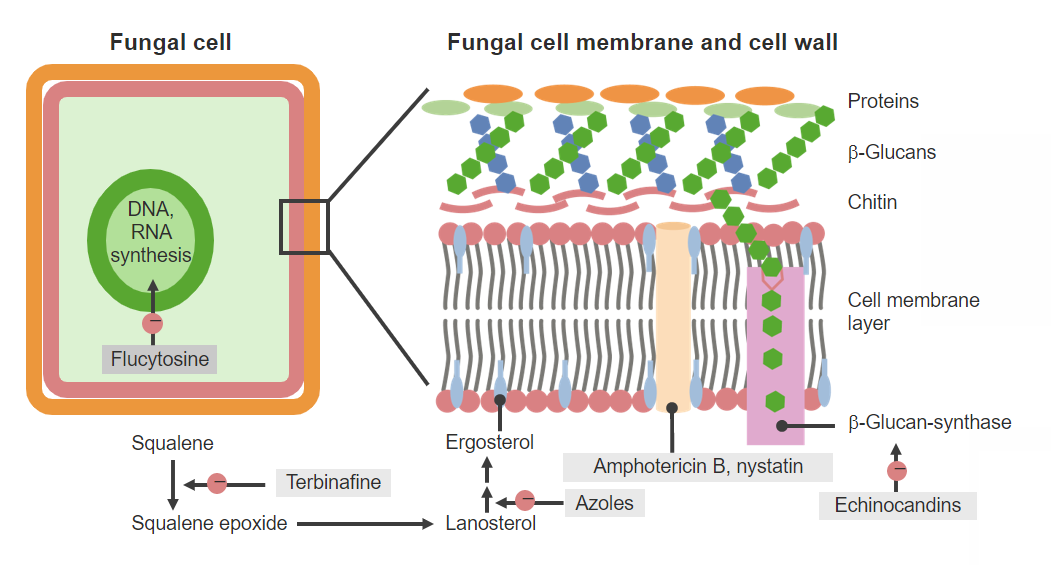
Agentes antifúngicos y mecanismos de acción.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Los LOS Neisseria diferentes azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles tienen una farmacocinética variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables (y a veces compleja).
| Medicamentos | Enlace proteico | Metabolismo y eliminación | Media vida | Inhibición de enzimas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imidazoles Imidazoles Compounds containing 1, 3-diazole, a five membered aromatic ring containing two nitrogen atoms separated by one of the carbons. Chemically reduced ones include imidazolines and imidazolidines. Distinguish from 1, 2-diazole (pyrazoles). Azoles | ||||
| Ketoconazol | 99% | Bifásico:inicial: 2 horas, terminal: 8 horas | ||
| Triazoles | ||||
| Fluconazol | Aproximadamente el 10% |
|
25 horas |
|
| Itraconazol | 99% |
|
24–48 horas |
|
| Voriconazol | Aproximadamente el 60% | |
6 horas |
|
| Posaconazol | 98% |
|
25–35 horas | |
| Isavuconazol | 99% | 130 horas |
|
|
Los LOS Neisseria azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles tienen una amplia variedad de usos e indicaciones únicas para cada medicamento.
Además de las indicaciones específicas enumeradas a continuación, la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria triazoles también se pueden usar como profilaxis contra infecciones fúngicas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas inmunodeprimidas.
Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos comunes que contribuyen a la resistencia antifúngica incluyen:
| Clase del medicamento (ejemplos) | Mecanismo de acción | Relevancia clínica |
|---|---|---|
| Azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles (fluconazol, voriconazol) | Inhibe la producción de ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles (un componente crítico de la membrana celular fúngica) al AL Amyloidosis bloquear la enzima lanosterol Lanosterol A triterpene that derives from the chair-boat-chair-boat folding of 2, 3-oxidosqualene. It is metabolized to cholesterol and cucurbitacins. Cholesterol Metabolism 14-α-desmetilasa |
|
| Polienos (anfotericina B, nistatina) | Se une al AL Amyloidosis ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana celular fúngica creando poros artificiales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la membrana → da como resultado la fuga de componentes celulares y conduce a la lisis celular (muerte) | Anfotericina B:
Nistatina:
|
| Equinocandinas (caspofungina, micafungina, anidulafungina) | Inhibe la β-glucano sintasa (la enzima que sintetiza el β-glucano y un componente estructural importante de la pared celular fúngica) → pared celular debilitada → lisis celular |
|
| Griseofulvina |
|
|
| Terbinafina | Inhibe la enzima escualeno epoxidasa → bloquea la producción de epóxido de escualeno, que es un precursor del ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles y un componente crítico de la membrana celular |
|
| Flucitosina | Un análogo de pirimidina con metabolitos:
|
|